Abstract
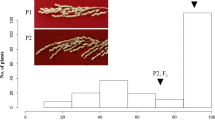
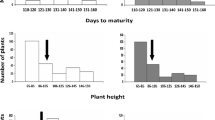
To further understand the nature of hybrid sterility between Oryza sativa and Oryza glaberrima, quantitative trait loci (QTL) controlling hybrid sterility between the two cultivated rice species were detected in BC1F1 and advanced backcross populations. A genetic map was constructed using the BC1F1 population derived from a cross between WAB450-16, an O. sativa cultivar, and CG14, an O. glaberrima cultivar. Seven main-effect QTLs for pollen and spikelet sterility were detected in the BC1F1. Forty-four sterility NILs (BC6F1) were developed via successive backcrosses using pollen sterility plants as female and WAB450-16 as the recurrent parent. Seven NILs, in which the target QTL regions were heterozygous while the other QTL regions as well as most of the reminder of the genome were homozygous for the WAB450-16 allele, were selected as the QTL identification materials. BC7F1 for the seven NILs showed a continuous variation in pollen and spikelet fertility. The four identified pollen sterility QTLs were located one each on chromosomes 1, 3, 7 and 7. Pollen sterility loci qSS-3 and qSS-7a were on chromosomes 3 and 7, respectively, which coincides with the previously identified S19, and S20, while loci qSS-1 and qSS-7b on chromosomes 1 and 7L appear distinct from all previously reported loci. An epistatic interaction controlling the hybrid sterility was detected between qSS-1 and qSS-7a.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basten CJ, Weir BS, Zeng ZB (1998) QTL CARTOGRAPHER: a reference manual and tutorial for QTL mapping. Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh
Bernardo R (2004) What proportion of declared QTL in plants are false? Theor Appl Genet 109:419–424
Carlborg O, Haley CS (2004) Epistasis: too often neglected in complex trait studies? Nat Rev Genet 5:618–625
Chu YE, Morishima H, Oka HI (1969) Reproductive barriers distributed in cultivated rice species and their wild relatives. Jap J Genet 44:207–223
Churchill GA, Doerge RW (1994) Empirical threshold values for quantitative trait mapping. Genetics 138:963–971
Doebley J, Stec A, Gustus C (1995) Teosinte branched1 and the origin of maize: evidence for epistasis and the evolution of dominance. Genetics 141:333–346
Doi K, Taguchi K, Yoshimura A (l998a) A new locus affecting high F1 pollen sterility found in backcross progenies between Japonica rice and African rice. Rice Genet Newsl 15:146–148
Doi K, Yoshimura A, Iwata N (1998b) RFLP mapping and QTL analysis of heading date and pollen sterility using backcross population between Oryza sativa L. and Oryza glaberrima Steud. Breed Sci 48:395–399
Doi K, Taguchi K, Yoshimura A (1999) RFLP mapping of S20 and S21 for F1 pollen semi-sterility found in backcross progeny of Oryza sativa and O. glaberrima. Rice Genet Newsl 16:65–68
Eshed Y, Zamir D (1996) Less-than-additive epistatic interaction of quantitative trait loci in tomato. Genetics 143:1807–1817
Fan CC, Xing YZ, HL, Lu TT, Han B, Xu CG, Li XH, Zhang QF (2006) GS3, a major QTL for grain length and weight and minor QTL for grain width and thickness in rice, encodes a putative transmembrane protein. Theor Appl Genet 112:1164–1171
Flint J, Mott R (2001) Finding the molecular basis of quantitative traits: successes and pitfalls. Nat Rev Genet 2:437–445
Frary A, Nesbitt TC, Frary A, Grandillo S, Knaap EVD, Cong B, Liu JP, Meller J, Elber R, Alpert KB, Tanksley SD (2000) fw2.2: A quantitative trait locus key to the evolution of tomato fruit size. Science 289:85–88
Ghesquiere A, Sequier J, Second G, Lorieux M (1997) First steps towards a rational use of African rice, Oryza glaberrima, in rice breeding through a ‘contig line’ concept. Euphytica 96:31–39
