Abstract
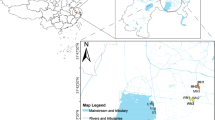
Mytilus galloprovincialis is a marine mollusk belonging to the Bivalvia class. It has been distributed largely in Turkish shores and worldwide aquatic environments. Besides being known as an environmental pollution indicator, it is highly consumed as a food and has a high economic value. Due to their nutritional mechanisms by filtering water, they are affected by pollution in seawater and mussels can host-microbial diversity of environmental origin as well as pathogenic bacteria. Therefore, in this study, bacterial species found in Mediterranean mussels collected from the coastal stations of Istanbul [Rumeli Kavagi (RK), Kucukcekmece (KC)], and Izmir [(Foca (MF), Urla (MU)] were investigated and compared with microbiological and metagenomic analyses. According to microbiological analysis results, 34 mussel-associated Enterobacteriaceae and Vibrionaceae family members were identified. As a result of the culture-independent metagenomic analysis, taxonomic groups for each station were identified and compared based on Operational Taxonomic Unit data. For all stations, the most abundant bacterial genera were the unclassified bacterial genera. The total number of mussel-related total richness identified in all groups was 4889 (RK = 1605; KC = 1930; MF = 1508; and MU = 1125). According to the metagenomic data obtained in this study, different relative amounts of Lachnospiraceae and Bacteroidetes taxa groups were reported for all stations. The pathogenic bacterial genera identified by metagenomic analyses which may be significant for the public health are Arcobacter, Clostridium, Aeromonas, Vibrio, Escherichia_Shigella, Klebsiella, Campylobacter, Helicobacter, Pseudomonas, Morganella, Serratia, Corynebacterium, Enterococcus, Staphylococcus, Yersinia, Mycoplasma, Brucellaceae_unclassified, Pantoea, and Proteus.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abayasekara, L. M., Perera, J., Chandrasekharan, V., Gnanam, V. Z., Udunuwara, N. A., et al. (2017). Detection of bacterial pathogens fromclinical specimens using conventional microbial culture and 16S metagenomics: a comparative study. BMC Infectious Diseases, 17, 631.
Aksoy, U., Marangi, M., Papini, R., Ozkoc, S., Bayram Delibas, S., & Giangaspero, A. (2014). Detection of toxoplasma gondii and Cyclospora cayetanensis in Mytilus galloprovincialis from Izmir province coast (Turkey) by real time PCR/high-resolution melting analysis (HRM). Food Microbiology, 44, 128–135.
Altug, G., & Guler, N. (2002). Determination of the levels of indicator bacteria, Salmonella spp. and heavy metals in sea snails (Rapana venosa) from the Northern Marmara Sea, Turkey. Turkish J Fish Aquat Sci, 2, 141–144.
Araj, G. F., Taleb, R., El Beayni, N. K., & Goksu, E. (2019). Vibrio albensis: An unusual urinary tract infection in a healthy male. Journal of Infection and Public Health.
Arfken, A., Song, B., Bowman, J. S., & Piehler, M. (2017). Denitrification potential of the eastern oyster microbiome using a 16S rRNA gene based metabolic inference approach. PLoS One, 12(9), e0185071.
Balbi, T., Auguste, M., Cortese, K., Montagna, M., Borello, A., Pruzzo, C., Vezzulli, L., & Canesi, L. (2019). Responses of Mytilus galloprovincialis to challenge with the emerging marine pathogen Vibrio coralliilyticus. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 84, 352–360.
Balcioglu, E. B., & Gonulal, O. (2017). A study on biometry of mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis, Lamarck,1819) collected from various regions of Marmara Sea. Suleyman Demirel University Journal of Natural and Applied Sciences, 21(2), 397–400.
Berendes, D. M., Kirby, A. E., Clennon, J. A., Agbemabiese, C., Ampofo, J. A., Armah, G. E., Baker, K. K., Liu, P., Reese, H. E., Robb, K. A., Wellington, N., Yakubu, H., & Moe, C. L. (2018). Urban sanitation coverage and environmental fecal contamination: links between the household and public environments of Accra, Ghana. PLoS One, 13(7), e0199304.
