Abstract
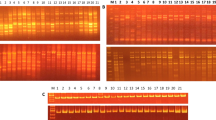
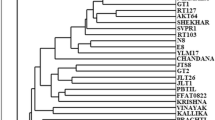
Jatropha curcas (Euphorbiaceae) is an oil-bearing species with multiple uses and considerable potential as a bioenergy crop. The present investigation has been undertaken to assess the extent of genetic diversity in a representative set of 42 accessions of J. curcas encompassing different crop growing regions in India along with a non-toxic genotype from Mexico as a prelude for utilization of promising and genetically divergent materials in the breeding programmes. Molecular polymorphism was 42.0% with 400 RAPD primers and 33.5% with 100 ISSR primers between accessions indicating modest levels of genetic variation in the Indian germplasm. The within-population variation based on RAPD polymorphism was 64.0% and was on par with the inter-population variation. Polymorphic ISSR markers have been identified that could differentiate the Indian accessions from the Mexican genotype and two of them were converted to SCAR markers. The SCAR primer pair ISPJ1 amplified a 543 bp fragment in all the Indian populations, while ISPJ2 with a specific amplicon of 1,096 bp was specific to the Mexican genotype. Population-specific bands have been identified for the accession from Kerala (2 RAPD markers), Neemuch-1 from Rajasthan (1 each of RAPD and ISSR markers) and the non-toxic genotype from Mexico (17 RAPD and 4 ISSR markers), which serve as diagnostic markers in genotyping. The study indicates an immediate need for widening the genetic base of J. curcas germplasm through introduction of accessions with broader geographical background.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asante IK, Offei SK (2003) RAPD-based genetic diversity study of fifty cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) genotypes. Euphytica 131:113–119
Becker K, Makkar HPS (1997) Potential of Jatropha seed cake as protein supplement in livestock feed and constraints to its utilization. Paper presented at International Symposium on Biofuel and Industrial Products from Jatropha curcas and other Tropical Oilseed Plants, Managua/Nicaragua, Mexico
Besse P, Seguin M, Lebrun P, Chevallier MH, Nicholas D, Lanaud C (1994) Genetic diversity among wild and cultivated populations of Hevea brasiliensis assessed by nuclear RFLP analysis. Theor Appl Genet 88:199–207
Bornet B, Muller C, Paulus F, Branchard M (2002) High informative nature of inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) sequences amplified with tri- and tetra-nucleotide primers from cauliflower (Brassica oleracea var. botrytis L.) DNA. Genome 45:890–896
Dehgan B (1984) Phylogenetic significance of interspecific hybridization in Jatropha (Euphorbiaceae). Sys Bot 9:467–478
Dehgan B, Webster GL (1979) Morphology and infrageneric relationships of the genus Jatropha (Euphorbiaceae). Univer California Publ Bot 74:1–73
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12:13–15
Fregene MA, Suarez M, Mkumbira J, Kulembeka H, Ndedva E, Kulaya A, Mitchel S, Gullberg U, Rosling H, Dixon AGO, Dean R, Kresovich S (2003) Simple sequence repeat marker diversity in cassava landraces: genetic diversity and differentiation in an asexually propagated crop. Thoer Appl Genet 107:1083–1093
Heller J (1996) Physic nut—Jatropha curcas L. Promoting the conservation and use of underutilized and neglected crops. 1. International Plant Genetic Resources Institute, Rome, Italy (http://www.ipgri.cgiar.org/publications/pdf/161.pdf)
Henning RK (2006) The Jatropha system, integrated rural development by utilization of Jatropha curcas L. (JCL) as raw material and as renewable energy. www.jatropha.org
Jones N, Miller JH (1991) Jatropha curcas. A multipurpose species for problematic sites. Land Resour Ser 1:1–12
