Abstract
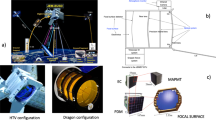
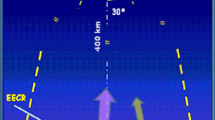
Mounted on the International Space Station(ISS), the Extreme Universe Space Observatory, on-board the Japanese Experimental Module (JEM-EUSO), relies on the well established fluorescence technique to observe Extensive Air Showers (EAS) developing in the earth’s atmosphere. Focusing on the detection of Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays (UHECR) in the decade of 1020eV, JEM-EUSO will face new challenges by applying this technique from space. The EUSO Simulation and Analysis Framework (ESAF) has been developed in this context to provide a full end-to-end simulation frame, and assess the overall performance of the detector. Within ESAF, angular reconstruction can be separated into two conceptually different steps. The first step is pattern recognition, or filtering, of the signal to separate it from the background. The second step is to perform different types of fitting in order to search for the relevant geometrical parameters that best describe the previously selected signal. In this paper, we discuss some of the techniques we have implemented in ESAF to perform the geometrical reconstruction of EAS seen by JEM-EUSO. We also conduct thorough tests to assess the performances of these techniques in conditions which are relevant to the scope of the JEM-EUSO mission. We conclude by showing the expected angular resolution in the energy range that JEM-EUSO is expected to observe.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
References
Adams, J.H. Jr., et al.: (JEM-EUSO Collaboration): an evaluation of the exposure in nadir observation of the JEM-EUSO mission. Astropart. Phys. 44, 76–90 (2013)
Takahashi, Y., et al.: The JEM-EUSO mission. New. J. of Phys. 11, 065009 (2009)
Berat, C., Bottai, S., De Marco, D., Moreggia, S., Naumov, D., Pallavicini, M., Pesce, R., Petrolini, A., et al.: ESAF: full simulation of space-based extensive air showers detectors. Astropart. Phys. 33, 221 (2010). arXiv:0907.5275 [astro-ph.IM].
Blaicher, M.: End-to-end simulation of the Extreme Universe Space Observatory (EUSO). Bachelor Thesis, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (2012)
Bertaina, M., et al.: For the JEM-EUSO Collaboration: the trigger system of the JEM-EUSO Project. 30th International Cosmic Ray Conference Proceedings (Mérida) (2007)
Bertaina, M., et al.: Performances and air-shower reconstruction techniques for the JEM-EUSO mission. Adv. Space Res. (submitted ) (2013)
Bobik, P., Garipov, G., Khrenov, B., Klimov, P., Morozenko, V., Shinozaki, K., Bertaina, M., Santangelo, A., Kudela, K., Pastircak, B., Urbar, J.: For the Jem-Euso Collaboration: estimation of JEM-EUSO experiment duty cycle based on Universitetsky Tatianameasurements, 32nd International Cosmic Ray Conference Proceedings (Beijing) (2011)
Casolino, M., Kajino, F.: An overview of the JEM-EUSO instrument. This volume of Experimental Astronomy
Catalano, O., D’Ali Staiti, G., Gabriele, M., La Fata, L.: 27th International Cosmic Ray Conference Proceedings (Hamburg) 2, 498 (2001)
Dagoret, S., Barrillon, P., Jung, A., Ebersoldt, A.: The Photodetector Module of the JEM-EUSO mission. This volume of Experimental Astronomy
Ebisuzaki, T., et al.: The JEM-EUSO Project: observing extremely high energy cosmic rays and neutrinos from the international space station. Nucl. Phys. B (Proc. Suppl.) 175–176, 237–240 (2008)
Ilina, N.P., Kalmykov, N.N., Prosin, V.V.: Cerenkov radiation and parameters of extensive air showers. Sov. J. Nucl. Phys. 55, 1540–1547 (1992)
Kalman, R.E.: Trans. ASME–J. Basic Eng. 82D, 35–45 (1960)
Kalmykov, N.N., Ostapchenko, S.S., Pavlov, A.I.: Quark-gluon string model and EAS simulation problems at ultra-high energies. Nucl. Phys. Proc. Suppl. 52B, 17 (1997)
Keilhauer, B., Bohacova, M., Fraga, M., et al.: Eur. Phys. J. Web Conf. 53, 1010 (2013)
Medina-Tanco, G.: Studying individual UHECR sources with high statistics 31st International Cosmic Ray Conference Proceedings (Łódź) (2009)
Medina-Tanco, G., Weiler, T., Teshima, M., Ebisuzaki, T., Picozza, P., Santangelo, A., Parizot, E., Bertaina, M.: Science Objectives of the JEM-EUSO mission. 32nd International Cosmic Ray Conference Proceedings (Beijing) (2011)
Nagano, M., Kobayakawa, K., Sakaki, N., Ando, K.: New measurement on photon yields from air and the application to the energy estimation of primary cosmic rays. Astropart. Phys. 22, 235 (2004)
Pallavicini, M., the EUSO Collaboration: the extreme universe space observatory. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 502, 155–157 (2003)
Pesce, R.: Studio ed ottimizzazione delle prestazioni di un apparato per la rilevazione di raggi cosmici di altissima energia dallo spazio. Tesi di Laurea, Universita degli studi di Genova (2004)
Santangelo, A., et al.: For the JEM-EUSO Collaboration: requirement and expected performances of the JEM-EUSO mission. 32nd International Cosmic Ray Conference Proceedings (Bejing) 3, 219 (2011)
Taddei, E.: Studio di algoritmi per la ricostruzione della direzione deglie sciami atmosferici in EUSO. Tesi di Laurea, Universita degli studi di Firenze (2004)
NASA, NOAA, USAF, US-Standard Atmosphere, NASA-TM-X-74335 (1976) NASA, US-Standard Atmosphere Supplements, U.S. Government Printing Office,Washington, D.C., 1976
Wiencke, L., et al.: For the JEM-EUSO Collaboration: the JEM-EUSO Global Light System. 33rd International Cosmic Ray Conference Proceedings (Rio de Janeiro) (2013)
Acknowledgments
The present work has been conducted under the support of Deutsches Zentrum fuer Luft und Raumfahrt (DLR). Moreover, it has partly been funded by the European Space Agency (ESA) Topical Team Activities Fund. It has been partially supported by Joint Institute for Nuclear Research (JINR) grant No. 13-902-07 and by the grant of Russian Foundation for Basic Research No. 13-02-12175-ofi-m. We wish to thank RICC, the RIKEN Integrated Cluster of Cluster in Tokyo, Japan for the allocation of computing resources and service.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
The JEM-EUSO Collaboration., Adams, J.H., Ahmad, S. et al. Performances of JEM-EUSO: angular reconstruction. Exp Astron 40, 153–177 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10686-013-9371-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10686-013-9371-0