Abstract
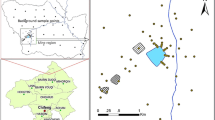
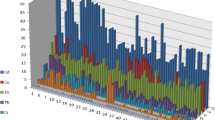
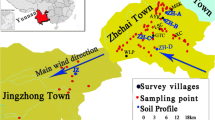
The environmental assessment and identification of sources of heavy metals in Zn-Pb ore deposits are important steps for the effective prevention of subsequent contamination and for the development of corrective measures. The concentrations of eight heavy metals (As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Hg, Ni, Pb, and Zn) in soils from 40 sampling points around the Jinding Zn-Pb mine in Yunnan, China, were analyzed. An environmental quality assessment of the obtained data was performed using five different contamination and pollution indexes. Statistical analyses were performed to identify the relations among the heavy metals and the pH in soils and possible sources of pollution. The concentrations of As, Cd, Pb, and Zn were extremely high, and 23, 95, 25, and 35% of the samples, respectively, exceeded the heavy metal limits set in the Chinese Environmental Quality Standard for Soils (GB15618-1995, grade III). According to the contamination and pollution indexes, environmental risks in the area are high or extremely high. The highest risk is represented by Cd contamination, the median concentration of which exceeds the GB15618-1995 limit. Based on the combination of statistical analyses and geostatistical mapping, we identified three groups of heavy metals that originate from different sources. The main sources of As, Cd, Pb, Zn, and Cu are mining activities, airborne particulates from smelters, and the weathering of tailings. The main sources of Hg are dust fallout and gaseous emissions from smelters and tailing dams. Cr and Ni originate from lithogenic sources.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahim, G. M. S. (2005). Holocene sediments of Tamaki estuary: Characterization and impact of recent human activity on an urban estuary in Auckland. Ph.D. thesis, University of Auckland.
Bai, J., Cui, B., Wang, Q., Gao, H., & Ding, Q. (2009). Assessment of heavy metal contamination of roadside soils in Southwest China. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment, 23, 341–347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-008-0219-5.
Brady, J. P., Ayoko, G. A., Martens, W. N., & Goonetilleke, A. (2015). Development of a hybrid pollution index for heavy metals in marine and estuarine sediments. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187, 306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4563-x.
Cai, L. M., Xu, Z. C., Qi, J. Y., Feng, Z. Z., & Xiang, T. S. (2015). Assessment of exposure to heavy metals and health risks among residents near Tonglushan mine in Hubei, China. Chemosphere, 127, 127–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.01.027.
Cheng, X., Qi, W., Danek, T., Matysek, D., Huang, Q., Zhao, X., Zhou, Z., Fang, R., Zou, L., & Xu, J. (2016). Heavy metal contamination of surface water and groundwater in and around Gejiu Tin Mine, Southwest China. Inzynieria Mineralna, 17, 93–98.
Håkanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Research, 14, 975–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8.
Hlavsová, A., Corsaro, A., Raclavská, H., Vallová, S., & Juchelková, D. (2016). The effect of feedstock composition and taxonomy on the products distribution from pyrolysis of nine herbaceous plants. Fuel Processing Technology, 144, 27–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2015.11.022.
Hong-Gui, D., Teng-Feng, G., Ming-Hui, L., & Xu, D. (2012). Comprehensive assessment model on heavy metal pollution in soil. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 7, 5286–5296.
Jung, M. C., & Thornton, I. (1996). Heavy metal contamination of soils and plants in the vicinity of a lead-zinc mine, Korea. Applied Geochemistry, 11, 53–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/0883-2927(95)00075-5.
Kříbek, B., Majer, V., Veselovský, F., & Nyambe, I. (2010). Discrimination of lithogenic and anthropogenic sources of metals and sulphur in soils of the central-northern part of the Zambian Copperbelt Mining District: a topsoil vs. subsurface soil concept. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 104, 69–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2009.12.005.
Li, J., Xie, Z. M., Zhu, Y. G., & Naidu, R. (2005). Risk assessment of heavy metal contaminated soil in the vicinity of a lead/zinc mine. Journal of Environmental Science, 17, 881–885.
Li, R. P., Wang, A. J., Cao, D. H., Wang, G. S., Li, Y. K., & Geng, N. (2008a). Geochemical characteristics of heavy metals in water bodies and sediments of the Bijiang River drainage area, Western Yunnan, China. Geological Bulletin of China, 27, 1071–1078.
Li, H., Xiao, T. F., Shuang, Y., He, L. B., Ning, Z. P., Li, D. H., & Zhu, C. S. (2008b). Geochemical distribution and environmental quality of cadmium in river sediment around the Jinding Pb-Zn mine area in Yunnan. Environmental Sciences, 29, 2894–2898.
Li, W. X., Zhang, X. X., Wu, B., Sun, S. L., Chen, Y. S., Pan, W. Y., Zhao, D. Y., & Cheng, S. P. (2008c). A comparative analysis of environmental quality assessment methods for heavy metal-contaminated soils. Pedosphere, 18, 344–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(08)60024-7.