Glazier AM, Nadeau JH, Aitman TJ (2002) Finding genes that underlie complex traits. Science 298:2345–2349
Hu FY, Xu P, Deng XN, Zhou JW, Li J, Tao DY (2006) Molecular mapping of a pollen killer gene S29(t) in Oryza glaberrima and co-linear analysis with S22 in O. glumaepatula. Euphytica 151:273–278
Jones MP, Dingkuhn M, Aluko GK, Senmon M (1997) Interspecific Oryza sativa L. × O. glaberrima Steud. progenies in upland rice improvement. Euphytica 92:237–246
Kitamura E (1962) Genetic studies on sterility observed in hybrids between distantly related varieties of rice, Oryza sativa L. Bull Chugoku Agric Exp Station A8:141–205
Kroymann J, Mitchell-Olds T (2005) Epistasis and balanced polymorphism influencing complex trait variation. Nature 435:95–98
Kubo T, Yoshimura A (2005) Epistasis underlying female sterility detected in hybrid breakdown in a Japonica-Indica cross of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 110:346–355
Lander E, Green P (1987) Construction of multilocus genetic maps in Humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:2363–2367
Li ZB (1980) A preliminary discussion about the classification of male sterile lines of rice in China. Acta Agron Sin 6(1):17–26
Lin HX, Yamamoto T, Sasaki T, Yano M (2000) Characterization and detection of epistatic interactions of 3 QTLs, Hd1, Hd2, and Hd3, controlling heading date in rice using nearly isogenic lines. Theor Appl Genet 101:1021–1028
Lincoln S, Daly M, Lander ES (1992) Constructing genetic maps with MAPMAKER/EXP3.0. Whitehead Institute Technical Report (3rd edn)
Liu JP, Eck JV, Cong B, Tanksley SD (2002) A new class of regulatory genes underlying the cause of pear-shape tomato fruit. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:13302–13306
Lorieux M, Ndjiondjop MN, Ghesquière A (2000) A first interspecific Oryza sativa × Oryza glaberrima microsatellite based genetic linkage map. Theor Appl Genet 100:593–601
Mackay TF (2001) The genetic architecture of quantitative traits. Ann Rev Genet 35:303–339
Manly KF, Cudmore Jr RH, Meer JM (2001) Map Manager QTX, cross-platform software for genetic mapping. Mamm Genome 12:930–932
Mizuta Y, Harushima Y, Kurata N (2006) Mapping of a pair of reproductive barrier loci observed in a cross between Nipponbare and Kasalath. Rice Genet Newsl 23:33–35
Morinaga T, Kuriyama H (1957) Cytogenetical studies on Oryza sativa L. IX. The F1 hybrid of O. sativa L and O. glaberrima. Steud. Jpn J Breed 12:153–165
Morishima H, Hinata K, Oka HI (1962) Comparison between two cultivated rice species, Oryza sativa L. and O. glaberrima Steud. Jap J Breed 12(3):153–165
Oka HI (1974) Analysis of genes controlling F1 sterility in rice by the use of isogenic lines. Genetics 77:521–534
Paterson AH, Lander ES, Hewitt JD, Peterson S, Lincoln SE, Tanksley SD (1988) Resolution of quantitative traits into Mendelian factors by using a complete map of restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Nature 335:721–726
Sano Y (1983) A new gene controlling sterility in F1 hybrids of two cultivated rice species. J Hered 74: 435–439
Sano Y (1986) Sterility barriers between Oryza sativa and O. glaberrima. In: International Rice Research Institute (eds) Rice genetics. International Rice Research Institute, Manila, pp 109–118
Sano Y (1990) The genic nature of gamete eliminator in rice. Genetics 125:183–191
Sano Y, Chu YE, Oka HI (1979) Genetic studies of speciation in cultivated rice. 1. Genic analysis for the F1sterility between Oryza sativa L. and O. glaberrima Steud. Jpn J Genet 54:121–132
Shinjyo C (1975) Genetical studies of cytoplasmic male sterility and fertility restoration in rice, Oryza sativa L. Sci Bull Coll Agr Univ Ryukyus 22:1–57
Sinha H, Nicholson BP, Steinmetz LM, McCusker JH (2006) Complex genetic interactions in a quantitative trait locus. PLOS Genet 2(2):140–147
