Abstract
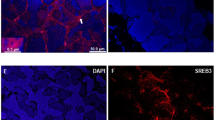
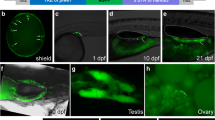
Endocrine-disrupting chemicals are known to impact multiple hormonal axes of vertebrates, among which the thyroid system is crucial for multiple developmental and physiological processes. Thus, the present study focused on the semi-quantitative visualization of intrafollicular triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxin (T4) in zebrafish embryos as a potential test system for the detection of disrupted thyroid hormone synthesis. To this end, an antibody-based fluorescence double-staining protocol for whole-mount zebrafish embryos and larvae was adapted to simultaneously detect intrafollicular T3 and T4. During normal development until 10 days post-fertilization (dpf), the number of thyroid follicles increased along the ventral aorta. Concentrations of T4 and T3, measured by fluorescence intensity, increased until 6 dpf, but decreased thereafter. Exposure of zebrafish embryos to propylthiouracil (PTU), a known inhibitor of TH synthesis, resulted in a significant decrease in the number of follicles that stained for T3, whereas a trend for increase in follicles that stained for T4 was observed. In contrast, fluorescence intensity for both thyroid hormones decreased significantly after exposure to PTU. Overall, the zebrafish embryo appears to be suitable for the simultaneous visualization and detection of changing intrafollicular TH contents during normal development and after PTU treatment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alt B, Elsalini OA, Schrumpf P, Haufs N, Lawson ND, Schwabe GC, Mundlos S, Grüters A, Krude H, Rohr KB (2006a) Arteries define the position of the thyroid gland during its developmental relocalisation. Development 133(19):3797–3804
Alt B, Reibe S, Feitosa NM, Elsalini OA, Wendl T, Rohr KB (2006b) Analysis of origin and growth of the thyroid gland in zebrafish. Dev Dyn 235:1872–1883
Balon EK (2006) Epigenesis of an epigeneticist: the development of some alternative concepts on the early ontogeny and evolution of fishes. Guelph Ichthyol Rev 1
Baumann L, Ros A, Rehberger K, Neuhauss SCF, Segner H (2016) Thyroid disruption in zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae: different molecular response patterns lead to impaired eye development and visual functions. Aquat Toxicol 172:44–55
Belanger SE, Balon EK, Rawlings JM (2010) Saltatory ontogeny of fishes and sensitive early life stages for ecotoxicology tests. Aquat Toxicol 97:88–95
Brar NK, Waggoner C, Reyes JA, Fairey R, Kelley KM (2010) Evidence for thyroid endocrine disruption in wild fish in San Francisco Bay, California, USA. Relationships to contaminant exposures. Aquat Toxicol 96:203–215
Brown DD (1997) The role of thyroid hormone in zebrafish and axolotl development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:13011–13016
Brucker-Davis F (1998) Effects of environmental synthetic chemicals on thyroid function. Thyroid 8(9):827–856
Chang J, Wang M, Gui W, Zhao Y, Yu L, Zhu G (2012) Changes in thyroid hormone levels during zebrafish development. Zool Sci 29(3):181–184
Colborn T, vom Saal FS, Soto AM (1993) Developmental effects of endocrine-disrupting chemicals in wildlife and humans. Environ Health Perspect 101:378–384
Cooper DS (2005) Antithyroid drugs. N Engl J Med 352(9):905–917
Crofton KM (2008) Thyroid disrupting chemicals: mechanisms and mixtures. Int J Androl 31(2):209–223
DeVito M, Biegel L, Brouwer A, Brown S, Brucker-Davis F, Cheek AO, Christensen R, Colborn T, Cooke P, Crissman J, Crofton K, Doerge D, Gray E, Hauser P, Hurley P, Kohn M, Lazar J, McMaster S, McClain M, McConnell E, Meier C, Miller R, Tietge J, Tyl R (1999) Screening methods for thyroid hormone disruptors. Environ Health Perspect 107(5):407–415
