Abstract
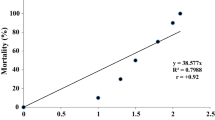
The present experiment was conducted to establish the relationship between selected physiological parameters and histological responses of Channa punctatus brain tissue to endosulfan exposure. The fish (35.6 ± 0.7 g) was exposed to sublethal endosulfan concentration (8.1 μg l−1) for a period of 12, 24, 36, 48, 72, and 96 h. Results showed that brain glucose level increased significantly after exposure, indicating a hyperglycemic state of the fish. Brain vitamin C level decreased with an increase in the exposure time. Acetylcholine esterase and adenosine triphosphatase enzyme activities also showed a significant reduction upon endosulfan exposure. Brain histopathology after 96 h endosulfan exposure showed that the apical lobe of the cerebrum (the only portion examined) had mild necrosis. Focal area of gliosis could be seen in the cerebrum, which were absent in the control fish. The results indicate that exposure of sublethal concentration of endosulfan to C. punctatus may have a direct effect on the histology of the fish's brain tissue, thereby affecting its metabolism.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Augustinsson KB (1957) The reaction of acetylcholine esters and other carboxylic acid derivatives with hydroxylamine and its analytical application. J Biol Chem 180:249–261
Azad IS, Dayal JS, Poornima M, Ali SA (2007) Supra dietary levels of vitamins C and E enhance antibody production and immune memory in juvenile milkfish (Chanos chanos) to formalin-killed Vibrio vulnificus. Fish Shellfish Immunol 23:54–163. doi:10.1016/j.fsi.2006.09.014
Cengiz EI, Unlu E (2002) Histological changes in the gill of mosquito fish, Gambusia affinis exposed to endosulfan. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 68:290–296
Chondor SL (1999) Biology of finfish and shellfish. SCSC Publishers, India
Coppage DO, Mathew E (1974) Short-term effects of organophosphate pesticides on cholinesterases of estuarine fishes and pink shrimp. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 11:483–488. doi:10.1007/BF01685308
Das BK (1997) Studies on the effect of some pesticides and common used chemicals on Indian major carp and their ecosystem. PhD Thesis, Orissa University of Agriculture and Technology, Bhubaneswar, Orissa, India
Das BK, Mukherjee SC (2000) A histological study of carp (Labeo rohita) exposed to hexachlorocyclohexane. Vet Arh 70:169–180
Devraj P, Selvarajan VR, Durairaj S (1991) Relationship between acetyl cholinesterase and monoamine oxidase in brain regions of O. mossambicus exposed to phosalone. Indian J Exp Biol 29:790–792
Dutta HM, Arends DA (2003) Effects of endosulfan on brain acetylcholinesterase activity in juvenile bluegill sunfish. Environ Res 91:157–162. doi:10.1016/S0013-9351(02)00062-2
Dutta HM, Munshi JSD, Dutta GR, Singh NK, Adhikari S, Richmonds CR (1995) Age-related differences in the inhibition of brain acetylcholinesterase activity of Heteropneustes fossilis (Bloch) by malathion. Comp Biochem Physiol A 11:331–334. doi:10.1016/0300-9629(94)00166-Q
EFSA (2005) Opinion of the scientific panel on contaminants in the food chain on a request from the commission related to endosulfan as undesirable substance in animal feed. EFS A J 234:1–29
Ferrando MD, Andreu E (1991) Change in selected biochemical parameters in the brain of fish, Anguilla anguilla (L.), exposed to lindane. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 47:459–464. doi:10.1007/BF01702211
Fiske CH, Subbarow Y (1925) The colorimetric determination of phosphorus. J Biol Chem 66:375–400
Garg UK, Pal AK, Jha GJ, Jadhao SB (2004) Haemato-biochemical and pathophysiological effects of chronic toxicity with synthetic pyrethroid, organophosphate and chlorinated pesticides in broiler chicks. Int Immunopharmacol 4:1709–1722. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2004.08.002
Heath AG (1995) Water pollution and fish physiology, 2nd edn. Lewis publishers, London, UK
Hota AK, Mishra DK, Tripathy PC (1993) Metabolic effects of kilex carbaryl on a freshwater teleost, Channa punctatus (Bloch). In: Agrawal VP, Abidi SAH, Verma GP (eds) Environmental impact on aquatic and terrestrial habitats. Berhampur Society of Biosciences, Muzaffarnagar, pp 335–342
