Abstract
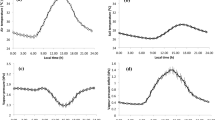
Lowland tropical rice-rice system has a unique micrometrological characteristic that affects both energy component and net ecosystem energy. Periodic and seasonal variations of methane (CH4), carbon dioxide (CO2), and energy exchange from irrigated lowland rice-rice ecosystem were studied using open-path eddy covariance (EC) system during the dry (DS) and wet (WS) seasons in 2015. Concurrently, the manual chamber method was employed in nitrous oxide (N2O) measurement efflux. Cumulative net ecosystem carbon exchange (NEE) was observed highest (− 232.55 g C m−2) during the WS and lowest (− 14.81 g C m−2) during wet fallow (WF). Similarly, the cumulative net ecosystem methane exchange (NEME) was found highest (13,456.5 mg CH4 m−2) during the WS and lowest (2014.3 mg CH4 m−2) during the WF. Surface energy fluxes, i.e., sensible (Hs) and latent heat (LE) fluxes, showed a similar trend. With the advancement of time, the ratio of ecosystem respiration (Re) and gross primary production (GPP) increased. The cumulative global warming potential (GWP) for the two cropping seasons including two fallows was 13,224.1 kg CO2 equivalent ha−1. The GWP and NEME showed a similar trend as soil enzymes and labile carbon pools in both seasons (except GWP at the harvesting stage in the wet season). The mean NEE exhibited a more negative value with decrease in labile pools from panicle initiation to harvesting stage in the WS. Soil labile C and soil enzymes can be used as an indicator of NEE, NEME, and GWP in lowland rice ecology.

Schematic presentation of GHG emission and energy exchange in lowland rice






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam, G., & Duncan, H. (2001). Development of a sensitive and rapid method for the measurement of total microbial activity using fluorescein diacetate (FDA) in a range of soils. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 33, 943–951.
Alberto, M. C. R., Wassmann, R., Hirano, T., Miyata, A., Kumar, A., Padre, & Amante, M. (2009). CO2/heat fluxes in rice fields: comparative assessment of flooded and non-flooded fields in the Philippines. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 149, 1737–1750.
Alberto, M. C. R., Wassmann, R., Hirano, T., Miyata, A., Hatano, R., Kumar, A., Padre, A., & Amante, M. (2011). Comparisons of energy balance and evapotranspiration between flooded and aerobic rice fields in the Philippines. Agricultural Water Management, 98, 1417–1430.
Alberto, M. C., Wassmann, R., Buresh, R. J., Quilty, J. R., Correa, T. Q., Sandro, J. M., & Centeno, C. A. (2014). Measuring methane flux from irrigated rice fields by eddy covariance method using open-path gas analyzer. Field Crops Research, 160, 12–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2014.02.008.
Aubinet, M., Grelle, A., Ibrom, A., Rannik, Ü., Moncrieff, J., Foken, T., Kowalski, A. S., Martin, P. H., Berbigier, P., Bernhofer, C., Clement, R., Elbers, J., Granier, A., Grün-wald, T., Morgenstern, K., Pilegaard, K., Rebmann, C., Snijders, W., Valentini, R., & Vesala, T. (2000). Estimates of the annual net carbon and water exchange of forests: the EUROFLUX methodology. Advances in Ecological Research, 30, 113–175.
Baldocchi, D. D. (2003). Assessing the eddy covariance technique for evaluating carbon dioxide exchange rates of ecosystems: past, present and future. Global Change Biology, 9(4), 479–492.
Bhatia, A., Pathak, H., Jain, N., Singh, P. K., & Singh, A. K. (2005). Global warming potential of manure amended soils under rice–wheat system in the Indo-Gangetic plains. Atmospheric Environment, 39(37), 6976–6984.
Bhatia, A., Ghosh, A., Kumar, V., Tomer, R., Singh, S. D., & Pathak, H. (2011). Effect of elevated tropospheric ozone on methane and nitrous oxide emission from rice soil in north India. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 144(1), 21–28.
Bhattacharyya, P., Roy, K. S., Neogi, S., Adhya, T. K., Rao, K. S., & Manna, M. C. (2012). Effects of rice straw and nitrogen fertilization on greenhouse gas emissions and carbon storage in tropical flooded soil planted with rice. Soil and Tillage Research, 124, 119–130.