Dohan O, De la Vieja A, Carrasco N (2000) Molecular study of the sodium–iodide symporter (NIS): a new field in thyroidology. Trends Endocrinol Metabol 11(3):99–105
Eales JG (1979) Thyroid functions in cyclostomes and fishes. Horm Evol 1:341–436
Ellis AE, Roberts RJ, Tytler P (1978) The anatomy and physiology of teleosts. In: Roberts RJ (ed) Fish Pathology, 1st edn. Baillière-Tindall, London, p. 13–54
Elsalini OA, Rohr KB (2003) Phenylthiourea disrupts thyroid function in developing zebrafish. Dev Genes Evol 212:593–598
Elsalini OA, von Gartzen J, Cramer M, Rohr KB (2003) Zebrafish hhex, nk2.1a, and pax2.1 regulate thyroid growth and differentiation downstream of nodal-dependent transcription factors. Dev Biol 263:67–80
EU, European Union (2010) Directive 2010/63/EU of the European parliament and of the council of 22 September 2010 on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes. Off J Eur L276:33–79
Gorbman A, Bern HA (1962) A textbook of comparative endocrinology. Am J Med Sci 244(2):262
Hadley ME (1996) Thyroid hormones. In: Hadley ME, editor. Endocrinol. 4. Chapter 13, vol 1996. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, pp 290–337
Heijlen M, Houbrechts AM, Darras VM (2013) Zebrafish as a model to study peripheral thyroid hormone metabolism in vertebrate development. Gen Comp Endocrinol 188:289–296
Howdeshell KL (2002) A model of the development of the brain as a construct of the thyroid system. Environ Health Perspect 110(Suppl. 3):337–348
Jianjie C, Wenjuan X, Jinling CS, Ruhui J, Meiyan L (2016) Fluoride caused thyroid endocrine disruption in male zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat Toxicol 171:48–58
Jomaa (2014) Developmental toxicity of thyroid-active compounds in a zebrafish embryotoxicity test. ALTEX 31(3):303–317
Kimmel CB, Ballard WW, Kimmel SR, Ullmann B, Schilling TF (1995) Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Dev Dyn 203:253–310
Kloas W, Urbatzka R, Opitz R, Würtz S, Behrends T, Hermelink B, Hofmann F, Jagnytsch O, Kroupova H, Lorenz C, Neumann N, Pietsch C, Trubiroha A, Van Ballegooy C, Wiedemann C, Lutz I (2009) Endocrine disruption in aquatic vertebrates. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1163:187–200
Kratzsch J, Pulzer F (2008) Thyroid gland development and defects. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 22:57–75
Lammer E, Carr GJ, Wendler K, Rawlings JM, Belanger SE, Braunbeck T (2009) Is the fish embryo toxicity test (FET) with the zebrafish (Danio rerio) a potential alternative for the fish acute toxicity test? Comp Biochem Physiol 149C:196–209
Leatherland J (1994) Reflections on the thyroidology of fishes: from molecules to humankind (Guelph Ichthyological reviews, 2). TFH Publications Inc., Neptune City
Leatherland JF, Ferguson HW (2006) Endocrine and reproductive systems. Systemic pathology of fish, 2nd edn. Scotian Press, London, pp 267–287
Liu YW, Chan WK (2002) Thyroid hormones are important for embryonic to larval transitory phase in zebrafish. Diff 70:36–45
Liu C, Zhang X, Deng J, Hecker M, Al-Khedhairy A, Giesy JP, Zhou B (2010) Effects of prochloraz or propylthiouracil on the cross-talk between the HPG, HPA, and HPT axes in zebrafish. Environ Sci Technol 45(2):769–775
McMenamin SK, Parichy DK (2013) Metamorphosis in Teleosts. In: Shi YB (ed) Animal Metamorphosis, Academic Press, San Diego, p. 127–166
Menke AL, Spitsbergen JM, Wolterbeek AP, Woutersen RA (2011) Normal anatomy and histology of the adult zebrafish. Toxicol Pathol 39:759–775
Mukhi S, Patiño R (2007) Effects of prolonged exposure to perchlorate on thyroid and reproductive function in zebrafish. Toxicol Sci 96(2):246–254