Bolger, A. M., Lohse, M., & Usadel, B. (2014). Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics., 30(15), 2114–2120.
Bozcal, E., Dagdeviren, M., Uzel, A., & Skurnik, M. (2017). LuxCDE-luxAB-based promoter reporter system to monitor the Yersinia enterocolitica O:3 gene expression in vivo. PLoS One, 12(2), e0172877.
Cappello, S., Volta, A., Santisi, S., Genovese, L., Maricchiolo, G., Bonsignore, M., et al. (2015). Study of bacterial communities in mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis (Bivalvia: Mytilidae) by a combination of 16s crDNA and 16s rDNA sequencing. JSM Microbiology, 3(1), 1016.
Cole, J. R., Wang, Q., Fish, J. A., Chai, B., McGarrell, D. M., Sun, Y., et al. (2014). Ribosomal database project: data and tools for high throughput rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Research, 42(D1), 633–642.
Collado, L., Guarro, J., & Figueras, M. J. (2009). Prevalence of Arcobacter in meat and shellfish. Journal of Food Protection, 72(5), 1102–1106.
Craft, J. A., Gilbert, J. A., Temperton, B., Dempsey, K. E., Ashelford, K., et al. (2010). Pyrosequencing of Mytilus galloprovincialis cDNAs: tissue-specific expression patterns. PLoS One, 5(1), e8875.
De Sousa, O. V., Vieira, R. H., De Menezes, F. G., Dos Reis, C. M., & Hofer, E. (2004). Detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio cholerae in oyster, Crassostrea rhizophorae, collected from a natural nursery in the coco river estuary, Fortaleza, Ceara. Brazil. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo., 46(2), 59–62.
Drzewiecka, D. (2016). Significance and roles of Proteus spp. bacteria in natural environments. Microbial Ecology, 72(4), 741–758.
Duman, M., Saticioglu, I. B., & Altun, S. (2019). Molecular characterization and antimicrobial resistance profile of fecal contaminants and spoilage bacteria that emerge in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) farms. Bioscience of Microbiota Food and Health., 38(2), 41–48.
Edgar, R. C., Haas, B. J., Clemente, J. C., Quince, C., & Knight, R. (2011). UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics., 27(16), 2194–2200.
Eggermont, M., Bossier, P., Sasmita, G., Pande, J., Delahaut, V., Gupta, N., et al. (2017). Isolation of Vibrionaceae from wild blue mussel (Mytilus edulis) adults and their impact on blue mussel larviculture. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 93(4), 39.
Erol, N., Delibas, S. B., Ozkoc, S., Erguden, C., & Aksoy, U. (2016). Investigation of parasitic and viral pathogens in mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) in the Gulf of Izmir, Turkey. Saudi Medical Journal, 37(6), 703–706.
Escobedo-Hinojosa, W., & Pardo-Lopez, L. (2017). Analysis of bacterial metagenomes from the Southwestern Gulf of Mexico for pathogens detection. Pathogens and Disease, 75(5).
Fernandez-Delgado, M., Contreras, M., Garcia-Amado, M. A., Gueneau, P., & Suarez, P. (2007). Occurrence of Proteus mirabilis associated with two species of Venezuelan oysters. Revista do Instituto de Medicina Tropical de São Paulo., 49(6), 355–359.
Frank, J. A., Reich, C. I., Sharma, S., Weisbaum, J. S., Wilson, B. A., & Olsen, G. J. (2008). Critical evaluation of two primers commonly used for amplification of bacterial 16S rRNA genes. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 74(8), 2461–2470.
Gensberger, E. T., Gossl, E. M., Antonelli, L., Sessitsch, A., & Kostic, T. (2015). Effect of different heterotrophic plate count methods on the estimation of the composition of the culturable microbial community. PeerJ, 3, e862.
