Abstract
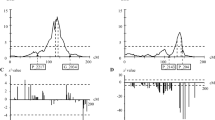
Apple chlorotic leaf spot virus (ACLSV), also known as apricot pseudo pox, “viruela” (in Spain) and “butteratura” (in Italy), has had a significant impact on the production of Prunus species, including apricot (P. armeniaca L.). Two apricot cultivars have recently been described as resistant to this virus: the traditional Spanish cultivar ‘Mauricio’ and the French cultivar ‘Bergeron’. However, as far as we know, no work on the genetic control of the resistance to ACLSV has been published in any Prunus species. In this study, the transmission of resistance to ACLSV and the related quantitative trait loci (QTLs) were analysed for 3 years in an F1 apricot progeny of 130 descendants derived from the cross ‘Bergeron’ (resistant to ACLSV) × ‘Currot’ (susceptible). The apricot descendants evaluated were classified as susceptible or resistant depending on the presence or absence of ACLSV evaluated through ELISA and RT-PCR. A non-parametric mapping method based on the Kruskal–Wallis (KW) test was used to score and identify linked QTLs. The ‘Bergeron’ cultivar showed a high capacity to transmit resistance to ACLSV, generating around 57% of the resistant descendants. Additionally, the results indicated an oligogenic control of ACLSV resistance in apricot, with significant QTLs in alternative years in linkage groups (LGs) 5 and 7 and in all years in LG2 and LG4.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al Rwahnih M, Torturo C, Minafra A, Saldarelli P, Myrta A, Pallás V, Savino V (2004) Molecular variability of Apple chlorotic leaf spot virus in different hosts and geographical regions. J Plant Pathol 86:117–122
Bernhard R, Marénaud C, Sutic D (1969) Le pêcher GF305 indicateur polyvalent des virus des espèces a noyau. Ann Phytopathol 1:603–617
Castède S, Campoy JA, Le Dantec L, Quero-García J, Barreneche T, Wenden B, Dirlewanger E (2015) Mapping of candidate genes involved in bud dormancy and flowering time in sweet cherry (Prunus avium). PLoS ONE 10:1–18
Cho IS, Igori D, Lim S, Choi GS, Hammond J et al (2016) Deep sequencing analysis of Apple infecting viruses in Korea. Plant Pathol J 32:441–451
Decroocq S, Chague A, Lambert P, Roch G (2014) Selecting with markers linked to the PPVres major QTL is not sufficient to predict resistance to Plum Pox Virus (PPV) in apricot. Tree Genet Genomics 10:1161–1170
Desvignes JC, Boyé R (1988) Different disease caused by the Chlorotic leaf spot virus on the fruit trees. Acta Hortic 235:31–35
Dirlewanger E, Graziano E, Joobeur T, Garriga-Caldré F, Cosson P, Howad W, Arús P (2004a) Comparative mapping and marker-assisted selection in Rosaceae fruit crops. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:9891–9896
Dirlewanger E, Cosson P, Howad W, Capdeville G, Bosselut N, Claverie M, Voisin R, Lafargue B, Baron O, Laigret F, Kleinhentz M, Arús P, Esmenjaud D (2004b) Microsatellite genetic linkage maps of myrobalan plum and an almond-peach hybrid—location of root-knot nematode resistance genes. Theor Appl Genet 109:827–838
Dirlewanger E, Quero-García J, Le Dantec L, Lambert P, Ruiz D, Dondini L, Illa E, Quilot B, Audergon JM, Tartarini S, Letourmy P, Arús P (2012) Comparison of the genetic determinism of two key phenological traits, flowering and maturity dates, in three Prunus species: peach, apricot and sweet cherry. Heredity (Edinb) 109:280–292
Dondini L, Lain O, Vendramin V, Rizzo M, Vivoli D, Adami M, Guidarelli M, Gaiotti F, Palmisano F, Bazzoni A et al (2011) Identification of QTL for resistance to plum pox virus strains M and D in Lito and Harcot apricot cultivars. Mol Breed 27:289–299
Fan S, Bielenberg DG, Zhebentyayeva TN, Reighard GL, Okie WR, Holland D, Abbott AG (2010) Mapping quantitative trait loci associated with chilling requirement, heat requirement and bloom date in peach (Prunus persica). New Phytol 185:917–930
Font i Forcada C, Fernández i Martí A, Socias i Company R (2012) Mapping quantitative trait loci for kernel composition in almond. BMC Genet 13:47
García-Ibarra A, Rubio M, Dicenta F, Martínez-Gómez P (2010) Evaluation of resistance to Apple chlorotic leaf spot virus (ACLSV) in controlled greenhouse conditions in the apricot breeding programme of CEBAS-CSIC in Murcia (Spain). Acta Hortic 862:487–490
García-Ibarra A, Dicenta F, Martínez-Gómez P, Rubio M (2012) Evaluation of apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) resistance to Apple chlorotic leaf spot virus in controlled greenhouse conditions. Eur J Plant Pathol 133:857–863
Hernández Mora JR, Micheletti D, Bink M, de Weg EV, Cantín C et al Integrated QTL detection for key breeding traits in multiple peach progenies. BMC Genom 18:404
Klagges C, Campoy JA, Quero-García J, Guzmán A, Mansur L, Gratacós E, Silva H, Rosyara UR, Iezzoni A, Meisel LA, Dirlewanger E et al (2013) Construction and comparative analyses of highly dense linkage maps of two sweet cherry intra-specific progenies of commercial cultivars. PLoS ONE 7:e54743
