Abstract
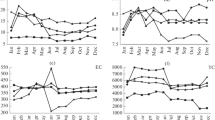
Dams and sluices break down the river continuum, alter the river hydrological regime, and intercept the migration processes of nutrients and pollutants. The regulation of dams and sluices will have great impacts on water quality characteristics in the river basin. In this study, variable fuzzy pattern recognition model (VFPR), principal component analysis/factor analysis (PCA/FA), and the absolute principal component score-multiple linear regression (APCS-MLR) were used to assess the water quality and identify the potential pollution sources in a highly regulated river of Northeast China. A set of water quality variables at three stations were measured from January 2015 to August 2017. The water quality assessment results showed that there were spatial and temporal variations of water quality and the total nitrogen (TN) and fecal coliforms (F. coli) were the major pollution factors of the study river section. Four pollution sources, including industrial effluent source, domestic sewage source, meteorological factor and atmospheric deposition source, and agricultural non-point source, were identified in dry and wet seasons using the PCA/FA method. The APCS-MLR results showed that the industrial effluent source was the main pollution source in dry seasons and had a decrease in wet seasons. While the mean contribution of the domestic sewage source had an increase in wet seasons, influenced by the sewage overflow and the flushing of pollutants during the extreme precipitation, the construction of dams decreased the flow obviously in wet seasons and increased in dry seasons. The increase in pollutants caused by storm runoff and the reduction of dilution water in the river channel could be the main reason for the water quality degradation in wet seasons.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
An, Y., Zou, Z., & Li, R. (2014). Water quality assessment in the Harbin reach of the Songhuajiang River (China) based on a fuzzy rough set and an attribute recognition theoretical model. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 11(4), 3507–3520. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110403507.
Bansal, S., & Ganesan, G. (2019). Advanced evaluation methodology for water quality assessment using artificial neural network approach. Water Resources Management, 33(9), 3127–3141. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-02289-6.
Barakat, A., Baghdadi, M. E., Rais, J., Aghezzaf, B., & Slassi, M. (2016). Assessment of spatial and seasonal water quality variation of Oum Er Rbia River (Morocco) using multivariate statistical techniques. International Soil and Water Conservation Research, 4(4), 284–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswcr.2016.11.002.
Best, J. (2018). Anthropogenic stresses on the world's big rivers. Nature Geoscience, 12(1), 7–21. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41561-018-0262-x.
Bora, M., & Goswami, D. C. (2017). Water quality assessment in terms of water quality index (WQI): case study of the Kolong River, Assam, India. Applied Water Science, 7(6), 3125–3135.
Bu, H., Meng, W., & Zhang, Y. (2014a). Spatial and seasonal characteristics of river water chemistry in the Taizi River in Northeast China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 186(6), 3619–3632. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3644-6.
Bu, H., Meng, W., Zhang, Y., & Wan, J. (2014b). Relationships between land use patterns and water quality in the Taizi River basin, China. Ecological Indicators, 41, 187–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.02.003.
Chen, S. (2009). Theory and model of variable fuzzy sets and its application (1st ed.pp. 23–29). Dalian: Dalian University of Technology Press.
Crockford, L., O’Riordain, S., Taylor, D., Melland, A. R., & Shortle, G. (2017). The application of high temporal resolution data in river catchment modelling and management strategies. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 189(9), 461. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6174-1.
Dalal, S. G., Shirodkar, P. V., Jagtap, T. G., Naik, B. G., & Rao, G. S. (2010). Evaluation of significant sources influencing the variation of water quality of Kandla creek, Gulf of Katchchh, using PCA. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 163(1-4), 49–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-0815-y.
Dila, D. K., Corsi, S. R., Lenaker, P., Baldwin, A. K., Bootsma, M. J., & McLellan, S. (2018). Patterns of host-associated fecal indicators driven by hydrology, precipitation, and land use attributes in Great Lakes watersheds. Environmental Science & Technology, 52(20), 11500–11509. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b01945.
Dolph, C. L., Boardman, E., Danesh-Yazdi, M., Finlay, J. C., Hansen, A. T., Baker, A. C., & Dalzell, B. (2019). Phosphorus transport in intensively managed watersheds. Water Resources Research, 55, 9148–9172. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018WR024009.
Dou, M., Zhang, Y., Zuo, Q. T., & Mi, Q. B. (2015). Identification of key factors affecting the water pollutant concentration in the sluice-controlled river reaches of the Shaying River in China via statistical analysis methods. Environmental Science: Processes and Impacts, 17(8), 1492–1502.
