Abstract
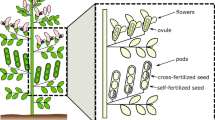
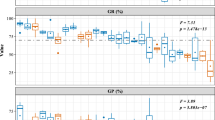
Moderate levels of selfing despite high inbreeding depression (ID) make runner bean an excellent model for mixed-mating reproductive biology studies in legumes. This work assesses the extent of the ID variation and consistency at different plant growth stages through selfing generations in seven runner bean populations. Field-collected populations after previous isolated multiplication were hand-pollinated in an isolated greenhouse during five generations to produce progeny. Generations were compared for inbreeding effects (δ) on seed germination, survival to flower, and seed weight and yield. The outcrossing rates of the founder populations and the genetic variation and Wright’s ID at the population and generation level were estimated by using 35 polymorphic microsatellite loci. Neutral microsatellite loci were analyzed through generations and populations using different outlier tests to identify loci directly associated with adaptation to inbreeding. Our study revealed patterns of genetic diversity (H e = 0.36) and outcrossing rates (ranged from 24 to 44 %) that are consistent with a mixed-mating system. Selfing-pollination procedure significantly affected germination and survival rates, yield, and to a lesser extent seed weight. Three loci had significant hits to genes related to embryonic development when performing BLAST searches to Phytozome database. Results showed a general inconsistency in δ across plant growth stages and populations, suggesting that different deleterious loci are acting at different stages. Inbreeding tended to purge individuals of deleterious recessive alleles to reduce ID. Variation among individuals within populations may lead to the development of inbreeding lineages with lower levels of ID. Several lines that have been self-pollinated for many generations became homozygous at almost all gene loci and produced a uniform population of true breeding progeny and acceptable performance.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allard RW, Jain SK, Workman PL (1968) The genetics of inbreeding populations. Adv Genet 14:55–131
Alvarez MT, de Miera LES, de la Vega MP (1998) Genetic variation in common and runner bean of the Northern Meseta in Spain. Genet Resour Crop Evol 45:243–251
Antao T, Lopes A, Lopes RJ, Beja-Pereira A, Luikart G (2008) LOSITAN: a workbench to detect molecular adaptation based on a Fst-outlier method. BMC Bioinform 9:323
Beaumont MA, Nichols RA (1996) Evaluating loci for use in the genetic analysis of population structure. Proc R Soc Lond Ser B 263:1619–1626
Bede EN (2007) Effect of quenching on cook ability of some food legumes. Food Control 18:1161–1164
Blackwall FLC (1971) Pod-seeding and yield in the runner bean (Phaseolus coccineus L.). Bull Natl Inst Agric Bot 12:45–56
Blair MW, Pedraza F, Buendia HF, Gaitán-Solís E, Beebe SE, Gepts P, Tohme J (2003) Development of a genome-wide anchored microsatellite map for common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Theor Appl Genet 107:1362–1374
Blair MW, Iriarte G, Beebe S (2006) QTL analysis of yield traits in an advanced backcross population derived from a cultivated Andean wild common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) cross. Theor Appl Genet 112:1149–1163
Brown AHD, Allard RW (1970) Estimation of mating system in open-pollinated maize populations using isozyme polymorphisms. Genetics 66:133–145
Bürglin TR (2008) The hedgehog protein family. Genome Biol 9:241
Buso GSC, Amaral ZPS, Brondani RPV, Ferreira ME (2006) Microsatellite markers for the common bean—Phaseolus vulgaris. Mol Ecol Notes 6:252–254
Byers DL, Waller DM (1999) Do plant populations purge their genetic load? Effects of population size and mating history on inbreeding depression. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 30:479–513
Carr DE, Dudash MR (1997) The effects of five generations of enforced selfing on potential male and female function in Mimulus guttatus. Evolution 51:1795–1805
Charlesworth D, Charlesworth B (1987) Inbreeding depression and its evolutionary consequences. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 18:237–268
Charlesworth B, Charlesworth D (1999) The genetic basis of inbreeding depression. Genet Res 74:329–340
