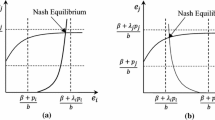
Abstract
This paper studies a model of principal-agent problem under loss aversion and inequity aversion. The model analyzes how loss aversion and inequity aversion affect the wage structure in optimal contract design. The results demonstrate that the presence of loss aversion would lead to a set of rising wage levels and that range of wage levels is wider if a principal is more loss averse. In addition, the principal’s profit decreases in the principal’s degree of loss aversion and in the risk neutral agent’s degree of inequity aversion. Nevertheless, the wage growth of risk averse agent will be reduced. Furthermore, the incentive mechanism of non-contractible effort will cause higher wage growth than the one of contractible effort. The increase of realized profit level or the decrease of loss aversion level would lead to too equitable allocations for the risk neutral agent. Under this incentive mechanism, an increase in the risk averse agent’s concern for equity will be convergence towards linear sharing rules, while the principal who has more sensitive to the loss may offer much lower wage level.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carbajal, J. C., & Ely, J. (2012). Optimal contracts for loss averse consumers. Technical report, University of Queensland, School of Economics.
Cato, S. (2013). The first-order approach to the principal-agent problems under inequality aversion. Operations Research Letters, 41(5), 526–529.
Chen, Z., Lan, Y., & Zhao, R. (2018). Impacts of risk attitude and outside option on compensation contracts under different information structures. Fuzzy Optimization and Decision Making, 17(1), 13–47.
Deng, X., Xie, J., & Xiong, H. (2013). Manufacturer-retailer contracting with asymmetric information on retailer’s degree of loss aversion. International Journal of Production Economics, 142(2), 372–380.
Dur, R., & Glazer, A. (2008). Optimal contracts when a worker envies his boss. Journal of Law, Economics, and Organization, 24(1), 120–137.
Englmaier, F., & Wambach, A. (2010). Optimal incentive contracts under inequity aversion. Games and Economic Behavior, 69(2), 312–328.
Fehr, E., & Schmidt, K. M. (1999). A theory of fairness, competition, and cooperation. Quarterly Journal of Economics, 114(3), 817–868.
Fehr, E., & Schmidt, K. M. (2004). Fairness and incentives in a multi-task principal-agent model. The Scandinavian Journal of Economics, 106(3), 453–474.
Foellmi, R., Rosenblatt-Wisch, R., & Schenk-Hoppé, K. R. (2011). Consumption paths under prospect utility in an optimal growth model. Journal of Economic Dynamics and Control, 35(3), 273–281.
Goukasian, L., & Wan, X. (2010). Optimal incentive contracts under relative income concerns. Mathematics and Financial Economics, 4(1), 57–86.
Kahneman, D., & Tversky, A. (1979). Prospect theory: An analysis of decision under risk. Econometrica: Journal of the Econometric Society, 47(2), 263–291.
Liu, B. (2007). Uncertainty theory (2nd ed.). Berlin: Springer.
Meza, D., & Webb, D. C. (2007). Incentive design under loss aversion. Journal of the European Economic Association, 5(1), 66–92.
Mu, R., Lan, Y., & Tang, W. (2013). An uncertain contract model for rural migrant workers employment problems. Fuzzy Optimization and Decision Making, 12(1), 29–39.
Popescu, I., & Wu, Y. (2007). Dynamic pricing strategies with reference effects. Operations Research, 55(3), 413–429.
Rasch, A., Wambach, A., & Wiener, K. (2012). Bargaining and inequity aversion: On the efficiency of the double auction. Economics Letters, 114(2), 178–181.
Rey-Biel, P. (2008). Inequity aversion and team incentives. The Scandinavian Journal of Economics, 110(2), 297–320.
Su, X. (2009). A model of consumer inertia with applications to dynamic pricing. Production and Operations Management, 18(4), 365–380.
Von Neumann, J., & Morgenstern, O. (1947). Theory of games and economic behavior (2nd ed.). Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Whitt, W. (1980). Uniform conditional stochastic order. Journal of Applied Probability, 17(1), 112–123.
Wu, X., Zhao, R., & Tang, W. (2014). Uncertain agency models with multi-dimensional incomplete information based on confidence level. Fuzzy Optimization and Decision Making, 13(2), 231–258.
Zhang, J., Gou, Q., Zhang, J., & Liang, L. (2014). Supply chain pricing decisions with price reduction during the selling season. International Journal of Production Research, 52(1), 165–187.
Zhou, C., Tang, W., & Zhao, R. (2017a). Optimal consumption with reference-dependent preferences in on-the-job search and savings. Journal of Industrial and Management Optimization, 13(1), 503–527.
Zhou, C., Tang, W., & Zhao, R. (2017b). An uncertain search model for recruitment problem with enterprise performance. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 28(3), 695–704.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 71702129 and 71371133), Humanity and Social Science Youth Foundation of Ministry of Education of China (No. 17YJC630232), and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2017M610160).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, C., Peng, J., Liu, Z. et al. Optimal incentive contracts under loss aversion and inequity aversion. Fuzzy Optim Decis Making 18, 85–102 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10700-018-9288-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10700-018-9288-1