Lorenzatti E, Altahus R, Lajmanovich R, Peltzer P (2004) Residues of endosulfan in soy plants in Argentina croplands. Fresenius Environ Bull 13:89–92
Lowry OH, Ronebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–276
Mauck WL, Mehrle PM, Mayer FL (1978) Effect of polychlorinated biphenyl Arochor 1254 on growth, survival and bone development in brook trout, Salvelinus fontinalis. J Fish Res Board Can 35:1084–1088
Montero D, Izquierdo MS, Tort L, Robaina L, Vergara JM (1999) High stocking density produces crowding stress altering some physiological and biochemical parameters in gilthead sea bream, Sparus aurata, juveniles. Fish Physiol Biochem 20:53–60. doi:10.1023/A:1007719928905
Naqvi SM, Vaishnavi C (1993) Bioaccumulative potential and toxicity of endosulfan insecticide to non-target animals. Comp Biochem Physiol C 105:347–361. doi:10.1016/0742-8413(93)90071-R
Oruc EO, Uner N, Tamer L (2002) Comparison of NA+, K+-ATPase activity and malondialdehyde contents in liver tissue for three fish species exposed to azinphosmethyl. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 69:271–277. doi:10.1007/s00128-002-0057-y
Pal AK, Kushwah H, Kushwah A (1989) Protective role of protein against endosulfan exposure. J Vet Physiol Allied Sci 8:19–23
Perez Campo R, Lopez–Torres M, Rojas C, Cadenas S, Barja G (1993) A comparative study of free radicals in vertebrates–1, antioxidant enzyme. Comp Biochem Physiol B 105:749–755. doi:10.1016/0305-0491(93)90116-M
Petri D, Glover CN, Ylving S, Kolås K, Fremmersvik G, Waagbø R, Berntssen MHG (2006) Sensitivity of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) to dietary endosulfan as assessed by haematology, blood biochemistry, and growth parameters. Aquat Toxicol 80:207–216. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2006.07.019
Post RL, Sen AK (1967) Methods in enzymology, vol 10. Academic Press, Inc., New York, p 762
Puspanjali Pal AK, Prasad RL, Prasad A, Singh SK, Kumar A, Jadhao SB (2005) In ovo embryotoxicity of α-endosulfan adversely influences liver and brain metabolism and immune system in chickens. Pestic Biochem Physiol 82:103–114
Roberts RJ (1989) Nutritional pathology of teleosts. In: Roberts RJ (ed) Fish pathology. Bailliere Tindall, London, pp 337–362
Roe JH, Keuther CA (1943) The determinations of ascorbic acid in whole blood and urine through the 2, 4-dinitrophenylhydrazine (DNPH) derivative of dehydroascorbic acid. J Biol Chem 147:399–407
Sarma K, Pal AK, Mukherjee SC, Datta S (2003) Acute toxicity of endosulfan of freshwater teleost, Channa punctatus (Bloch). J Environ Res 13:80–84
Sharma RM (1988) Effect of endosulfan on adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase) activity in liver, kidney and muscles of Channa gachua. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 41:317–323. doi:10.1007/BF01688873
Srivastava AK, Singh NN (1981) Effects of endosulfan on fish carbohydrate metabolism. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 15:257–261
Trevors JI (1986) A basic programme for estimating LD50 values using IBM- PC. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 37:18–26. doi:10.1007/BF01607723
Vijayan MM, Foster GD, Moon TW (1993) Cortisol implantation alters hepatic metabolism and hormonal responsiveness in the sea raven. Fish Physiol Biochem 12:327–335. doi:10.1007/BF00004417
Winston G, Di Giulio R (1991) Pro-oxidant and antioxidant mechanisms in aquatic organisms. Aquat Toxicol 19:137–161. doi:10.1016/0166-445X(91)90033-6
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the director of the Central Institute of Fisheries Education, Versova, Mumbai, India, for providing the facilities used during this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarma, K., Pal, A.K., Sahu, N.P. et al. Biochemical and histological changes in the brain tissue of spotted murrel, Channa punctatus (Bloch), exposed to endosulfan. Fish Physiol Biochem 36, 597–603 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-009-9333-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-009-9333-7