Checa OE, Blair MW (2008) Mapping QTL climbing ability and component traits in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Mol Breed 22:201–215
Chen DH, Ronald PC (1999) A rapid DNA minipreparation method suitable for AFLP and other PCR applications. Plant Mol Biol Rep 17:53–57
Coello G, Escalante AM (1989) Estructura genética y estimación de los parámetros del sistema de apareamiento en poblaciones silvestres y cultivadas de Phaseolus coccineus. B.Sc. Thesis, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México. D.F., México
Cornish MA (1990a) Selection during a selfing programme. I. The effects of a single round of selection. Heredity 65:201–211
Cornish MA (1990b) Selection during a selfing programme. II. The effects of two or more rounds of selection. Heredity 65:213–220
Crow JF (1986) Basic concepts in population, quantitative, and evolutionary genetics. W. H. Freeman, New York
Crow JF, Kimura M (1970) An introduction to population genetics theory. Harper and Row, New York
Curie C, Cassin G, Couch D, Divol F, Higuchi K, Jean ML, Misson J, Schikora A, Czernic P, Mari S (2009) Metal movement within the plant: contribution of nicotianamine and yellow stripe 1-like transporters. Ann Bot 103:1–11
Daehler CC (1999) Inbreeding depression in smooth cordgrass Spartina alterniflora (Poaceae) invading San Francisco Bay. Am J Bot 86:131–139
Delgado Salinas A (1988) Variation, taxonomy, domestication and germplasm potentialities in Phaseolus coccineus. In: Gepts P (ed) Genetic resources of Phaseolus beans, 2nd edn. Kluwer Academic, Boston, pp 441–463
Dudash MR, Carr DE, Fenster CB (1997) Five generations of enforced selfing and outcrossing in Mimulus guttatus: ID variation at the population and family level. Evolution 51:54–65
El Mousadik A, Petit RJ (1996) High level of genetic differentiation for allelic richness among populations of the argan tree [Argania spinosa (L.) Skeels] endemic of Morocco. Theor Appl Genet 92:832–839
Escalante AM, Coello G, Eguiarte LE, Pinero D (1994) Genetic structure and mating systems in wild and cultivated populations of Phaseolus coccineus and P. vulgaris (Fabaceae). Am J Bot 81:1096–1103
Fisher RA (1941) Average excess and average effect of a gene substitution. Ann Eugen 11:53–63
Fox CW, Scheibly KL, Reed DH (2008) Experimental evolution of the genetic load and its implications for the genetic basis of inbreeding depression. Evolution 62:2236–2249
Frusciante L, Monti LM (1980) Direct and indirect effects of insect pollination on the yield of the field bean (Vicia faba L.). Pflanzenzüchtg 84:323–328
Fryxell PA (1957) Mode of reproduction in higher plants. Bot Rev 23:135–233
Gao H, Williamson S, Bustamante CD (2007) An MCMC approach for joint inference of population structure and inbreeding rates from multi-locus genotype data. Genetics 176(3):1635–1651
Gepts P (1981) Hibridaciones interespecíficas para el mejoramiento de Phaseolus vulgaris. Internal seminar, SE-10–81, Centro Internacional de Agricultura Tropical, Cali, Colombia
Gepts P (2004) Crop domestication as a long-term selection experiment. Plant Breed Rev 24:1–44
Gillaspie AG, Hopkins MS, Dean RE (2005) Determining genetic diversity between lines of Vigna unguiculata subspecies by AFLP and SSR markers. Genet Res Crop Evol 52:245–247
Gilmore B, Myers JR (2000) Examining the Phaseolus coccineus collection for white mold resistance. HortScience 35:399
Gilmore B, Myers JR (2004) A preliminary molecular marker map for Phaseolus coccineus. Annu Rep Bean Improv Coop 47:87–88
Gilmore B, Myers JR, Kean D (2002) Completion of testing of Phaseolus coccineus plant introductions (PIs) for white mold, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, resistance. Annu Rept Bean Improv Coop 45:64–65
Goodstein DM, Shu S, Howson R, Neupane R, Hayes RD, Fazo J, Mitros T, Dirks W, Hellsten U, Putnam N, Rokhsar DS (2012) Phytozome: a comparative platform for green plant genomics. Nucleic Acids Res 40:D1178–D1186. doi:10.1093/nar/gkr944
Goodwillie C, Kalisz S, Eckert CG (2005) The evolutionary enigma of mixed mating systems in plants: occurrence, theoretical explanations, and empirical evidence. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 36:47–79
Hanai LR, Campos T, Camargo LEA, Benchimol LL, Souza AP, Melotto M, Carbonell AM, Chioratto AF, Consoli L, Formighieri EF, Bohrer MV, Tsai SM, Vieira MLC (2007) Development, characterization, and comparative analysis of polymorphism at common bean SSR loci isolated from genic and genomic source. Genome 50:266–277
