Abstract
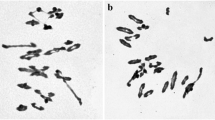
A partial amphiploid, TE-3, between Triticum aestivum cv. Chinese Spring (CS) and Thinopyrum intermedium ssp. trichophorum was characterized by cytological observation, genomic in situ hybridization (GISH), seed storage protein electrophoresis and disease resistance screening. The TE-3 plants were deeply covered with pubescence, which is characteristic of the Th. intermedium ssp. trichophorum parent. Feulgen staining of the somatic metaphases revealed that the chromosome number varied from 52 to 56. TE-3 pollen mother cells (PMCs) regularly showed two to four univalents and 25 to 27 bivalents, indicating a degree of cytological instability. Giemsa-C banding showed that the Thinopyrum chromosomes in TE-3 produced strong heterochromatin bands. GISH analysis suggested that the alien chromosomes in TE-3 consisted of eight St chromosomes, four Js chromosomes, and two J genome chromosomes, as well as two St-J translocation chromosomes. Seeds storage proteins separated by acid polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (APAGE) and sodium dodecyl sulphate – polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) showed that TE-3 expressed some of Th. intermedium ssp. trichophorum specific gliadin and glutenin bands. When inoculated with stripe rust and powdery mildew isolates, TE-3 expressed resistance derived from its Thinopyrum parent. It appears that TE-3 can be used as a donor source in wheat breeding programs to introduce novel variation for quality and disease resistance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aizatulina, K.S., G.L. Yachevskaya & T.P. Pereladova, 1989. Study of the genome structure of Agropyron intermedium (Host) Beauv. Tsitologiya I Genetika 23: 15–22.
Banks, P.M., P.J. Larkin, H.S. Bariana, E.S. Lagudah, R. Appels, P.M. Waterhouse, R.I.S. Brettell, X. Chen, H.J. Xu, Z.Y. Xin, Y.T. Qian, X.M. Zhou, Z.M. Cheng & G.H. Zhou, 1995. The use of cell culture for subchromosomal introgressions of barley yellow dwarf virus resistance from Thinopyrum intermedium to wheat. Genome 38: 395–405.
Cauderon Y., B. Saigne & M. Dauge, 1973. The resistance to wheat rusts of Agropyron intermedium and its use in wheat improvement. In: E.R. Sears & L.M.S. Sears (Eds.), Proc 4th International Wheat Genet Symposium, pp. 401–407. University of Missouri, Columbia, MO.
Chang, Z.J., Z.L. Ren, H. Zhan, Z.J. Yang, X.J. Zhang & X.R. Guo, 2003. Production of a new partial wheat – Thinopyrum intermedium amphiploid and its genome analysis using in situ hybridization. In: Proceedings of the Tenth International Wheat Genetics Symposium, pp. 557–560. Instituto Sperimentale Per La Cerealcultura, Paestum, Italy.
Chen, Q., R.L. Conner & A. Laroche, 1995. Identification of the parental chromosomes of the wheat – alien amphiploid Agrotona by genomic in situ hybridization. Genome 38: 1163-1169.
Chen, Q., R.L. Conner, A. Laroche & J.B. Thomas, 1998. Genome analysis of Thinopyrum intermedium and Thinopyrum ponticum using genomic in situ hybridization. Genome 41: 580-586.
Chen Q., R.L. Conner, H.J. Li, S.C. Sun, F. Ahmad, A. Laroche & R.J. Graf, 2003. Molecular cytogenetic discrimination and reaction to wheat streak mosaic virus and the wheat curl mite in Zhong series of wheat – Thinopyrum intermedium partial amphiploids. Genome 46:135–145.
Conner, R.L., E.D.P. Whelan & M.D. MacDonald, 1989. Identification of sources of resistance to common root rot in wheat – alien amphiploid and chromosome substitution lines. Crop Sci 29: 916–919.
Dewey, D.R., 1984. The genomic system of classification as a guide to intergeneric hybridization with the perennial Triticeae. In: J.P. Gustafson (Ed.) Gene Manipulation in Plant Improvement. Vol 16. pp. 209–279. Plenum Press, New York.
Dvořák, J., 1985. Transfer of salt tolerance from Elytigia pontica (Podp.) Holub. to wheat by the addition of an incomplete Elytrigia genome. Crop Sci 21: 306–309.
Fedak, G., Q. Chen, R.L. Conner, A. Laroche, A. Comeau & C.A. St-Pierre, 2001. Characterization of wheat-Thinopyrum partial amphiploids for resistance to barley yellow dwarf virus. Euphytica 120: 373–378.