Mukhi S, Carr JA, Anderson TA, Patiño R (2005) Novel biomarkers of perchlorate exposure in zebrafish. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:1107–1115
Nagasaka A, Hidaka H (1976) Effect of antithyroid agents 6-propyl-2-thiouracil and 1-mehtyl-2-mercaptoimidazole on human thyroid iodine peroxidase. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 43:152–158
Nagel R (2002) DarT: the embryo test with the zebrafish Danio rerio - a general model in ecotoxicology and toxicology. ALTEX 19(Suppl 1):38–48
O'Connor JC, Frame SR, Davis LG, Cook JC (1999) Detection of the environmental antiandrogen p, p-DDE in CD and long-Evans rats using a tier I screening battery and a Hershberger assay. Toxicol Sci 51(1):44–53
OECD (1992a) OECD guideline for the testing of chemicals. Section 2: Effects on biotic systems. OECD Test Guideline 203: Fish, Acute toxicity test. Paris, France: Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development
OECD (1992b) OECD guideline for the testing of chemicals. Section 2: Effects on biotic systems. OECD Test Guideline 210: Fish, Early-life Stage Toxicity Test. Paris, France: Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development
OECD (1998) OECD guideline for the testing of chemicals. Section 2: Effects on biotic systems. OECD Test Guideline 212: Fish, Short-term Toxicity Test on Embryo and Sac-Fry Stages. Paris, France: Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development
OECD (2000) OECD guideline for the testing of chemicals. Section 2: Effects on biotic systems. OECD Test Guideline 215: Fish, Juvenile Growth Test. Paris, France: Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development
OECD (2009a) OECD guideline for the testing of chemicals. Section 2: Effects on biotic systems. OECD Test Guideline 229: Fish Short Term Reproduction Assay. Paris, France: Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development
OECD (2009b) OECD guideline for the testing of chemicals. Section 2: Effects on biotic systems. OECD Test Guideline 230: 21-day Fish Assay. Paris, France: Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development
OECD (2009c) OECD guideline for the testing of chemicals. Section 2: Effects on biotic systems. OECD Test Guideline 231: Amphibian Metamorphosis Assay. Paris, France: Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development
OECD (2011) OECD guideline for the testing of chemicals. Section 2: Effects on biotic systems. OECD Test Guideline 234: Fish Sexual Development Test. Paris, France: Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development
OECD (2013) OECD guideline for the testing of chemicals. Section 2: Effects on biotic systems. OECD Test Guideline 236: Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity (FET) Test. Paris, France: Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development
Opitz R, Hartmann S, Blank T, Braunbeck T, Lutz I, Kloas W (2006) Evaluation of histological and molecular endpoints for enhanced detection of thyroid system disruption in Xenopus laevis tadpoles. Toxicol Sci 90(2):337–348
Oppenheimer JH, Schwartz HL, Strait KA (1995) An integrated view of thyroid hormone actions in vivo. Mol Endocrinol: Basic Concepts and Clinical Correlations 249–268
Pack M, Solnica-Krezel L, Malicki J, Neuhauss SC, Schier AF, Stemple DL, Driever W, Fishman MC (1996) Mutations affecting development of zebrafish digestive organs. Development 123:321–328
Parichy DM, Tumer JM (2003) Zebrafish puma mutant decouples pigment pattern and somatic metamorphosis. Dev Biol 256:242–257
Parichy DM, Elizondo MR, Mills MG, Gordon TN, Engeszer RE (2009) Normal table of postembryonic zebrafish development: staging by externally visible anatomy of the living fish. Dev Dyn 238:2975–3015
