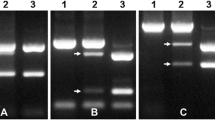
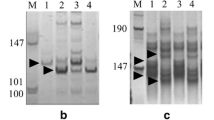
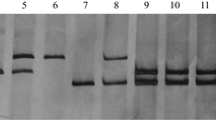
Abstract
Pm12, transferred from Aegilops speltoides (2n = 2x = 14, genome SS) to wheat, confers effective resistance to powdery mildew worldwide. By applying bulked segregant analysis in a BC3F2 segregating population consisting of 305 plants, 18 wheat genomic and EST-SSR markers linked to the resistance gene were identified. Pm12 was located in the 6SS portion of the T6BS-6SS.6SL translocation chromosome based on the physical bin positions of the genomic and EST-SSR markers in the Chinese Spring group six deletion stocks and their linkage relationship to the resistance gene. Twenty eight recombinants among 305 F2 plants indicated a low frequency of recombination between the alien chromosome segment and wheat chromosome 6B. Since recombination events occurred on both sides of Pm12, the materials generated provide opportunities for further reduction of alien chromatin by intercrossing selected individuals and using markers to select the required plants.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cho YG, Ishii T, Temnykh S et al (2000) Diversity of microsatellite derived from genomic libraries and GenBank sequences in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 100:713–722
Duan XY, Sheng BQ, Zhou YL et al (1998) Monitoring of the virulence population of Erysiphe graminis f.sp. tritici. Acta Phytophylactica Sin 25:31–36
Dubcovsky J, Lukaszewski AJ, Echaide M et al (1998) Molecular characterization of two Triticum speltoides interstitial translocations carrying leaf rust and greenbug resistance genes. Crop Sci 38:1655–1660
Dvorak J (1977) Transfer of leaf rust resistance from Aegilops speltoides to Triticum aestivum. Can J Genet Cytol 19:133–141
Dvorak J, Knott DR (1990) Location of a Triticum speltoides chromosome segment conferring resistance to leaf rust in Triticum aestivum. Genome 33:892–897
Dvorak J, Zhang HB (1990) Variation in repeated nucleotide sequences sheds light on the phylogeny of the wheat B and G genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:9640–9644
Eujayl I, Sorrells ME, Baum M et al (2002) Isolation of EST-derived microsatellite markers for genotyping the A and B genomes of wheat. Theor Appl Genet 104:399–407
Friebe B, Jiang J, Raupp WJ et al (1996) Characterization of wheat-alien translocations conferring resistance to diseases and pests: current status. Euphytica 91:59–87
Gupta PK, Balyan HS, Edwards KJ et al (2002) Genetic mapping of 66 new microsatellite (SSR) loci in bread wheat. Theor Appl Genet 105:413–422
Gupta PK, Rustgi S, Sharma S et al (2003) Transferable EST-SSR markers for the study of polymorphism and genetic diversity in bread wheat. Mol Gen Genomics 270:315–323
Guyomarc′h H, Sourdille P, Charmet G et al (2002) Characterization of polymorphic microsatellite markers from Aegilops tauschii and transferability to the D genome of bread wheat. Theor Appl Genet 104:1164–1172
Hsam SLK, Lapochkina IF, Zeller FJ (2003) Chromosomal location of genes for resistance to powdery mildew in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L. em Thell.). 8. Gene Pm32 in a wheat-Aegilops speltoides translocation line. Euphytica 133:367–370
Huang XQ, Hsam SLK, Zeller FJ et al (2000) Molecular mapping of the wheat powdery mildew resistance gene Pm24 and marker validation for molecular breeding. Theor Appl Genet 101:401–414
Huang XQ, Röder MS (2004) Molecular mapping of powdery mildew resistance genes in wheat: a review. Euphytica 137:203–223
Huang SX, Sirikhachornkit A, Su XJ et al (2002) Genes encoding plastid acetyl-CoA carboxylase and 3-phosphoglycerate kinase of the Triticum/Aegilops complex and the evolutionary history of polyploid wheat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:8133–8138
Huang XQ, Wang LX, Xu MX et al (2003) Microsatellite mapping of the powdery mildew resistance gene Pm5e in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Theor Appl Genet 106:858–865
Järve K, Peusha HO, Tsymbalova J et al (2000) Chromosomal location of a Triticum timopheevii-derived powdery mildew resistance gene transferred to common wheat. Genome 43:377–381
Jia JZ, Devos KM, Chao S et al (1996) RFLP-based maps of the homoeologous group-6 chromosomes of wheat and their application in the tagging of Pm12, a powdery mildew resistance gene transferred from Aegilops speltoides to wheat. Theor Appl Genet 92:559–565
Kerber ER, Dyck PL (1990) Transfer to hexaploid wheat of linked genes for adult-plant leaf rust and seedling stem rust resistance from an ampliploid of Aegilops speltoides × Triticum monococcum. Genome 33:530–537