Lalli DA, Decroocq V, Blenda AV, Schurdi-Levraud V, Garay L, Le Gall O, Damsteegt V, Reighard GL, Abbott AG (2005) Identification and mapping of resistance gene analogues (RGAs) in Prunus: a resistance map for Prunus. Theor Appl Genet 111:1504–1513
Lambert P, Hagen LS, Arus P, Audergon JM (2004) Genetic linkage maps of two apricot cultivars (Prunus armeniaca L.) compared with the almond Texas 9 peach Earlygold reference map for Prunus. Theor Appl Genet 108:1120–1130
Lambert P, Dicenta F, Rubio M, Audergon JM (2007) QTL analysis of resistance to Sharka disease in the apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) ‘Polonais’ 9 ‘Stark Early Orange’ F1 progeny. Tree Genet Genomes 3:299–309
Myrta A, Matic S, Malinowski T, Pasquini G, Candresse T (2011) Apple chlorotic leaf spot virus in stone fruits. In: Hadidi A, Barba M, Candresse T, Jelkmann W (eds) Virus and virus-like diseases of pome and stone fruits. APS Press, St. Paul, pp 85–90
Osman F, Al Rwahnih M, Rowhani A (2017) Real-time RT-qPCR detection of Cherry rasp leaf virus, Cherry green ring mottle virus, Cherry necrotic rusty mottle virus, Cherry virus a and apple chlorotic leaf spot virus in stone fruits. J Plant Pathol 99:279–285
Rubio M, Martínez-Gómez P, Audergon JM, Dicenta F (2007) Testing genetic control hypotheses for Plum pox virus (sharka) resistance in apricot. Sci Hortic 112:361–365
Rubio M, García-Ibarra A, Soler A, Martínez-Gómez P, Dicenta F (2013) Relationship of viruses and viroids with apricot “viruela” disease. Phytopathol Mediterr 52:148–153
Rubio M, Ruiz D, Egea J, Martínez-Gómez P, Dicenta F (2014) Opportunities of marker-assisted selection for Plum pox virus resistance in apricot breeding programs. Tree Genet Genomes 10:513–525
Salazar JA, Ruiz D, Egea J, Martínez-Gómez P (2013) Inheritance of fruit quality traits in apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) and analysis of linked quantitative trait loci (QTLs) using simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers. Plant Mol Biol Rep 31:1506–1517
Salazar JA, Ruiz D, Campoy JA, Sánchez-Pérez R, Crisosto CH et al (2014) Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL) and Mendelian Trait Loci (MTL) analysis in Prunus: a breeding perspective and beyond. Plant Mol Biol Rep 32:1–18
Salazar JA, Rubio M, Ruiz D, Tartarini S, Martínez-Gómez P, Dondini L (2015) SNP development for genetic diversity analysis in apricot. Tree Genet Genomes 11:15
Salazar JA, Ruiz JA, Tartarini S, Dondini L, Martínez-Gómez P (2016a) Inheritance of reproductive phenology traits and related QTL Identification in apricot. Tree Genet Genomes 12:71
Salazar JA, Batnini MA, Trifi-Farah N, Ruiz D, Martínez-Gómez P, Rubio M (2016b) Quantitative trait loci (QTLs) identification and the transmission of resistance to powdery mildew in apricot. Euphytica 211:245–254
Salazar JA, Pacheco I, Shinya P, Zapata P, Silva C, Aradhya M, Velasco D, Ruiz D, Martínez-Gómez P, Infante R (2017) Genotyping by Sequencing for SNP-Based Linkage Analysis and Identification of QTLs Linked to Fruit Quality Traits in Japanese Plum (Prunus salicina Lindl.). Front Plant Sci 8:1–14
Sánchez-Navarro JA, Aparicio F, Herranz MC, Minafra A, Myrta A, Pallás V (2005) Simultaneous detection and identification of eight stone fruit viruses by one-step RT-PCR. Eur J Plant Pathol 111:77–84
Sánchez-Pérez R, Howad D, Dicenta F, Arús P, Martínez-Gómez P (2007) Mapping major genes and quantitative trait loci controlling agronomic traits in almond. Plant Breed 126:310–318
Socquet-Juglard D, Christen D, Devènes G, Gessler C, Duffy B, Patocchi A (2013) Mapping Architectural, phonological, and fruit quality QTLs in apricot. Plant Mol Biol Rep 31:387–397
Soriano JM, Domingo ML, Zuriaga E, Romero C, Zhebentyayeva T, Abbott AG, Badenes ML (2012) Identification of simple sequence repeat markers tightly linked to Plum pox virus resistance in apricot. Mol Breed 30:1017–1026
Zhang JB, Sebolt AM, Wang D, Bink M, Olmstead JW, Iezzoni AF (2010) Fruit size QTL analysis of an F-1 population derived from a cross between a domesticated sweet cherry cultivar and a wild forest sweet cherry. Tree Genet Genomes 6:25–36
Acknowledgements
This study has mainly been supported by the project “Genetic and molecular basis of the multiplex resistance to Plum pox virus (PPV, “sharka”) and Apple chlorotic leaf spot virus (ACLSV, “viruela”) in apricot” (AGL2015-68021-R) of the Spanish Ministry of Science, Education and Universities. Additionally, the Seneca Foundation of the Region of Murcia has contributed to this study by means of the projects “Breeding stone fruit species assisted by molecular tools” (19879/GERM/15) and “Jiménez de la Espada Interchange Program” (20574/EE/18).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rubio, M., Salazar, J.A., Dicenta, F. et al. Identification of quantitative trait loci (QTLs) linked to Apple chlorotic leaf spot virus (ACLSV) resistance in apricot. Euphytica 215, 170 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-019-2481-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-019-2481-7