Abstract
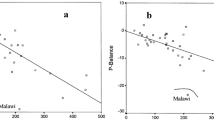
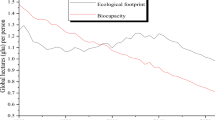
The overall aim of this study is to analyse the relationship between economic growth and environmental degradation with particular reference to carbon emissions and deforestation. The analysis is based upon the Environmental Kuznets Curve (EKC) model, which posits an inverted-U relationship between incomes per capita and environmental quality. In particular, the present analysis tries to take into account the current process of globalisation with the aim of defining the impact of the progressive global economic integration on the relationship between economic growth and environmental degradation. The study confirms that there is an inverted-U relationship between income growth and carbon emissions, while the relationship results less clear in the case of forest change. The inclusion of globalisation in the analysis confirms similar results and suggests a direct link between an increase in the rate of integration with the global economy and a worsening in terms of environmental degradation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Angelsen D. Kaimowitz (1999) ArticleTitle‘Rethinking the causes of deforestation: lessons from economic models’ The World Bank Observer 14 73–98 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD38ngsVygsg%3D%3D
K. Arrow (1962) ArticleTitle‘The economic implications of learning by doing’ Review of Economic Studies 29 155–173
M. Bhattarai M. Hammig (2001) ArticleTitle‘Institutions and the environmental Kuznets curve for deforestation: a crosscountry analysis for Latin America’, Africa and Asia World Development 29 995–1010 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0305-750X(01)00019-5
R. Bilsborrow M. Geores (1994) ‘Population, land-use and environment in developing countries: what can we learn from cross-national data’ Brown (Eds) et al. The Causes of Tropical Deforestation Earthscan London 106–130
S. Bimonte (2002) ArticleTitle‘Information access, income distribution and the environmental Kuznets curve’ Ecological Economics 41 145–156 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0921-8009(02)00022-8
S. Borghesi A. Vercelli (2003) ArticleTitleSustainable globalisation Ecological Economics 44 77–89 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0921-8009(02)00222-7
K. Brown D. Pearce (1994) The Causes of Tropical Deforestation London Earthscan
A. Matteis ParticleDe (2004) ArticleTitle‘International trade and economic growth in a global environment’ Journal of International Development 16 575–588
FAO: 2000, ‘Global Forest Resources Assessment 2000’, Forestry Papers, 140, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome
InstitutionalAuthorNameFAO (2002) State of the World’s Forests 2001 Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Rome
G.M. Grossman A.B. Krueger (1995) ArticleTitle‘Economic growth and the environment’ Quarterly Journal of Economics 110 353–377
M.T. Heil T.M. Selden (2001) ArticleTitle‘Carbon emissions and economic development: future trajectories based on historical experience’ Environment and Development Economics 6 63–83 Occurrence Handle10.1017/S1355770X01000043
N. Khana (2000) ‘The income elasticity of air pollution: revisiting the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis’ Binghamton University New York
R. Lopez (1994) ArticleTitle‘The Environment as a factor of production: the effects of economic growth and trade liberalization’ Journal of Environmental Economics and Management 27 163–184
S. Nemat (1994) ‘Macroeconomic causes of deforestation: barking up the wrong tree?’ Brown (Eds) et al. The Causes of Tropical Deforestation Earthscan London 86–94
T. Rudel (1994) Population, development and tropical deforestation: a cross-national study Brown (Eds) et al. The Causes of Tropical Deforestation Earthscan London 96–103
T.M. Selden D. Song (1994) ArticleTitleEnvironmental quality and development: is there a Kuznets curve for air pollutions? Journal of Environmental Economics and Management 27 147–162 Occurrence Handle10.1006/jeem.1994.1031
N. Shafik (1994) ArticleTitle‘Economic development and environmental quality: an econometric analysis’ Oxford Economic Papers 46 757–773
A. Shi (2003) ArticleTitle‘The impact of population pressure on global carbon dioxide emissions’, 1975–1996: evidence from pooled cross-country data Ecological Economics 44 29–42 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0921-8009(02)00223-9
D.I. Stern M.S. Common E.B. Barbier (1996) ArticleTitle‘Economic growth and environmental degradation: the environmental Kuznets curve and sustainable development’ World Development 24 1151–1160 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0305-750X(96)00032-0
C.A. Tisdell (1999) ‘Conditions for Sustainable development: weak and strong’ A.K. Dragun C. Tisdell (Eds) Sustainable Agriculture and Environment: Globalisation and the Impact of Trade Liberalisation Edward Elgar Cheltenham 23–36
C.A. Tisdell (2001) ArticleTitle‘Globalisation and sustainability: environmental Kuznets curve and the WTO’ Ecological Economics 39 185–196 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0921-8009(01)00234-8
M.P. Vogel (1999) Environmental Kuznets curves. A Study on the Economic Theory and Political Economy of Environmental Quality Improvements in the Course of Economic Growth Berlin Springer
R. Watson J. Dixon S. Hamburg A. Janetos R. Moss (1998) Protecting Our Planet, Securing Our Future: Linkages among Global Environmental Issues and Human Needs UNEP Nairobi
InstitutionalAuthorNameWorld Bank (2002) World Development Indicators 2002 World Bank Washington
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kahuthu, A. Economic Growth and Environmental Degradation in a Global Context. Environ Dev Sustain 8, 55–68 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-005-0785-3
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-005-0785-3