Patiño R, Wainscott MR, Cruz-Li EI, Balakrishnan S, McMurry C, Blazer VS, Anderson TA (2003) Effects of ammonium perchlorate on the reproductive performance and thyroid follicle histology of zebrafish. Environ Toxicol Chem 22:1115–1121
Pinto PIS, Guerreiro EM, Power DM (2013) Triclosan interferes with the thyroid axis in the zebrafish (Danio rerio). Toxicol Res 2:60–69
Power DM, Llewellyn L, Faustino M, Nowell MA, Björnsson BT, Einarsdottir IE, Canario AVM, Sweeney GE (2001) Thyroid hormones in growth and development of fish. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 130:447–459
Power DM, Silva N, Campinho MA (2008) Metamorphosis. In: Finn RN, Kapoor BG (eds) Fish larval physiology. Science Publishers, Enfield, pp 607–638
Pradet-Balade B, Burel C, Dufour S, Boujard T, Kaushik SJ, Quérat B, Boeuf G (1999) Thyroid hormones down-regulate thyrotropin β mRNA level in vivo in the turbot (Psetta maxima). Fish Physiol Biochem 20(3):193–199
Raine JC, Leatherland JF (1999) Ontogeny of thyroid tissue and tissue thyroid hormone clearance in rainbow trout embryos reared at two temperatures. Fish Physiol Biochem 20:209–217
Raine JC, Leatherland JF (2000) Morphological and functional development of the thyroid tissue in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) embryos. Cell Tissue Res 301:235–244
Raine JC, Takemura A, Leatherland JF (2001) Assessment of thyroid function in adult medaka (Oryzias latipes) and juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) using immunostaining methods. J Exp Zool 290:366–378
Raldua D, Babin PJ (2009) Simple, rapid zebrafish larva bioassay for assessing the potential of chemical pollutants and drugs to disrupt thyroid gland function. Environ Sci Technol 43:6844–6850
Raldua D, Piña B (2014) In vivo zebrafish assays for analyzing drug toxicity. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 10:685–697
Rohr KB, Concha ML (2000) Expression of nk2.1a during early development of the thyroid gland in zebrafish. Mech Dev 95:267–270
Rolland RM (2000) A review of chemically-induced alterations in thyroid and vitamin a status from field studies of wildlife and fish. J Wildl Dis 36(4):615–635
Russell WMS, Burch RL, Hume CW (1959) The principles of humane experimental technique
Schmidt F, Braunbeck T (2011) Alterations along the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid Axis of the zebrafish (Danio rerio) after exposure to Propylthiouracil. J Thyroid Res 2011:376243
Schmidt F, Schnurr S, Wolf R, Braunbeck T (2011) Effects of the anti-thyroidal compound potassium-perchlorate on the thyroid system of the zebrafish. Aquat Toxicol 109:47–58
Schmidt F, Wolf R, Baumann L, Braunbeck T (2017) Ultrastructural alterations in zebrafish thyrocytes after exposure to thyroid disruptors propylthiouracil and perchlorate. Toxicol Pathol 45(5):649–662
Schmutzler C, Gotthart I et al (2007) Endocrine disruptors and the thyroid gland—a combined in vitro and in vivo analysis of potential new biomarkers. Environ Health Perspect 115(Suppl. 1):77–83
Sharma P, Patino R (2013) Regulation of gonadal sex ratios and pubertal development by the thyroid endocrine system in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Gen Comp Endocrinol 184:111–119
Sharma P, Grabowski T, Patino R (2016) Thyroid endocrine disruption and external body morphology of zebrafish. Gen Comp Endocrinol 226:42–49
Shi X, Liu C, Wu G, Zhou B (2009) Waterborne exposure to PFOS causes disruption of the hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid axis in zebrafish larvae. Chemosphere 77:1010–1018
Spence R, Fatema MK, Reichard M, Huq KA, Wahab MA, Ahmed ZF, Smith C (2006) The distribution and habitat preferences of the zebrafish in Bangladesh. J Fish Biol 69:1435–1448