Haq N, Smartt J (1978) Interspecific hybridization in Phaseolus and the production of inbred lines. Annu Rep Bean Improv Coop 21:62–63
Hauser BA, He JQ, Park SO, Gasser CS (2000) TSO1 is a novel protein that modulates cytokinesis and cell expansion in Arabidopsis. Development 127(10):2219–2226
Hedrick PW, Kalinowski ST (2000) Inbreeding depression in conservation biology. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 31:139–162
Holsinger KE (2000) Reproductive systems and evolution in vascular plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:7037–7042
Husband B, Schemske D (1996) Evolution of the magnitude and timing of in plants. Evolution 50:54–70
Ibarra-Perez FJ, Ehdaie B, Waines JG (1997) Estimation of outcrossing rate in common bean. Crop Sci 37:60–65
Kelly JE (2005) Family level inbreeding depression and the evolution of plant mating systems. New Phytol 165:55–62
Kittelson PM, Maronet JL (2000) Outcrossing rate and inbreeding depression in the perennial yellow bush lupine, Lupinus arboreus (Fabaceae). Am J Bot 87(5):652–660
Koelewijn HP (1998) Effects of different levels of inbreeding on progeny fitness in Plantago coronopus. Evolution 52:692–702
Kraic J, Gregová E, Jomová K, Hudcovicová M (2002) Microsatellite markers discriminating accessions within collections of plant genetic resources. Cell Mol Biol Lett 7:745–751
Link W (1990) Autofertility and rate of cross-fertilization: crucial characters for breeding synthetic varieties in faba beans (Vicia faba L.). Theor Appl Genet 79:713–717
Liu J, Muse SV (2005) Power Marker: integrated analysis environment for genetic marker data. Bioinformatics 21(9):2128–2129
Liu P, Zhu J, Lu Y (2004) Marker-assisted selection in segregating generations of self-fertilizing crops. Theor Appl Genet 109:370–376
Meinke DW (1991) Perspectives on genetic analysis of plant embryogenesis. Plant Cell 3:857–866
Meyer S, Pospisil H, Scholten S (2007) Heterosis associated gene expression in maize embryos 6 days after fertilization exhibits additive, dominant and overdominant pattern. Plant Mol Biol 63:381–391
Morgan MT, Wilson WG (2005) Self-fertilization and the escape from pollen limitation in variable pollination environments. Evolution 59:1143–1148
Nei M (1973) Analysis of gene diversity in subdivided populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 70:3321–3323
Nei M (1987) Molecular evolutionary genetics. Columbia University Press, New York
Nei M, Tajima F (1981) DNA polymorphism detectable by restriction endonucleases. Genetics 97:145–163
Peakall R, Smouse PE (2006) Genalex 6: genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research. Mol Ecol Notes 6:288–295
Petit RJ, El Mousadik A, Pons O (1998) Identifying populations for conservation on the basis of genetic markers. Conserv Biol 12:844–855
Powell W, Machray GC, Provan J (1996) Polymorphism revealed by simple sequence repeats. Trends Plant Sci 1:215–222
Pray LA, Goodnight CJ (1995) Genetic variation in inbreeding depression on the red flour beetle Tribolium castaneum. Evolution 49:176–188
Radhika P, Gowda SJM, Kadoo NY, Mhase LB, Jamadagni BM, Sainani MN, Chandra S, Gupta VS (2007) Development of an integrated intraspecific map of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) using two recombinant inbred line populations. Theor Appl Genet 115:115–209
Real D, Rizza MD, Quesenberry KH, Echenique M (2004) Reproductive and molecular evidence for allogamy in Lotononis bainesii baker. Crop Sci 44:394–400
Rick CM, Fobes JF, Holle M (1977) Genetic variation in Lycopersicon pimpinellifolium: evidence of evolutionary change in mating systems. Plant Syst Evol 127:139–170
Ritland K (1984) The effective proportion of self-fertilization with consanguineous matings in inbreed populations. Genetics 106:139–152
Ritland K (1996) Estimators for pairwise relatedness and inbreeding coefficients. Genet Res 67:175–186
Rodríguez M, Rau D, Angioi SA, Bellucci E, Bitocchi E, Nanni L, Knüpffer H, Negri V, Papa R, Attene R (2013) European Phaseolus coccineus L. landraces: population structure and adaptation, as revealed by cpSSRs and phenotypic analyses. PLoS One 8(2):e57337. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0057337