Bhattacharyya, P., Nayak, A. K., Mohanty, S., Tripathi, R., Shahid, M., Kumar, A., & Dash, P. K. (2013a). Greenhouse gas emission in relation to labile soil C, N pools and functional microbial diversity as influenced by 39 years long-term fertilizer management in tropical rice. Soil and Tillage Research, 129, 93–105.
Bhattacharyya, P., Neogi, S., Roy, K. S., & Rao, K. S. (2013b). Gross primary production, ecosystem respiration and net ecosystem exchange in Asian rice paddy: an eddy covariance-based approach. Current Science, 104, 67–75.
Bhattacharyya, P., Neogi, S., Roy, K. S., Dash, P. K., Nayak, A. K., & Mohapatra, T. (2014). Tropical low land rice ecosystem is a net carbon sink. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 189, 127–135.
Campbell Scientific, Inc. (2009). Open path eddy covariance system operator’s manual (instruction manual). Canada: Campbell Scientific Corporation.
Casida Jr., L. E., Klein, D. A., & Santoro, T. (1964). Soil dehydrogenase activity. Soil Science, 98(6), 371–376.
Chapin, F. S., Woodwell, G. M., Randerson, J. T., Rastetter, E. B., Lovett, G. M., Baldocchi, D. D., et al. (2006). Reconciling carbon-cycle concepts, terminology, and methods. Ecosystems, 9(7), 1041–1050. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-005-0105-7.
Chatterjee, D., Mohanty, S., Guru, P. K., Swain, C. K., Tripathi, R., Shahid, M., Kumar, U., Kumar, A., Bhattacharyya, P., Gautam, P., & Lal, B. (2018). Comparative assessment of urea briquette applicators on greenhouse gas emission, nitrogen loss and soil enzymatic activities in tropical lowland rice. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 252, 178–190.
Crafts-Brandner, S. J., & Salvucci, M. E. (2000). Rubisco activase constrains the photosynthetic potential of leaves at high temperature and CO2. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 97(24), 13430–13435. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.230451497.
Cruz, F. T., Narisma, G. T., Villafuerte, M. Q., Chua, K. C., & Olaguera, L. M. (2013). A climatological analysis of the southwest monsoon rainfall in the Philippines. Atmospheric Research, 122, 609–616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2012.06.010.
Das, S. K., & Varma, A. (2011). Role of enzymes in maintaining soil health. In G. Shukla & A. Varma (Eds.), Soil enzymology, soil biology 22. Berlin: Springer.
Das, S., Ghosh, A., & Adhya, T. K. (2011). Nitrous oxide and methane emission from a flooded rice field as influenced by separate and combined application of herbicides bensulfuron methyl and pretilachlor. Chemosphere, 84(1), 54–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.02.055.
Datta, A., Nayak, D. R., Sinhababu, D. P., & Adhya, T. K. (2009). Methane and nitrous oxide emissions from an integrated rainfed rice–fish farming system of eastern India. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 129(1), 228–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2008.09.003.
Detto, M., Verfaillie, J., Anderson, F., Xu, L., & Baldocchi, D. (2011). Comparing laser-based open- and closed-path gas analyzers to measure methane fluxes using the eddy covariance method. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 151(10), 1312–1324.
Dlugokencky, E. J., Nisbet, E. G., Fisher, R., & Lowry, D. (2011). Global atmospheric methane: budget, changes and dangers. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 369(1943), 2058–2072. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2010.0341.
Eivazi, F., & Tabatabai, M. A. (1988). Glucosidases and galactosidases in soils. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 20(5), 601–606 https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-0717(88)90141-1.
Falge, E., Baldocchi, D., Olson, R., Anthoni, P., Aubinet, M., Bernhofer, C., Burba, G., Ceulemans, R., Clement, R., Dolman, H., & Granier, A. (2001). Gap filling strategies for defensible annual sums of net ecosystem exchange. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 107(1), 43–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-1923(00)00225-2.
Forster, P., Ramaswamy, V., Artaxo, P., Berntsen, T., Betts, R., Fahey, D. W, Haywood, J., Lean, J., Lowe, D.C., Myhre, G., & Nganga, J. (2007). Changes in atmospheric constituents and in radiative forcing. Chapter 2. In Climate change 2007. The physical science basis. http://www.ipcc.ch/pdf/assessment-report/ar4/wg1/ar4-wg1-chapter2.pdf.