Steinmetz LM, Sinha H, Richards DR, Spiegelman JI, Oefner PJ, McCusker JH, Davis RW (2002) Dissecting the architecture of a quantitative trait locus in yeast. Nature 416:326–330
Taguchi K, Doi K, Yoshimura A (1999) RFLP mapping of S19, a gene for F1 pollen semi-sterility found in backcross progeny of Oryza sativa and O. glaberrima. Rice Genet Newsl 16:70–71
Takahashi Y, Shomura A, Sasaki T, Yano M (2001) Hd-6, a rice quantitative trait locus involved in photoperiod sensitivity, encodes the a subunit of protein kinase CK2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:7922–7927
Takeuchi Y, Lin SY, Sasaki T, Yano M (2003) Fine linkage mapping enables dissection of closely linked quantitative trait loci for seed dormancy and heading in rice. Theor Appl Genet 107:1174–1180
Tanksley SD (1993) Mapping polygenes. Annu Rev Genet 27:205–233
Tao DY, Hu FY, Yang G, Yang J, Tao H (1997) Exploitation and utilization of interspecific hybrid vigor between Oryza sativa and O. glaberrima. In: Jones MP, M Dingkuhn, Johnson DE, Fagade SO (eds) Interspecific hybridization: progress and prospects. WARDA/ADRAO, Cote d’Ivoire, pp 103–112
Tao DY, Xu P, Hu FY, Yang YQ, Li J, Zhou JW, Jones MP (2002) Hybrid sterility among near-isogenic lines derived from interspecific hybrid between cultivated rice species Oryza sativa and O. glaberrima. Chinese J Rice Sci 16(2):106–110
Wan XY, Wan JM, Jiang L, Wang JK, Zhai HQ, Weng JF, Wang HL, Lei CL, Wang JL, Zhang X, Cheng ZJ, Guo XP (2006) QTL analysis for rice grain length and fine mapping of an identified QTL with stable and major effects. Theor Appl Genet 112:1258–1270
Xu Y, Zhu L, Xiao J, Ning N, McCouch SR (1997) Chromosomal region associated with segregation distortion of molecular markers in F2, backcross, doubled haploid, and recombinant inbred population in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Gen Genet 253:535–545
Yabuno T (1995) A gametocidal factor of Oryza galberrima Steud. in O. sativa L. Euphytica 45:191–195
Yamamoto T, Kuboki Y, Lin SY, Sasaki T, Yano M (1998) Fine mapping of quantitative trait loci Hd-1, Hd-2 and Hd-3, controlling heading date of rice, as single Mendelian factors. Theor Appl Genet 97:37–44
Yamamoto T, Lin HX, Sasaki T, Yano M (2000) Identification of heading date quantitative trait locus Hd6, and characterization of its epistatic interaction with Hd2 in rice using advanced backcross progeny. Genetics 154:885–891
Yan LL, Loukoianov A, Tranquilli G, Helguera M, Fahima T, Dubcovsky J (2003) Positional cloning of the wheat vernalization gene VRN1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:6263–6268
Yan LL, Loukoianov A, Blechl A, Tranquilli G, Ramakrishna W, SanMiguel P, Bennetzen JL, Echenique V, Dubcovsky J (2004) The wheat VRN2 gene is a flowering repressor down-regulated by vernalization. Science 303:1640–1644
Yano M, Sasaki T (1997) Genetic and molecular dissection of quantitative traits in rice. Plant Mol Biol 35:145–153
Yano M, Katayose Y, Ashikari M, Yamanouchi U, Monna L, Fuse T, Baba T, Yamamoto K, Umehara Y, Nagamura Y, Sasaki T (2000) Hd-1, a major photoperiod sensitivity quantitative trait locus in rice, is closely related to the Arabidopsis flowering time gene CONSTANS. Plant cell 12:2473–2483
Acknowledgements
This research was funded partially by grants from Ministry of Science and Technology (2006CB708207), and Yunnan Department of Science and Technology (2002C0009Z, 2003RC02, 2004PY01-21, 2006GP09), the People’s Republic of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Xu, P., Deng, X. et al. Identification of four genes for stable hybrid sterility and an epistatic QTL from a cross between Oryza sativa and Oryza glaberrima . Euphytica 164, 699–708 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-008-9684-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-008-9684-7