Rodríguez-Suárez C, Méndez-Vigo B, Pañeda A, Ferreira JJ, Giraldez R (2007) A genetic linkage map of Phaseolus vulgaris L. and localization of genes for specific resistance to six races of anthracnose (Colletotrichum lindemuthianum). Theor Appl Genet 114:713–722
Sandoval-Castellanos E (2010) Testing temporal changes in allele frequencies: a simulation approach. Genet Res 92(4):309–320
Santalla M, Monteagudo AB, González AM, De Ron AM (2004) Agronomical and quality traits of runner bean germplasm and implications for breeding. Euphytica 135:205–215
Santalla M, Ron AM, De La Fuente M (2010) Integration of genome and phenotypic scanning gives evidence of genetic structure in Mesoamerican common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) landraces from the southwest of Europe. Theor Appl Genet 120:1635–1651
Schoen DJ, Brown AHD (1991) Whole-flower and part-flower self-pollination in Glycine clandestina and G. argyrea and the evolution of autogamy. Evolution 45:1651–1664
Schultz ST, Willis JH (1995) Individual variation in inbreeding depression: the roles of inbreeding history and mutation. Genetics 141:1209–1223
Schwartz HF, Otto K, Teran H, Lema M, Singh SP (2006) Inheritance of white mold resistance in Phaseolus vulgaris × P. coccineus crosses. Plant Dis 90:1167–1170
Seavey SR, Carter SK (1994) Self-sterility in Epilobium obcordatum (Onagraceae). Am J Bot 81:331–338
Sicard D, Nanni L, Porfiri O, Bulfon D, Papa R (2005) Genetic diversity of Phaseolus vulgaris L. and P. coccineus L. landraces in Central Italy. Plant Breed 124(5):464–472
Song JY, Leung T, Ehler LK, Wang C, Liu Z (2000) Regulation of meristem organization and cell division by TSO1, an Arabidopsis gene with cysteine-rich repeats. Development 127:2207–2217
Sorensen FC (2001) Effect of population outcrossing rate on inbreeding depression in Pinus contorta var. murrayana seedlings. Scand J For Res 16:391–403
Spataro G, Tiranti B, Arcaleni P, Bellucci E, Attene G, Papa R, Spagnoletti Zeuli P, Negri V (2011) Genetic diversity and structure of a worldwide collection of Phaseolus coccineus L. Theor Appl Genet 122:1281–1291
Suso MJ, Pierre J, Moreno MT, Esnault R, Guen JL (2001) Variation in outcrossing levels in faba bean cultivars: role of ecological factors. J Agric Sci 136:399–405
Uyenoyama M, Waller DM (1991) Coevolution of self-fertilization and inbreeding depression. I. Genetic modification in response to mutation-selection balance at one and two loci. Theor Popul Biol 40:14–46
Vargas-Vázquez P, Muruaga JS, Martínez SE, Ruiz R, Hernández S, Mayek N (2011) Morphologic diversity of ayocote beans from Huasteco Karst of Mexico. Rev Mex Biodivers 82:767–775
Vargas-Vázquez P, Muruaga JS, Mayek N, Pérez A, Ramírez SE (2013) Characterization of the runner bean (Phaseolus coccineus L.) of theTrans-Mexican Neovolcanic Belt and Sierra Madre Oriental. Rev Mex Cienc Agríc 5(2):191–200
Waples R (1989) Temporal variation in allele frequencies: testing the right hypothesis. Evolution 43(6):1236–1251
Wilkinson RE (1983) Incorporation of Phaseolus coccineus germplasm may facilitate production of high yielding P. vulgaris lines. Annu Rep Bean Improv Coop 26:28–29
Xiong LZ, Liu KD, Dai XK, Xu CG, Zhang Q (1999) Identification of genetic factors controlling domestication-related traits of rice using an F2 population of a cross between Oryza sativa and O. rufipogon. Theor Appl Genet 98:243–251
Yu KF, Park SJ, Poysa V (1999) Abundance and variation of microsatellite DNA sequences in beans (Phaseolus and Vigna). Genome 42:27–34
Yu K, Park SJ, Poysa V, Gepts P (2000) Integration of simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers into a molecular linkage map of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). J Hered 91:429–434
Acknowledgments
Support was provided by Spanish Government (AGL2008-02091 and AGL2011-25562), EU-FEDER, JAE-Doc contract from National Spanish Research Council (CSIC) to A. M. González. The authors thank the Diputación Provincial de Pontevedra (Spain) for farm facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
González, A.M., De Ron, A.M., Lores, M. et al. Effect of the inbreeding depression in progeny fitness of runner bean (Phaseolus coccineus L.) and it is implications for breeding. Euphytica 200, 413–428 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-014-1177-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-014-1177-2