Gilbert, J. A., Field, D., Huang, Y., Edwards, R., Li, W., Glina, P., et al. (2008). Detection of large numbers of novel sequences in the metatranscriptomes of complex marine microbial communities. PLoS One, 3(8), e3042.
Goulas, A. E., Chouliara, I., Nessi, E., Kontominas, M. G., & Savvaidis, I. N. (2005). Microbiological, biochemical and sensory assessment of mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) stored under modified atmosphere packaging. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 98(3), 752–760.
Grevskott, D. H., Svanevik, C. S., Wester, A. L., & Lunestad, B. T. (2016). The species accuracy of the most probable number (MPN) European Union reference method for enumeration of Escherichia coli in marine bivalves. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 131, 73–77.
Grevskott, D. H., Svanevik, C. S., Sunde, M., Wester, A. L., & Lunestad, B. T. (2017). Marine bivalve mollusks as possible indicators of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli and other species of the Enterobacteriaceae family. Frontiers in Microbiology, 8, 24.
Gugliandolo, C., Lentini, V., Spano, A., & Maugeri, T. L. (2011). Conventional and molecular methods to detect bacterial pathogens in mussels. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 52(1), 15–21.
Hernroth, B., Lothigius, A., & Bolin, I. (2010). Factors influencing survival of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli, Salmonella enterica (serovar Typhimurium) and Vibrio parahaemolyticus in marine environments. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 71(2), 272–280.
Hiergeist, A., Glasner, J., Reischl, U., & Gessner, A. (2015). Analyses of intestinal microbiota: culture versus sequencing. ILAR Journal., 56(2), 228–240.
Iino, T., Mori, K., Uchino, Y., Nakagawa, T., Harayama, S., & Suzuki, K. (2010). Ignavibacterium album gen. nov., sp. nov., a moderately thermophilic anaerobic bacterium isolated from microbial mats at a terrestrial hot spring and proposal of Ignavibacteria classis nov., for a novel lineage at the periphery of green sulfur bacteria. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 60(6), 1376–1382.
Kacar, A. (2011). Some microbial characteristics of mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) in coastal city area. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 18(8), 1384–1389.
Kayhan, F. E., Sesal, N. C., & Guldur, S. (2016). The identification of gram-negative bacterial flora of black mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis). Marmara Fen Bilim Derg., 28(2), 66–69.
King, G. M., Judd, C., Kuske, C. R., & Smith, C. (2012). Analysis of stomach and gut microbiomes of the Eastern oyster (Crassostrea virginica) from coastal Louisiana, USA. PLoS One, 7(12), e51475.
Klindworth, A., Pruesse, E., Schweer, T., Peplies, J., Quast, C., Horn, M., et al. (2013). Evaluation of general 16S ribosomal RNA gene PCR primers for classical and next-generation sequencing-based diversity studies. Nucleic Acids Research, 41(1), 1–11.
Kozich, J. J., Westcott, S. L., Baxter, N. T., Highlander, S. K., & Schloss, P. D. (2013). Development of a dual-index sequencing strategy and curation pipeline for analyzing amplicon sequence data on the miseq illumina sequencing platform. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 79(17), 5112–5120.
Kucuksezgin, F., Kontas, A., Altay, O., Uluturhan, E., & Darilmaz, E. (2006). Assessment of marine pollution in Izmir Bay: nutrient, heavy metal and total hydrocarbon concentrations. Environment International, 32(1), 41–51.
Li, Y. F., Xu, J. K., Chen, Y. W., Ding, W. Y., Shao, A. Q., Liang, X., et al. (2019). Characterization of gut microbiome in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis in response to the thermal stress. Frontiers in Physiology, 10, 1086.
Liu, H., Zhu, J., Hu, Q., & Rao, X. (2016). Morganella morganii, a non-negligent opportunistic pathogen. International Journal of Infectious Diseases, 50, 10–17.
Liyanage, C. P., & Yamada, K. (2017). Impact of population growth on the water quality of natural water bodies. Sustain, 9(8), 1405 1-14.