Kimber G, Athwal RS (1972) A reassessment of the course of evolution of wheat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 69:912–915
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J et al (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Liu ZY, Sun QX, Ni ZF et al (2002) Molecular characterization of a novel powdery mildew resistance gene Pm30 in wheat originating from wild emmer. Euphytica 123:21–29
Lukaszewski AJ (2000) Manipulation of the 1RS.1BL translocation in wheat by induced homoeologous recombination. Crop Sci 40:216–225
McIntosh RA, Miller TE, Chapman V (1982) Cytogenetical studies in wheat XII. Lr28 for resistance to Puccinia recondita and Sr34 for resistance to P. graminis tritici. Z Pflanzenzuchtung 89:295–306
McIntosh RA, Yamazaki Y, Devos KM (2003) Catalogue of gene symbols for wheat. In: Pogna NE et al (eds) Proc 10th Int Wheat Genet Symp. Pasetum, Italy, vol 4. Istituto Sperimentale per la Cerealicoltura, Rome, Italy
Miller TE, Reader SM, Ainsworth CC et al (1988) The introduction of a major gene for resistance to powdery mildew of wheat, Erysiphe graminis f. sp. tritici, from Aegilops speltoides into wheat, Triticum aestivum. In: Jorna M, Shootmaker L (eds) Cereal breeding related to integrated cereal production: proceedings of the EUCARPIA conference. Pudoc, Wageningen, The Netherlands, pp 179–183
Miranda LM, Murphy JP, Marshall D et al (2006) Pm34: a new powdery mildew resistance gene transferred from Aegilops tauschii Coss. to common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 113:1497–1504
Mohler V, Zeller FJ, Wenzel G et al (2005) Chromosomal location of genes for resistance to powdery mildew in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L. em Thell.). 9. Gene MlZec1 from the Triticum dicoccoides-derived wheat line Zecoi-1. Euphytica 142:161–167
Niewoehner AS, Leath S (1998) Virulence of Blumeria graminis f. sp. tritici on winter wheat in the eastern United States. Plant Dis 82:64–68
Pestsova E, Ganal MW, Röder MS (2000) Isolation and mapping of microsatellite markers specific for the D genome of bread wheat. Genome 43:689–697
Riley R, Unrau J, Chapman V (1969) Evidence on the origin of the B genome of wheat. J Heredity 49:90–98
Röder MS, Korzun V, Gill BS et al (1998a) The physical mapping of microsatellite markers in wheat. Genome 41:278–283
Röder MS, Korzun V, Wendehake K et al (1998b) A microsatellite map of wheat. Genetics 149:2007–2023
Saghai-Maroof MA, Soliman KM, Jorgensen RA et al (1984) Ribosomal DNA spacer-length polymorphisms in barley: Mendelian inheritance, chromosomal locations and population dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:8014–8018
Sarkar P, Stebbins GL (1956) Morphological evidence concerning the origin of the B genome in wheat. Am J Bot 43:297–304
Scott KD, Eggler P, Seaton G et al (2000) Analysis of SSRs derived from grape ESTs. Theor Appl Genet 100:723–726
Somers DJ, Isaac P, Edwards K (2004) A high density microsatellite consensus map for bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 109:1105–1114
Song QJ, Fickus EW, Cregan PB (2002) Characterization of trinucleotide SSR motifs in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 104:286–293
Sourdille P, Singh S, Cadalen T et al (2004) Microsatellite-based deletion bin system for the establishment of genetic-physical map relationships in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Funct Integr Genomics 4:12–25
Stephenson P, Bryan G, Kirby J et al (1998) Fifty new microsatellite loci for the wheat genetic map. Theor Appl Genet 97:946–949
Yu JK, Dake TM., Singh S et al (2004) Development and mapping of EST-derived simple sequence repeat markers for hexaploid wheat. Genome 47:805–818
Zhu ZD, Zhou RH, Kong XY et al (2005) Microsatellite markers linked to 2 powdery mildew resistance genes introgressed from Triticum carthlicum accession PS5 into common wheat. Genome 48:585–590
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Dr. R. McIntosh for improving the manuscript. This work was financially supported by the National Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (30425039), National Natural Science Foundation of China (30200174, 30571151), Fok Ying Tung Education Foundation (94021) and the State High Tech Programs (2006AA100102, 2006AA10Z1E9, 2006AA10Z1C4).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Wei Song and Hao Xie are contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, W., Xie, H., Liu, Q. et al. Molecular identification of Pm12-carrying introgression lines in wheat using genomic and EST-SSR markers. Euphytica 158, 95–102 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-007-9432-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-007-9432-4