Li, R. P., Wang, A. J., Cao, D. H., Gao, L., Geng, N., Zhao, Y. X., Zou, W. L., & Xiu, Q. Y. (2009a). Research on the distribution characteristics of Zn, Cd in the soil of Jinding Pb-Zn deposit, Lanping County. Geological Review, 55, 126–133.
Li, R. P., Wang, A. J., Cao, D. H., Geng, N., Gao, L., Zou, W. L., Zhao, Y. X., & Xiu, Q. Y. (2009b). Distribution of Pb in soils of the Jinding Pb-Zn deposit, Lanping, Yunnan Province. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 30, 72–78.
Li, J., He, M., Han, W., & Gu, Y. (2009c). Analysis and assessment on heavy metal sources in the coastal soils developed from alluvial deposits using multivariate statistical methods. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 164, 976–981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.08.112.
Li, R. P., Wang, A. J., Cao, D. H., Li, Y. K., & Wang, G. S. (2010). Distributing characteristics of heavy metal elements in the sediment profiles of Bijiang River, western Yunnan, China. Geological Bulletin of China, 29, 1383–1390.
Li, Z., Ma, Z., Van der Kuijp, T. J., Yuan, Z., & Huang, L. (2014a). A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: pollution and health risk assessment. Science of the Total Environment, 468-469, 843–853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.08.090.
Li, Y., Wang, H., Wang, H., Yin, F., Yang, X., & Hu, Y. (2014b). Heavy metal pollution in vegetables grown in the vicinity of a multi-metal mining area in Gejiu, China: total concentrations, speciation analysis, and health risk. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21, 12569–12582. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3188-x.
Li, J. G., Pu, L. J., Liao, Q. L., Zhu, M., Dai, X. Q., Xu, Y., Zhang, L. F., Hua, M., & Jin, Y. (2015). How anthropogenic activities affect soil heavy metal concentration on a broad scale: a geochemistry survey in Yangtze River Delta, Eastern China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 73, 1823–1835. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3536-7.
Lim, H. S., Lee, J. S., Chon, H. T., & Sager, M. (2008). Heavy metal contamination and health risk assessment in the vicinity of the abandoned Songcheon Au–Ag mine in Korea. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 96, 223–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2007.04.008.
Lin, Q., Liu, E., Zhang, E., Li, K., & Shen, J. (2016). Spatial distribution, contamination and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Erhai Lake, a large eutrophic plateau lake in southwest China. Catena, 145, 193–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2016.06.003.
Liu, X., Song, Q., Tang, Y., Li, W., Xu, J., Wu, J., Wang, F., & Brookes, P. C. (2013). Human health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil–vegetable system: a multi-medium analysis. Science of the Total Environment, 463-464, 530–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.06.064.
Ma, L., Sun, J., Yang, Z., & Wang, L. (2015). Heavy metal contamination of agricultural soils affected by mining activities around Ganxi River in Chenzou, southern China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187, 731. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4966-8.
Matschullat, J., Ottenstein, R., & Reimann, C. (2000). Geochemical background—can we calculate it? Environmental Geology, 39, 990–1000. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002549900084.
Meloun, M., & Militký, J. (2011). Statistical data analysis: a practical guide with 1250 exercises and answer key on CD (p. 124). Philadelphia: Woodhead Publishing India Pvt Ltd.
Nakić, Z., Posavec, K., & Bačani, A. (2007). A visual basic spreadsheet macro for geochemical background analysis. Groundwater, 45, 642–647. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.2007.00325.x.
Oliveira, S. M. B., de Moya Partiti, C. S., & Enzweiler, J. (2001). Ochreous laterite: a nickel ore from Punta Gorda, Cuba. Journal of South American Earth Sciences, 14, 307–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0895-9811(01)00026-8.
Potts, P. J. (1992). A handbook of silicate rock analysis (pp. 11–12). Boston, MA: Springer US.
Rieuwerts, J. S., Farago, M. E., Cikrt, M., & Bencko, V. (2000). Differences in lead bioavailability between a smelting and a mining area. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 122, 203–229. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005251527946.
Rodríguez, L., Ruiz, E., Alonso-Azcárate, J., & Rincón, J. (2009). Heavy metal distribution and chemical speciation in tailings and soils around a Pb–Zn mine in Spain. Journal of Environmental Management, 90, 1106–1116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2008.04.007.
Schwertmann, U., & Pfab, G. (1996). Structural vanadium and chromium in lateritic iron oxides: genetic implications. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 60, 4279–4283. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7037(96)00259-1.
Sekabira, K., Origa, H. O., Basamba, T. A., Mutumba, G., & Kakudidi, E. (2010). Heavy metal assessment and water quality values in urban stream and rain water. Environmental Science & Technology, 7, 759–770. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326185.