Frankenberger, W., & Dick, W. A. (1983). Relationships between enzyme activities and microbial growth and activity indices in soil. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 47(5), 945–951. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1983.03615995004700050021x.
García-Orenes, F., Guerrero, C., Roldán, A., Mataix-Solera, J., Cerdà, A., Campoy, M., Zornoza, R., Bárcenas, G., & Caravaca, F. (2010). Soil microbial biomass and activity under different agricultural management systems in a semiarid Mediterranean agroecosystem. Soil and Tillage Research, 109(2), 110–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2010.05.005.
Government of India (GOI). (2014). All India report on number and area of operational holdings. New Delhi: Agriculture Census Division, Department of Agriculture & Co-Operation & Farmers Welfare. Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare.
Guo, J., & Zhou, C. (2007). Greenhouse gas emissions and mitigation measures in Chinese agroecosystems. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 142(2), 270–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2006.03.029.
Inubushi, K., Brookes, P. C., & Jenkinson, D. S. (1991). Soil microbial biomass C, N and ninhydrin-N in aerobic and anaerobic soils measured by the fumigation-extraction method. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 23(8), 737–741. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-0717(91)90143-8.
IPCC. (2007). Climate change 2007: the physical science basis, contribution of working group-I to the fourth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Joosten, H., & Clarke, D. (2002). Wise use of mires and peatlands. Background and principles including a framework for decision-making. Finland: International Mire Conservation Group and International Peat Society, p. 304.
Kirk, D.M. & Bickert, W.G. (2004). The use of biochemical methane potential tests to evaluate the digestibility of processed dairy manure. ASAE Annual Meeting (p.1). American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers. doi: https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.16776.
Kristensen, L., Mann, J., Oncley, S. P., & Wyngaard, J. C. (1997). How close is close enough when measuring scalar fluxes with displaced sensors? Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 14(4), 814–821. https://doi.org/10.1175/15200426(1997)014<0814:HCICEW>2.0.CO;2.
Kyaw, K. M., & Toyota, K. (2007). Suppression of nitrous oxide production by the herbicides glyphosate and propanil in soils supplied with organic matter. Soil Science & Plant Nutrition, 53(4), 441–447. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1747-0765.2007.00151.x.
Li, X., Gao, Z., Li, Y., & Tong, B. (2017). Comparison of sensible heat fluxes measured by a large aperture scintillometer and eddy covariance system over a heterogeneous farmland in east China. Atmosphere, 8(6), 101.
LICOR, Inc. (2011). Open path CO 2 /H 2 O gas analyzer instruction manual. Lincoln: LICOR Biosciences.
Ling, Z. H., Guo, H., Cheng, H. R., & Yu, Y. F. (2011). Sources of ambient volatile organic compounds and their contributions to photochemical ozone formation at a site in the Pearl River Delta, southern China. Environmental Pollution, 159(10), 2310–2319.
Liu, H. P., Peters, G., & Foken, T. (2001). New equations for sonic temperature variance and buoyancy heat flux with an omnidirectional sonic anemometer [J]. Boundary Layer Meteorology, 100, 459–468. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019207031397.
Liu, Q. H., Zhou, X. B., Yang, L. Q., Li, T., & Zhang, J. J. (2009). Effects of early growth stage shading on rice flag leaf physiological characters and grain growth at grain-filling stage. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 20(9), 2135–2141 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://doi.org/S1672630813601924.
Lu, Y., Watanabe, A., & Kimura, M. (2002). Contribution of plant-derived carbon to soil microbial biomass dynamics in a paddy rice microcosm. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 36(2), 136–142.
Maljanen, M., Hytönen, J., & Martikainen, P. J. (2001). Fluxes of N2O, CH4 and CO2 on afforested boreal agricultural soils. Plant and Soil, 231(1), 113–121. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010372914805.
Manna, M. C., Swarup, A., Wanjari, R. H., & Ravankar, H. N. (2007). Long-term effect of NPK fertiliser and manure on soil fertility and a sorghum–wheat farming system. Australian Journal of Experimental Agriculture, 47, 700–711. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4518-2.
Masseroni, D., Facchi, A., Romani, M., Chiaradia, E. A., Gharsallah, O., & Gandolfi, C. (2015). Surface energy flux measurements in a flooded and an aerobic rice field using a single eddy-covariance system. Paddy and Water Environment, 13(4), 405–424.