Mannas, H., Mimouni, R., Chaouqy, N., Hamadi, F., & Martinez-Urtaza, J. (2014). Occurrence of Vibrio and Salmonella species in mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) collected along the Moroccan Atlantic coast. Springerplus., 3(1), 1–11.
Marcinkiewicz, A. L., Schuster, B. M., Jones, S. H., Cooper, V. S., & Whistler, C. A. (2017). Bacterial community profiles and Vibrio parahaemolyticus abundance in individual oysters and their association with estuarine ecology. bioRxiv, 156851.
Matozzo, V., Ercolini, C., Serracca, L., Battistini, R., Rossini, I., Granato, G., Quaglieri, E., Perolo, A., Finos, L., Arcangeli, G., Bertotto, D., Radaelli, G., Chollet, B., Arzul, I., & Quaglio, F. (2018). Assessing the health status of farmed mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) through histological, microbiological and biomarker analyses. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 153, 165–179.
Miotto, M., Ossai, S. A., Meredith, J. E., Barretta, C., Kist, A., Prudencio, E. S., R W Vieira, C., & Parveen, S. (2019). Genotypic and phenotypic characterization of Escherichia coli isolated from mollusks in Brazil and the United States. Microbiologyopen., 8(5), e00738.
Normanno, G., Parisi, A., Addante, N., Quaglia, N. C., Dambrosio, A., Montagna, C., & Chiocco, D. (2006). Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Vibrio vulnificus and microorganisms of fecal origin in mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) sold in the Puglia region (Italy). International Journal of Food Microbiology, 106(2), 219–222.
O’Callaghan, A., & van Sinderen, D. (2016). Bifidobacteria and their role as members of the human gut microbiota. Frontiers in Microbiology, 7, 925.
Offret, C., Jegou, C., Mounier, J., Fleury, Y., & Le Chevalier, P. (2019). New insights into the haemo- and coelo-microbiota with antimicrobial activities from Echinodermata and Mollusca. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 126(4), 1023–1031.
Onarinde, B. A., & Dixon, R. A. (2018). Prospects for biocontrol of Vibrio parahaemolyticus contamination in blue mussels (Mytilus edulis)-a year-long study. Frontiers in Microbiology, 9, 1043.
Ozkan, D., Dagdeviren, M., Katalay, S., Guner, A., & Yavasoglu, N. U. (2017). Multi-biomarker responses after exposure to pollution in the Mediterranean mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis L.) in the Aegean coast of Turkey. Bulletin of Environment Contamination and Toxicology, 98(1), 46–52.
Papadopoulou, C., Economou, E., Zakas, G., Salamoura, C., Dontorou, C., & Apostolou, J. (2007). Microbiological and pathogenic contaminants of seafood in Greece. Journal of Food Quality, 30(1), 28–42.
Pfister, C. A., Meyer, F., & Antonopoulos, D. A. (2010). Metagenomic profiling of a microbial assemblage associated with the California mussel: a node in networks of carbon and nitrogen cycling. PLoS One, 5(5), e10518.
Pruesse, E., Peplies, J., & Glockner, F. O. (2012). SINA: accurate high-throughput multiple sequence alignment of ribosomal RNA genes. Bioinformatics, 28, 1823–1829.
Quast, C., Pruesse, E., Yilmaz, P., Gerken, J., Schweer, T., Yarza, P., et al. (2013). The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Research, 41(D1), 590–596.
Reis, R. S., & Horn, F. (2010). Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli, Samonella, Shigella and Yersinia: cellular aspects of host-bacteria interactions in enteric diseases. Gut Pathog., 2(1), 8.
Rippey, S. R. (1994). Infectious diseases associated with molluscan shellfish consumption. Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 7(4), 419–425.
Romanenko, L. A., Uchino, M., Kalinovskaya, N. I., & Mikhailov, V. V. (2008). Isolation, phylogenetic analysis and screening of marine mollusc-associated bacteria for antimicrobial, hemolytic and surface activities. Microbiological Research, 163(6), 633–644.