Singovszka, E., Balintova, M., & Holub, M. (2016). Heavy metal contamination and its indexing approach for sediment in Smolnik creek (Slovakia). Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy, 18, 305–313. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-015-0991-0.
Tang, Y., Bi, X., Yin, R., Feng, X., & Hu, R. (2017). Concentrations and isotopic variability of mercury in sulfide minerals from the Jinding Zn-Pb deposit, Southwest China. Ore Geology Reviews (in press), 90, 958–969. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.12.009.
Wang, L. H., Jiao, Y. M., Ming, Q. Z., He, L. L., & Zhou, H. B. (2009). Evaluation of heavy metal pollution in Bijiang Basin in Yunnan Province. Research of Environmental Sciences, 22, 595–606.
Wang, Q., Feng, Y. M., Wang, S. M., Du, Y. Q., Yin, J. Z., & Yang, Y. L. (2015). Assessment of the cadmium exposure in the blood, diet, and water of the Pumi people in Yunnan, China. Biological Trace Element Research, 168, 349–355. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0452-y.
Wei, C., Wang, C., & Yang, L. (2009). Characterizing spatial distribution and sources of heavy metals in the soils from mining-smelting activities in Shuikoushan, Hunan Province, China. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 21, 1230–1236. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62409-2.
Wen, H., Zhang, Y., Cloquet, C., Zhu, C., Fan, H., & Luo, C. (2015). Tracing sources of pollution in soils from the Jinding Pb–Zn mining district in China using cadmium and lead isotopes. Applied Geochemistry, 52, 147–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2014.11.025.
Wu, Q., Leung, J. Y. S., Geng, X., Chen, S., Huang, X., Li, H., Huang, Z., Zhu, L., Chen, J., & Lu, Y. (2015). Heavy metal contamination of soil and water in the vicinity of an abandoned e-waste recycling site: Implications for dissemination of heavy metals. Science of the Total Environment, 506-507, 217–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.10.121.
Xue, C., Zeng, R., Liu, S., Chi, G., Qing, H., Chen, Y., Yang, J., & Wang, D. (2007). Geologic, fluid inclusion and isotopic characteristics of the Jinding Zn-Pb deposit, western Yunnan, South China: A review. Ore Geology Reviews, 31, 337–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2005.04.007.
Yan, Y. (1998). Back-ground value research of the soil environment of Jinding district in Lanping County. Yunnan Environmental. Science, 17, 15–17.
Yang, Y., Li, S., Bi, X., Wu, P., Liu, T., Li, F., & Liu, C. (2010). Lead, Zn, and Cd in slags, stream sediments, and soils in an abandoned Zn smelting region, southwest of China, and Pb and S isotopes as source tracers. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 10, 1527–1539. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-010-0253-z.
Yi, Q., Dou, X. D., Huang, Q. R., & Zhao, X. Q. (2012). Pollution characteristics of Pb, Zn, As, Cd in the Bijiang River. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 13, 43–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2012.01.004.
Zhang, C., Wu, L., Luo, Y., Zhang, H., & Christie, P. (2008). Identifying sources of soil inorganic pollutants on a regional scale using a multivariate statistical approach: role of pollutant migration and soil physicochemical properties. Environmental Pollution, 151, 470–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2007.04.017.
Zhang, X., Yang, L., Li, Y., Li, H., Wang, W., & Ye, B. (2012). Impacts of lead/zinc mining and smelting on the environment and human health in China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184, 2261–2273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2115-6.
Zhang, J., Deng, H., Wang, D., Chen, Z., & Xu, S. (2013). Toxic heavy metal contamination and risk assessment of street dust in small towns of Shanghai suburban area, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20, 323–332. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-0908-y.
Zheng, N., Wang, Q., & Zheng, D. (2007). Health risk of Hg, Pb, Cd, Zn, and Cu to the inhabitants around Huludao Zinc Plant in China via consumption of vegetables. Science of the Total Environment, 383, 81–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.05.002.
Zhong, T., Chen, D., & Zhang, X. (2016). Identification of potential sources of mercury (Hg) in farmland soil using a decision tree method in China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 13, 1111. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13111111.
Acknowledgements
All sources of funding of the study should be disclosed. Please clearly indicate grants that you have received in support of your research work. Clearly state if you received funds for covering the costs to publish in open access. Financial support from the Department of Land Resources of Yunnan Province of China (Grant No.Yun Land Resources Scientific 2013-1) is gratefully acknowledged. This publication has been financially supported by the Moravian-Silesian Region within the project Support of VŠB-TUO activities with China. We are particularly grateful to Lanping County Land Resources Bureau and Yunnan Jinding Zinc Industry Limited Company for help with field work. This paper was prepared within the framework of the project LO1404: Sustainable development of ENET Centre.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, X., Danek, T., Drozdova, J. et al. Soil heavy metal pollution and risk assessment associated with the Zn-Pb mining region in Yunnan, Southwest China. Environ Monit Assess 190, 194 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6574-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6574-x