Duan, W., He, B., Nover, D., Yang, G., Chen, W., Meng, H., Zou, S., & Liu, C. (2016). Water quality assessment and pollution source identification of the eastern Poyang Lake Basin using multivariate statistical methods. Sustainability., 8(2), 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8020133.
Farnham, I. M., Singh, A. K., Stetzenbach, K. J., & Johannesson, K. H. (2002). Treatment of nondetects in multivariate analysis of groundwater geochemistry data. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 60(1), 265–281.
Feng, F., Xu, S., Liu, J., Liu, D., & Wu, B. (2010). Comprehensive benefit of flood resources utilization through dynamic successive fuzzy evaluation model: a case study. Science China Technological Sciences, 53(2), 529–538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-009-0396-6.
Fones, G. R., Bakir, A., Gray, J., Mattingley, L., Measham, N., Knight, P., Bowes, M. J., Greenwood, R., & Mills, G. A. (2020). Using high-frequency phosphorus monitoring for water quality management: a case study of the upper River Itchen, UK. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 192(3), 184. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-8138-0.
Gholizadeh, M. H., Melesse, A. M., & Reddi, L. (2016). Water quality assessment and apportionment of pollution sources using APCS-MLR and PMF receptor modeling techniques in three major rivers of South Florida. Science of the Total Environment, 566, 1552–1567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.06.046.
Gillespie, B., Kay, P., & Brown, L. E. (2020). Limited impacts of experimental flow releases on water quality and macroinvertebrate community composition in an upland regulated river. Ecohydrology., 13(2), e2174. https://doi.org/10.1002/eco.2174.
Grill, G., Lehner, B., Lumsdon, A. E., MacDonald, G. K., Zarfl, C., & Liermann, C. R. (2015). An index-based framework for assessing patterns and trends in river fragmentation and flow regulation by global dams at multiple scales. Environmental Research Letters, 10(1), 015001.
Habets, F., Molénat, J., Carluer, N., Douez, O., & Leenhardt, D. (2018). The cumulative impacts of small reservoirs on hydrology: a review. Science of the Total Environment, 643, 850–867. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.188.
Harvey, J., Gomez-Velez, J., Schmadel, N., Scott, D., Boyer, E., Alexander, R., & Choi, J. (2019). How hydrologic connectivity regulates water quality in river corridors. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 55(2), 369–381. https://doi.org/10.1111/1752-1688.12691.
Hayes, D. F., Labadie, J. W., Sanders, T. G., & Brown, J. K. (1998). Enhancing water quality in hydropower system operations. Water Resources Research, 34(3), 471–483. https://doi.org/10.1029/97WR03038.
He, Y., Meng, W., Xu, J., Zhang, Y., & Guo, C. (2016). Spatial distribution and potential toxicity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments from Liaohe River Basin, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188, 193. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5201-y.
Hu, S. D., Wang, T. X., Xu, S. G., Ma, L. X., & Sun, X. G. (2019). Seasonal release potential of sediments in reservoirs and its impact on water quality assessment. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(18), 3303. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16183303.
Huang, F., Wang, X., Lou, L., Zhou, Z., & Wu, J. (2010). Spatial variation and source apportionment of water pollution in Qiantang River (China) using statistical techniques. Water Research, 44(5), 1562–1572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.11.003.
Jeong, K. S., Kim, D. K., Shin, H. S., Kim, H. W., Cao, H., Jang, M. H., & Joo, G. J. (2010). Flow regulation for water quality (chlorophyll a) improvement. International Journal of Environmental Research, 4(4), 713–724 http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7721-4937.
Kang, P., Liu, P., & Wang, F. (2019). Use of multiple isotopes to evaluate the impact of mariculture on nutrient dynamics in coastal groundwater. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(12), 12399–12411. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04645-w.
Kolesar, P., & Serio, J. (2011). Breaking the deadlock: improving water-release policies on the Delaware River through operations research. Interfaces, 41(1), 18–34. https://doi.org/10.1287/inte.1100.0536.
Larson, T., Gould, T., Riley, E. A., Austin, E., Fintzi, J., Sheppard, L., Yost, M., & Simpson, C. (2017). Ambient air quality measurements from a continuously moving mobile platform: Estimation of area-wide, fuel-based, mobile source emission factors using absolute principal component scores. Atmospheric Environment, 152, 201–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2016.12.037.