Stinckens E, Vergauwen L, Schroeder AL, Maho W, Blackwell BR, Witters H, Blust R, Ankley GT, Covaci A, Villeneuve DL (2016) Impaired anterior swim bladder inflation following exposure to the thyroid peroxidase inhibitor 2-mercaptobenzothiazolepart II: zebrafish. Aquat Toxicol 201–217
Strähle U, Scholz S, Geisler R, Greiner P, Hollert H, Rastegar S, Schumacher A, Selderslaghs I, Weiss C, Witters H, Braunbeck T (2011) Zebrafish embryos as an alternative to animal experiments - a commentary on the definition of the onset of protected life stages in animal welfare regulations. Reprod Toxicol 33:245–153
Studer H, Forster R, Conti A, Kohler H, Haeberli A, Engler H (1978) Transformation of normal follicles into thyrotropin-refractory “cold” follicles in the aging mouse thyroid gland. Endocrinol 102:1576–1586
Tata JR (2006) Amphibian metamorphosis as a model for the developmental actions of thyroid hormone. Mol Cell Endocrinol 246(1–2):10–20
Thienpont B, Tingaud-Sequeira A, Prats E, Barata C, Babin PJ, Raldua D (2011) Zebrafish eleutheroembryos provide a suitable vertebrate model for screening chemicals that impair thyroid hormone synthesis. Environ Sci Technol 45:7525–7532
Thienpont B, Barata C, Raldua D (2013) Modeling mixtures of thyroid gland function disruptors in a vertebrate alternative model, the zebrafish eleutheroembryo. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 269:169–175
Tonyushkina KN, Shen MC, Ortiz-Toro T, Karlstrom RO (2014) Embryonic exposure to excess thyroid hormone causes thyrotrope cell death. J Clin Investig 124(1):321–327
van der Ven LT, van den Brandhof EJ, Vos JH, Power DM, Wester PW (2006) Effects of the antithyroid agent propylthiouracil in a partial life cycle assay with zebrafish. Environ Sci Technol 40:74–81
Vos JG, Dybing E, Greim HA, Ladefoged O, Lambré C, Tarazona JV, Brandt I, Vethaak AD (2000) Health effects of endocrine-disrupting chemicals on wildlife, with special reference to the European situation. Crit Rev Toxicol 30(1):71–133
Wabuke-Bunoti MA, Firling CE (1983) The prehatching development of the thyroid gland of the fathead minnow, Pimephales promelas (Rafinesque). Gen Comp Endocrinol 49:320–331
Webb JF (1999) Larvae in fish development and evolution. In: Hall BK, Wake MH (eds) The origin and evolution of larval forms. Academic Press, New York, pp 109–158
Wendl T, Lun K, Mione M, Favor J, Brand M, Wilson SW, Rohr KB (2002) Pax2.1 is required for the
Wilson JM, Bunte RM, Carty AJ (2009) Evaluation of rapid cooling and tricaine methanesulfonate (MS222) as methods of euthanasia in zebrafish (Danio rerio). J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci 48:785–789
Wixon J (2000) Featured organism: Danio rerio, the zebrafish. Yeast 17:225–231
Yen PM (2001) Physiological and molecular basis of thyroid hormone action. Physiol Rev 81:1097–1142
Yoshiura Y, Sohn Y, Munakata A, Kobayashi M, Aida K (1999) Molecular cloning of the cDNA encoding the β subunit of thyrotropin and regulation of its gene expression by thyroid hormones in the goldfish, Carassius auratus. Fish Physiol Biochem 21(3):201–210
Yu L, Lam JC et al (2011) Parental transfer of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and thyroid endocrine disruption in zebrafish. Environ Sci Technol 45(24):10652–10659
Zoeller RT (2003) Challenges confronting risk analysis of potential thyroid toxicants. Risk Anal 23(1):143–162
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 89 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rehberger, K., Baumann, L., Hecker, M. et al. Intrafollicular thyroid hormone staining in whole-mount zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos for the detection of thyroid hormone synthesis disruption. Fish Physiol Biochem 44, 997–1010 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-018-0488-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-018-0488-y