Matthews, R. B., Wassmann, R., Knox, J. W., & Buendia, L. V. (2000). Using a crop/soil simulation model and GIS techniques to assess methane emissions from rice fields in Asia. IV. Upscaling to national levels. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 58(1–3), 201–217. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009850804425.
Mauder, M. & Foken, T. (2011). Documentation and instruction manual of the eddy covariance software package TK3, Work Report University of Bayreuth, Dept. of Micrometeorology, ISSN: 1614-8916, pp. 46, 58.https://doi.org/ARBERG046.
McDermitt, D., Burba, G., Xu, L., Anderson, T., Komissarov, A., Riensche, B., Schedlbauer, J., Starr, G., Zona, D., Oechel, W., & Oberbauer, S. (2011). A new low-power, open-path instrument for measuring methane flux by eddy covariance. Applied Physics B: Lasers and Optics, 102(2), 391–405. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-010-4307-0.
McMillan, A., Goulden, M. L. & Tyler, S. C. (2007). Stoichiometry of CH4 and CO2 flux in a California rice paddy. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 112(G01008). https://doi.org/10.1029/2006JG000198.
Mitchell, P.L, Sheehy, J.E. & Woodward, F.I. (1998). Potential yields and the efficiency of radiation use in rice. IRRI Discussion Paper Ser. 32. IRRI, Manila, Philippines. https://doi.org/S0378429015001793.
Miyata, A., Leuning, R., Denmead, O. W., Kim, J., & Harazano, Y. (2000). Carbon dioxide and methane fluxes from an intermittently flooded paddy field. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 102, 287–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-1923(00)00092-7.
Nair, R., Juwarkar, A. A., Wanjari, T., Singh, S. K., & Chakrabarti, T. (2011). Study of terrestrial carbon flux by eddy covariance method in revegetated manganese mine spoil dump at Gumgaon, India. Climatic Change, 106, 609–619. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-010-9953-z.
Nannipieri, P., Grego, S., Ceccanti, B. (1990). Ecological significance of the biological activity in soil. In: Bollag JM, Stotzky G (eds) Soil biochemistry. Vol. 6, 293–355. doi https://doi.org/10.1016/19911950379.
Nayak, D. R., Babu, Y. J., & Adhya, T. K. (2007). Long-term application of compost influences microbial biomass and enzyme activities in a tropical Aeric Endoaquept planted to rice under flooded condition. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 39, 1897–1906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2007.02.003.
Neue, H. (1993). Methane emission from rice fields: wetland rice fields may make a major contribution to global warming. Bioscience, 43, 466–473 http://www.ciesin.org/docs/004-032/004-032.html.
Nisbet, R. E., Fisher, R., Nimmo, R. H., Bendall, D. S., Crill, P. M., Gallego-Sala, A. V., Hornibrook, E. R., López-Juez, E., Lowry, D., Nisbet, P. B., & Shuckburgh, E. F. (2009). Emission of methane from plants. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B: Biological Sciences., 276(1660), 1347–1354. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2008.1731.
Papale, D., & Valentini, R. (2003). A new assessment of European forests carbon exchanges by eddy fluxes and artificial neural network spatializaion. Global Change Biology, 9, 525–535. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2486.2003.00609.x.
Reichstein, M., Falge, E., Baldocchi, D., Papale, D., Aubinet, M., Berbigier, P., Bernhofer, C., Buchmann, N., Gilmanov, T., Granier, A., & Grünwald, T. (2005). On the separation of net ecosystem exchange into assimilation and ecosystem respiration: review and improved algorithm. Global Change Biology, 11, 1424–1439. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2005.001002.x.
Ren, W. J., Yang, W. Y., Xu, J. W., Fan, G. Q., Wang, L. Y., & Guan, H. (2002). Impact of low-light stress on leaves characteristics of rice after heading. Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University, 20(3), 205–208 http://dx.doi.org/285892666.
Ruimy, A., Jarvis, P. G., Baldocchi, D. D., & Saugier, B. (1995). CO2 fluxes over plant canopies and solar radiation: a review. Advances in Ecological Research, 26, 1–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2504(08)60063-X.
Saito, M., Miyata, A., Nagai, H., & Yamada, T. (2005). Seasonal variation of carbon dioxide exchange in rice paddy field in Japan. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 135(1), 93–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2005.10.007.