McLellan, S. L., Hollis, E. J., Depas, M. M., Van Dyke, M., Harris, J., & Scopel, C. O. (2007). Distribution and fate of Escherichia coli in Lake Michigan following contamination with urban stormwater and combined sewer overflows. Journal of Great Lakes Research, 33(3), 566–580.
McMillan, S. K., Wilson, H. F., Tague, C. L., Hanes, D. M., Inamdar, S., Karwan, D. L., Loecke, T., Morrison, J., Murphy, S. F., & Vidon, P. (2018). Before the storm: antecedent conditions as regulators of hydrologic and biogeochemical response to extreme climate events. Biogeochemistry, 141(3), 487–501.
Nilsson, C., Reidy, C. A., Dynesius M., & Revenga, C. (2005). Fragmentation and flow regulation of the world’s large river systems. Science, 308(5720), 405–408. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1107887.
Ogundele, L. T., Owoade, O. K., Olise, F. S., & Hopke, P. K. (2016). Source identification and apportionment of PM2.5 and PM2.5-10 in iron and steel scrap smelting factory environment using PMF, PCFA and UNMIX receptor models. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188(10), 574. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5585-8.
Panasiuk, O., Hedstrom, A., Marsalek, J., Ashley, R. M., & Viklander, M. (2015). Contamination of stormwater by wastewater: a review of detection methods. Journal of Environmental Management, 152, 241–250.
Pettit, N. E., Jardine, T. D., Hamilton, S. K., Sinnamon, V., Valdez, D., Davies, P. M., Douglas, M. M., & Bunn, S. E. (2012). Seasonal changes in water quality and macrophytes and the impact of cattle on tropical floodplain waterholes. Marine and Freshwater Research, 63(9), 788–800. https://doi.org/10.1071/MF12114.
Pinto, C. C., Calazans, G. M., & Oliveira, S. C. (2019). Assessment of spatial variations in the surface water quality of the Velhas River Basin, Brazil, using multivariate statistical analysis and nonparametric statistics. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191(3), 164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7281-y.
Quinn, C. L., Armitage, J. M., Wania, F., & Arnot, J. A. (2019). Development and evaluation of a combined bioenergetics and organic chemical mass-balance bioaccumulation model for fish. Environmental Science & Technology, 53(2), 752–759. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b04382.
Ren, Y., Li, J., Ren, N., & Li, X. (2012). The application of fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method in non-point pollution on wetland water environmental impact. Advanced Materials, 518, 4948–4962.
Sercu, B., Van De Werfhorst, L. C., Murray, J. L. S., & Holden, P. A. (2011). Sewage exfiltration as a source of storm drain contamination during dry weather in urban watersheds. Environmental Science & Technology, 45(17), 7151–7157.
Shehzad, M. T., Murtaza, G., Shafeeque, M., Shafeeque, M., Sabir, M., Nawaz, H., & Khan, M. J. (2019). Assessment of trace elements in urban topsoils of Rawalpindi-Pakistan: a principal component analysis approach. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191(2), 65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7212-y.
Shi, W., Xia, J., & Zhang, X. (2016). Influences of anthropogenic activities and topography on water quality in the highly regulated Huai River basin, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(21), 21460–21474.
Shrestha, S., & Karama, F. (2007). Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of the Fuji river basin, Japan. Environmental Modelling & Software, 22(4), 464–475.
Simeonov, V., Stratis, J. A., Samara, C., Zachariadis, G., Voutsa, D., Anthemidis, A., et al. (2003). Assessment of the surface water quality in Northern Greece. Water Research, 37(17), 4119–4124. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(03)00398-1.
Soto, D. X., Koehler, G., Wassenaar, L. I., & Hobson, K. A. (2019). Spatio-temporal variation of nitrate sources to Lake Winnipeg using N and O isotope (delta N-15, delta O-18) analyses. Science of the Total Environment, 647, 486–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.346.
Srinivas, R., & Singh, A. P. (2018). An integrated fuzzy-based advanced eutrophication simulation model to develop the best management scenarios for a river basin. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(9), 9012–9039. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1206-0.
Templar, H. A., Dila, D. K., Bootsma, M. J., Corsi, S. R., & McLellan, S. L. (2016). Quantification of human-associated fecal indicators reveal sewage from urban watersheds as a source of pollution to Lake Michigan. Water Research, 100, 556–567.
Thurston, G. D., & Spengler, J. D. (1985). A quantitative assessment of source contributions to inhalable particulate matter pollution in metropolitan Boston. Atmospheric Environment, 19, 9–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/0004-6981(85)90132-5.