Rubini, S., Galletti, G., D’Incau, M., Govoni, G., Boschetti, L., Berardelli, C., et al. (2018). Occurrence of Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica in bivalve molluscs and associations with Escherichia coli in molluscs and faecal coliforms in seawater. Food Control, 84, 429–435.
Salvesen, I., & Vadstein, O. (2000). Evaluation of plate count methods for determination of maximum specific growth rate in mixed microbial communities, and its possible application for diversity assessment. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 88, 442–448.
Santo Domingo, J. W., & Edge, T. A. (2010). Identification of primary sources of faecal pollution. In G. Rees et al. (Eds.), Safe management of shellfish and harvest waters (Vol. Chapter 5, pp. 51–91). London: IWA Publishing.
Schloss, P. D., Westcott, S. L., Ryabin, T., Hall, J. R., Hartmann, M., Hollister, E. B., Lesniewski, R. A., Oakley, B. B., Parks, D. H., Robinson, C. J., Sahl, J. W., Stres, B., Thallinger, G. G., van Horn, D., & Weber, C. F. (2009). Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 75(23), 7537–7541.
Sengor, G. F., Kalafatoglu, H., & Gun, H. (2004). The determination of microbial flora, water activity and chemical analyses in smoked, canned mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis, L.). Turkish Journal of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, 28, 793–797.
Thomas, T., Gilbert, J., & Meyer, F. (2012). Metagenomics - a guide from sampling to data analysis. Microbial Informatics and Experimentation, 2(1), 3.
Utermann, C., Parrot, D., Breusing, C., Stuckas, H., Staufenberger, T., Blumel, M., et al. (2018). Combined genotyping, microbial diversity and metabolite profiling studies on farmed Mytilus spp. from Kiel Fjord. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 7983.
Vernocchi, P., Maffei, M., Lanciotti, R., Suzzi, G., & Gardini, F. (2007). Characterization of Mediterranean mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) harvested in Adriatic Sea (Italy). Food Control, 18(12), 1575–1583.
Vezzulli, L., Stagnaro, L., Grande, C., Tassistro, G., Canesi, L., & Pruzzo, C. (2018). Comparative 16SrDNA gene-based microbiota profiles of the Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas) and the Mediterranean mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) from a shellfish farm (Ligurian Sea, Italy). Microbial Ecology, 75(2), 495–504.
Vieira, R. H., Lima, E. A., Sousa, D. B., Reis, E. F., Costa, R. G., & Rodrigues Ddos, P. (2004). Vibrio spp. and Salmonella spp., presence and susceptibility in crabs Ucides cordatus. Revista do Instituto de Medicina Tropical de São Paulo, 46(4), 179–182.
Wilmes, P., & Bond, P. L. (2006). Metaproteomics: studying functional gene expression in microbial ecosystems. Trends in Microbiology, 14(2), 92–97.
Yilmaz, F., Savci, S., Pazar-Yildirim, E., Gonullu, N., Bavunoglu, I., Koksal-Cakirlar, F., et al. (2015). A catheter related sepsis case caused by Pantoea agglomerans. Turk Hij Den Biyol Derg., 72(1), 59–62.
Zannella, C., Mosca, F., Mariani, F., Franci, G., Folliero, V., Galdiero, M., et al. (2017). Microbial diseases of bivalve mollusks: infections, immunology and antimicrobial defense. Marine Drugs, 15(6), 182.
Funding
The authors received financial support from Istanbul University BAP unit for the project under FBA-2018-30817 code. Authors used the facilities of BM Labosis (Ankara, Turkey) for Sanger Sequencing. The meta-data analysis and numerical calculations reported in this paper were partially carried out at TUBITAK ULAKBIM, High Performance and Grid Computing Center (TRUBA resources).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This study was partly presented as a poster at the EMBO|EMBL Symposium: New Approaches and Concepts in Microbiology, 10–13 July 2019, Heidelberg-Germany.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bozcal, E., Dagdeviren, M. Bacterial metagenome analysis of Mytilus galloprovincialis collected from Istanbul and Izmir coastal stations of Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 192, 186 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-8129-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-8129-1