Lakawipat N, Teerawatanasuk K, Rodier-Goud M, Seguin M, Vanavichit A, Toojinda T, Tragoonrung S (2003) Genetic diversity analysis of wild germplasm and cultivated clones of Hevea brasiliensis Muell. Arg by using microsatellite markers. J Rubber Res 6:36–47
Makkar HPS, Aderibigbe AO, Becker K (1998) Comparative evaluation of non-toxic and toxic varieties of Jatropha curcas for chemical composition, digestibility, protein degradability and toxic factors. Food Chem 62:207–215
Martin G, Mayeux A (1985) Curcas oil (Jatropha curcas L.): a possible fuel. Agr Trop 9:73–75
Mc Gregor CE, Lambert CA, Greyling MM, Louw JH, Warnich L (2000) A comparative assessment of DNA fingerprinting techniques (RAPD, ISSR, AFLP and SSR) in tetraploid potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) germplasm. Euphytica 113:135–144
Openshaw K (2000) A review of Jatropha curcas: an oil plant of unfulfilled promise. Biomass Bioener 19:1–15
Paran I, Michelmore RW (1993) Development of reliable PCR based markers linked to downy mildew resistance genes in lettuce. Theor Appl Genet 85:985–993
Prabakaran AJ, Sujatha M (1999) Jatropha tanjorensis Ellis & Saroja, a natural interspecific hybrid occurring in Tamil Nadu, India. Genet Resour Crop Evol 46:213–218
Rafalski JA, Vogel JM, Morgante M, Powell W, Andre C, Tingey SV (1996) Generating and using DNA markers in plants. In: Birren B, Lai E (eds) Analysis of non-mammalian genomes-A practical guide, Academic Press, New York, pp 75–134
Sakaguchi S, Somabhi M (1987) Exploitation of promising crops of Northeast Thailand Siriphan Offset, Khon Kaen, Thailand, pp 50
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York, USA
Sathaiah V, Reddy TP (1985) Seed protein profiles of castor (Ricinus communis L.) and some Jatropha species. Genet Agr 39:35–43
Sujatha M, Prabakaran AJ (2003) New ornamental Jatropha hybrids through interspecific hybridization. Genet Resour Crop Evol 50:75–82
Sujatha M, Makkar HPS, Becker K (2005) Shoot bud proliferation from axillary nodes and leaf sections of non-toxic Jatropha curcas L. Plant Growth Regul 47:83–90
Takeda Y (1982) Development study of Jatropha curcas (SabuDum) oil as a substitute for diesel engine oil in Thailand. J Agri Assoc China 120:1–8
vander Nest MA, Steenkamp ET, Wingfield BD, Wingfield MJ (2000) Development of simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers in Eucalyptus from amplified inter-simple sequence repeats (ISSR). Plant Breed 119:433–436
Varghese YA, Knaak C, Sethuraj MR, Ecke W (1997) Evaluation of random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) on Hevea brasiliensis. Plant Breed 116:47–57
Williams JGK, Kubelik AR, Livak KJ, Rafalski JA, Tingey SV (1990) DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acid Res 18:6531–6535
Zietkiewicz E, Rafalski A, Labuda D (1994) Genome fingerprinting by simple sequence repeat (SSR)-anchored polymerase chain reaction amplification. Genomics 20:176–183
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by the RSAD project on J. curcas sponsored by the Government of Andhra Pradesh, India. The authors thank the Principal Investigators of the cooperating centers of the RSAD project for sparing the Indian accessions and Prof. Klaus Becker, University of Hohenheim, Stuttgart, Germany for the non-toxic Mexican genotype. The authors thank the Project Director, Directorate of Oilseeds Research for extending all the facilities for carrying out the investigation and Dr. V. Dinesh Kumar (DOR) and Dr. J. Hu (USDA, USA) for their helpful suggestions during this investigation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Basha, S.D., Sujatha, M. Inter and intra-population variability of Jatropha curcas (L.) characterized by RAPD and ISSR markers and development of population-specific SCAR markers. Euphytica 156, 375–386 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-007-9387-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-007-9387-5