Todd, A. S., Manning, A. H., Verplanck, P. L., Crouch, C., McKnight, D. M., & Dunham, R. (2012). Climate-change-driven deterioration of water quality in a mineralized watershed. Environmental Science and Technology, 46(17), 9324–9332. https://doi.org/10.1021/es3020056.
Vorosmarty, C. J., McIntyre, P. B., Gessner, M. O., Dudgeon, D., Prusevich, A., Green, P., et al. (2010). Global threats to human water security and river biodiversity. Nature, 467(7315), 555–561. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09440.
Wan, J., Bu, H., Zhang, Y., & Meng, W. (2013). Classification of rivers based on water quality assessment using factor analysis in Taizi River basin, northeast China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 69(3), 909–919.
Wang, T., Xu, S., & Liu, J. (2017). Dynamic assessment of comprehensive water quality considering the release of sediment pollution. Water, 9(4), 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9040275.
Wei, G., Yang, Z., Cui, B., Li, B., Chen, H., Bai, J., & Dong, S. (2009). Impact of dam construction on water quality and water self-purification capacity of the Lancang River, China. Water Resources Management, 23(9), 1763–1780. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-008-9351-8.
Winton, R. S., Calamita, E., & Wehrli, B. (2019). Reviews and syntheses: dams, water quality and tropical reservoir stratification. Biogeosciences, 16(8), 1657–1671. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-16-1657-2019.
Xu, S., Wang, T., & Hu, S. (2015). Dynamic assessment of water quality based on a variable fuzzy pattern recognition model. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 12, 2230–2248. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120202230.
Yang, J., & Zhang, L. (2012). Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method on water environmental quality based on entropy weight with consideration of toxicology of evaluation factors. Advanced Materials, 356, 2383–2388. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.356-360.2383.
Yang, L., Mei, K., Liu, X., Wu, L., Zhang, M., Xu, J., & Wang, F. (2013). Spatial distribution and source apportionment of water pollution in different administrative zones of Wen-Rui-Tang (WRT) river watershed, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20, 5341–5352. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1536-x.
Zhai, X., Xia, J., & Zhang, Y. (2014). Water quality variation in the highly disturbed Huai River Basin, China from 1994 to 2005 by multi-statistical analyses. Science of the Total Environment, 496, 594–606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.06.101.
Zhai, X., Xia, J., & Zhang, Y. (2017). Integrated approach of hydrological and water quality dynamic simulation for anthropogenic disturbance assessment in the Huai River Basin, China. Science of the Total Environment, 598, 749–764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.04.092.
Zhang, Y., Xia, J., Shao, Q., & Zhai, X. (2012a). Experimental and simulation studies on the impact of sluice regulation on water quantity and quality processes. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, 17(4), 467–477. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0000463.
Zhang, Y., Arthington, A. H., Bunn, S. E., Mackay, S., Xia, J., & Kennaed, M. (2012b). Classification of flow regimes for environmental flow assessment in regulated rivers: the Huai River Basin, China. River Research and Applications, 28(7), 989–1005.
Zhang, Y., Xia, J., Shao, Q., & Zhai, X. (2013). Water quantity and quality simulation by improved SWAT in highly regulated Huai River Basin of China. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment, 27, 11–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-011-0546-9.
Zhang, Q., Hirsch, R., & Ball, P. W. (2016). Long-Term changes in sediment and nutrient delivery from Conowingo Dam to Chesapeake Bay: effects of reservoir sedimentation. Environmental Science & Technology, 50, 1877–1886. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b04073.
Zhou, F., Guo, H., & Liu, L. (2007). Quantitative identification and source apportionment of anthropogenic heavy metals in marine sediment of Hong Kong. Environmental Geology, 53(2), 295–305.
Zielinski, M., Dopieralska, J., Belka, Z., Walczak, A., Siepak, M., & Jakubowicz, M. (2016). Sr isotope tracing of multiple water sources in a complex river system, Notec River, Poland. Science of the Total Environment, 548, 307–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.01.036.
Acknowledgments
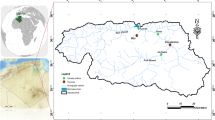
The datasets were obtained from the Benxi city sub-center of the Liaoning province water environment monitoring center.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFC0400903) and the Natural Sciences Foundation of China (51679026; 51809032; 51879031).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, G., Liu, J., Xu, S. et al. Water quality assessment and pollution source apportionment in a highly regulated river of Northeast China. Environ Monit Assess 192, 446 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08404-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08404-0