Santanello, J. A., & Friedl, M. A. (2003). Diurnal covariation in soil heat flux and net radiation. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 42, 851–862. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0450(2003)042<0851:DCISHF>2.0.CO2.
Sinclair, T. R., & Muchow, R. C. (1999). Radiation use efficiency. Advances in Agronomy, 65, 215–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2113(08)60914-1.
Smith, P., Lanigan, G., Kutsch, W. L., Buchmann, N., Eugster, W., Aubinet, M., Ceschia, E., Béziat, P., Yeluripati, J. B., Osborne, B., & Moors, E. J. (2010). Measurements necessary for assessing the net ecosystem carbon budget of croplands. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 139(3), 302–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2010.04.004.
Swain, C. K., Bhattacharyya, P., Singh, N. R., Neogi, S., Sahoo, R. K., Nayak, A. K., Zhang, G., & Leclerc, M. Y. (2016). Net ecosystem methane and carbon dioxide exchange in relation to heat and carbon balance in lowland tropical rice. Ecological Engineering, 95, 364–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.06.053.
Tanner, C.B. & Thurtell, GW. (1969). Anemoclinometer measurements of Reynolds stress and heat transport in the atmospheric surface layer. Wisconsin Univ-Madison Dept of Soil Science. http://dx.doi.org/AD0689487.
Tsai, J. L., Tsuang, B. J., & Lu, P. S. (2007). Surface energy components and land characteristics of a rice paddy. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 46, 1879–1900. https://doi.org/10.1175/2007JAMC1568.1.
Tseng, H. K., Tsai, L. J., Alagesan, A., Tsuang, J. B., Yao, H. M., & Kuo, H. P. (2010). Determination of methane and carbon dioxide fluxes during the rice maturity period in Taiwan by combining profile and eddy covariance measurements. Agriculture and Forest Meteorology, 150, 852–859. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2010.04.007.
Vance, E. D., Brookes, P. C., & Jenkinson, D. S. (1987). An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass carbon. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 19, 703–707. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-0717(87)90052-6.
Vickers, D., & Mahrt, L. (1997). Quality control and flux sampling problems for tower and aircraft data. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 14, 512–526. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0426(1997)014<0512:QCAFSP>2.0.CO;2.
Wassmann, R., Lantin, R. S., Neue, H. U., Buendia, L. V., Corton, T. M., & Lu, Y. (2000). Characterization of methane emissions from rice fields in Asia. III. Mitigation options and future research needs. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 58(1), 23–36.
Webb, E. K., Pearman, G. I., & Leuning, R. (1980). Correction of flux measurements for density effects due to heat and water vapour transfer. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 106, 85–100. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.49710644707.
Wilczak, J. M., Oncley, S. P., & Stage, S. A. (2001). Sonic anemometers tilt correction algorithms. Boundary Layer Meteorology, 99, 127–150. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018966204465.
Win, K. T., Nonaka, R., Win, A. T., Sasada, Y., Toyota, K., Motobayashi, T., & Hosomi, M. (2012). Comparison of methanotrophic bacteria, methane oxidation activity, and methane emission in rice fields fertilized with anaerobically digested slurry between fodder rice and a normal rice variety. Paddy and Water Environment, 10(4), 281–289. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-011-0279-x.
Witt, C., Gaunt, J. L., Galicia, C. C., Ottow, J. C. G., & Neue, H. U. (2000). A rapid chloroform fumigation–extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen in flooded rice soils, Biology and Fertility of Soils., 30, 510–519. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740050030.
Zheng, X., Han, S., Huang, Y., Wang, Y., & Wang, M. (2004). Re-quantifying the emission factors based on field measurements and estimating the direct N2O emission from Chinese croplands. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 18(2).
Funding
The work has been partially supported by a grant from the ICAR-NICRA project and NRRI. Part of the result is the finding for the doctorate degree of Mr. Chinmaya Kumar Swain. The authors are thankful to LICOR Inc., Campbell Scientific Corp. (Canada), and Elcome Technologies Pvt. Ltd. for their technical assistance and support during the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Swain, C.K., Nayak, A.K., Bhattacharyya, P. et al. Greenhouse gas emissions and energy exchange in wet and dry season rice: eddy covariance-based approach. Environ Monit Assess 190, 423 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6805-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6805-1