Friebe, B., Y. Mukai, B.S. Gill & Y. Cauderon, 1992. C-banding and in situ hybridization analyses of Agropyron intermedium, a partial wheat × Ag. intermedium amphiploid, and six derived chromosome addition lines. Theor Appl Genet 84: 899-905.
Gill, B.S., B. Friebe & T.R. Endo, 1991. Standard karyotype and nomenclature system for description of chromosome bands and structural aberrations in wheat (Triticum aestivum). Genome 34: 830–839.
Gupta, P. K. & G. Fedak, 1986. Intergeneric hybrids between X Triticosecale cv. Welsh (2n = 42) and three genotypes of Agropyron intermedium (2n = 42). Can J. Genet. Cytol 28: 176–179.
Han F.P., B. Liu, G. Fedak & Z. Liu, 2004. Genomic constitution and variation in five partial amphiploids of wheat – Thinopyrum intermedium as revealed by GISH, multicolor GISH and seed storage protein analysis. Theor. Appl. Genet 109: 1070–1076.
He, M.Y., Z.Y. Xu, M.Q. Zou, H. Zhang, Z.S. Piao & S. Hao, 1988. The establishment of two sets of alien addition lines of wheatgrass. Sci China Ser B 32: 695–705.
Jiang, J., B. Friebe & B.S. Gill, 1994. Recent advances in alien gene transfer in wheat. Euphytica 73: 199–212.
Larkin, P.J., P.M. Banks, E.S. Lagudah, R. Apple, X. Chen, Z.Y. Xin, H.W. Ohm & R.A. McIntosh, 1995. Disomic Thinopyrum intermedium addition lines in wheat with barley yellow dwarf virus resistance and with rust resistances. Genome 38: 385–394.
Liu, S. B & H.G. Wang, 2002. Development and molecular cytogenetic identification of wheat-Thinopyrum intermedium addition lines for resistance to powdery mildew. Chinese Science Bulletin 47: 1500–1503.
Ma, H., R.P. Singh & A. Mujeeb-Kazi, 1995. Suppression/expression of resistance to stripe rust in synthetic hexaploid wheat (Triticum turgidum × T. tauschii). Euphytica 83: 87–93.
Mukai, Y., B. Friebe, J.H. Hatchett, M. Yamamoto & B.S. Gill, 1993. Molecular cytogenetic analysis of radiation-induced wheat-rye terminal and intercalary chromosomal translocations and the detection of rye chromatin specifying resistance to Hessian fly. Chromosoma 102: 88–95.
Sun, S.C., 1981. The approach and methods of breeding new varieties and new species from Agrotriticum hybrids. Acta Agron Sin 7: 51–58.
Tang, S., Z. Li, X. Jia & P.J. Larkin, 2000. Genomic in situ hybridization (GISH) analyses of Thinopyrum intermedium, its partial amphiploid Zhong 5, and disease-resistant dervatives in wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet 100: 344–352.
Wan, Y. F., C. Yen, J.L. Yang & D.C. Liu, 1997. The diversity of resources resistant to scab in Triticeae (Poaceae). Wheat Information Service 84: 7–12.
Wang, R.R.C., R. von Bothmer, J. Dvoák, G. Fedak, I. Linde- Laursen & M. Muramatsu, 1994. Genomic symbols in the Triticeae. In: Proceedings of the 2nd International Triticeae Symposium, pp. 29–34. Utah State University Press, Logan, UT.
Xu, J., R.L. Conner & A. Laroche, 1994. C-banding and fluorescence in situ hybridization studies of the wheat-alien hybrid “Agrotona”. Genome 37: 477–481.
Xu, J. & R.L. Conner, 1994. Intravarietal variation in satellites and C-banded chromosomes of Agropyron intermedium ssp. trichophorum cv. Greenleaf. Genome 37: 305–310.
Yang, Z. J., D. C. Liu & G.R. Li. 2000. Development of new wheat – Thinopyrum germplasms for multi-resistance. J. Sichuan University (Natural Science Edition) 37(Suppl): 20–25.
Yang, Z.J., G.R. Li, H.R. Jiang & Z.L. Ren, 2001. Expression of nucleolus, endosperm storage proteins and disease resistance in an amphiploid between Aegilops tauschii and Secale silvestre. Euphytica 119: 317–321.
Zeller, F.J., U. Stephan & J. Lutz, 1993. Chromosomal location of powdery mildew resistance genes in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) . 1. Mlk and other alleles in Pm3 locus. Euphytica 68: 223–229.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zu-Jun, Y., Guang-Rong, L., Zhi-Jian, C. et al. Characterization of a partial amphiploid between Triticum aestivum cv. Chinese Spring and Thinopyrum intermedium ssp. trichophorum. Euphytica 149, 11–17 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-005-9010-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-005-9010-6