Abstract
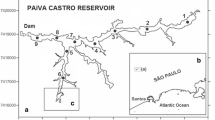
Depending on the environmental conditions, surface sediments can retain all the contaminants present and provide a record of the anthropic activities affecting the aquatic environment. In order to analyze the impacts on reservoirs, surface sediments were collected in three characteristic regions (riverine, transitional, and limnetic zones) of seven reservoirs in São Paulo State, Brazil. Analyses were made of grain size, organic matter (OM), total phosphorus (TP), and total nitrogen (TN). Inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES) was used to determine pseudo-total and bioavailable metals (Cu, Cd, Cr, Ni, Pb, Zn, Mn, Fe, and Al). A Horiba probe was used to measure dissolved oxygen (DO), pH, redox potential (ORP), and temperature (Temp) in the bottom water. The data were analyzed using multivariate statistics. Enrichment factors (EF), pollution load index values (PLI), and background values (BG) were also determined in order to evaluate the potential toxicity. Intra-reservoir and inter-reservoir spatial heterogeneity (p < 0.05) were observed using two-way analysis of similarities. Principal component analysis indicated greater influence of metals in the Barra Bonita, Salto Grande, and Rio Grande reservoirs, corroborating the PLI, EF, and BG data. Bioavailable Cu was found in the Rio Grande reservoir, possibly associated with copper sulfate used to control algal blooms, while bioavailable Ni in the Barra Bonita reservoir was attributed to the presence of industrial wastes and natural geology. The bottom water conditions indicated that the metals remained in insoluble forms.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnason, J. G., & Fletcher, B. A. (2003). A 40+ year record of Cd, Hg, Pb, and U deposition in sediments of Patroon Reservoir, Albany County, NY, USA. Environmental Pollution, 123(3), 383–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(03)00015-0.
Becker, V., Caputo, L., Ordóñez, J., Marcé, R., Armengol, J., Crossetti, L. O., & Huszar, V. L. M. (2010). Driving factors of the phytoplankton functional groups in a deep Mediterranean reservoir. Water Research, 44(11), 3345–3354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.03.018.
Beghelli, F. G. S., Frascareli, D., Pompeo, M. L. M., & Moschini-Carlos, V. (2016). Trophic state evolution over 15 years in a tropical reservoir with low nitrogen concentrations and cyanobacteria predominance. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 227, 94.
Belluta, I., Jesus, S. A. D. E., Vieira, M. P., Corrêa, N. M., Rall, V. L. M., & Valente, J. P. S. (2016). Water quality, organic loading and nutrient loading in the Mouth of Cascata Brook: the subbasin contribution to Barra Bonita Reservoir (Tietê River—São Paulo (Brazil)). Journal Brazilian of Physical Geography, 9, 305–318.
Bing, H., Zhou, J., Wu, Y., Wang, X., Sun, H., & LI, R. (2016). Current state, sources, and potential risk of heavy metals in sediments of Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Environmental Pollution, 214, 485–496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.04.062.
Burger, D. F., Hamilton, D. P., Pilditch, C. A., & Gibbs, M. M. (2007). Benthic nutrient fluxes in a eutrophic, polymictic lake. Hydrobiologia, 584(1), 13–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-007-0582-0.
Buzelli, G. M., & Cunha-Santino, M. B. D. (2013). Diagnosis and analysis of water quality and trophic state of Barra Bonita reservoir, SP. Journal Environmental & Water, 8(1), 186–205.
Cardoso-Silva, S., Nishimura, P. Y., Padial, P. R., Mariani, C. F., Moschini-Carlos, V., & Pompêo, M. L. M. (2014). Compartmentalization and water quality: billings reservoir case. Bioikos, Campinas, 28, 31–43.
Cardoso-Silva, S., Ferreira, P. A. L., Moschini-Carlos, V., Figueira, R. C. L., & Pompeo, M. L. M. (2016a). Temporal and spatial accumulation of heavy metals in the sediments at Paiva Castro Reservoir (São Paulo, Brazil). Environmental Earth Sciences, 75, 1–16.
Cardoso-Silva, S., Silva, D. C. V. R., Lage, F., Rosa, A. H., Moschini-Carlos, V., & Pompeo, M. L. M. (2016b). Metals in sediments: bioavailability and toxicity in a tropical reservoir used for public water supply. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment (Dordrecht. Online), 188, 310.
Carlson, R. E. (1977). A trophic state index for lakes. Limnology and Oceanography., 22, 261–269.
CCME, Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment. (1999). Canadian sediment quality guidelines for the protection of aquatic life—protocol for the derivation of Canadian Sediment Quality Guidelines for the Protection of Aquatic Life (CCME EPC-98E). 35 p.
Chapman, P. M., Wang, F., Adams, W. J., & Green, A. (1999). Appropriate applications of sediment quality values for metals and metalloids. Environmental Science & Technology, 33, 3937–3941.
CIS—Common Implementation Strategy for The Water Framework Directive (2000/ 60/EC) (2000). Guidance on typology, reference conditions and classification systems for transitional and coastal waters, 119 p.
Cole, G. A. (1994). Textbook of limnology. Illinois: Waveland Press Inc., Prospect Heights.
Depaula, F. C., & Mozeto, A. A. (2001). Biogeochemical evolution of trace elements in a pristine watershed in the Brazilian southeastern coastal region. Applied Geochemistry, 16(9), 1139–1151. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-2927(00)00084-6.
Di Toro, D. M., Mahony, J. D., Hansen, D. J., Scott, K. J., Hicks, M. B., Mayr, S. M., & Redmon, M. S. (1990). Toxicity of cadmium in sediments: the role of acid volatile sulfide. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 9(12), 1487–1502. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620091208.
Díez, E. G., Corella, J. P., Adatte, T., Thevenon, F., & Loizeau, J. L. (2017). High-resolution reconstruction of the 20th century history of trace metals, major elements, and organic matter in sediments in a contaminated area of Lake Geneva, Switzerland. Applied Geochemistry, 78, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2016.12.007.
Dornfeld, C. B.; Espindola, E.L.G.; Leite, M. A.; Nogueira, A.M. (2001). Acute toxicity bioassays with sediment from the Salto Grande reservoir (Americana, SP, Brazil) using Daphnia similis and Chironomus xanthus.In: IV Reunión Anual de SETAC Latinoamérica Oportunidades para la protección ambiental en América Latina, 2001, Buenos Aires. IV Reunión Anual de SETAC Latinoamérica Oportunidades para la protección ambiental en América Latina.
Dornfeld, C. B., Espindola, E. L. G., & Leite, M. A. (2005). Evaluation of eutrophication and its relationship with Chironomidae in the Atibaia river and Salto Grande reservoir (Americana, SP—Brazil). Journal Brazilian of Water Resources, Porto Alegre—RS, 10, 53–62.
Eaton, A. D., Clesceri, L. S., Rice, E. W., Greenberg, A. E., & Franson, M. A. H. A. (2005). APHA: standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. Washington, DC: Centennial Edition., APHA, AWWA, WEF.
Fagnani, E., Guimarães, J. R., Mozeto, A. A., & Fadini, P. S. (2011). Acid volatile sulfides and simultaneously extracted metals in the assessment of freshwater sediments. New Chemistry, 34, 1618–1628.
Flemming, C. A., & Trevors, J. T. (1989). Copper toxicity and chemistry in the environment: a review. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 44(1–2), 143–158. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00228784.
Fonseca, M. F., & Matias, L. F. (2014). Analysis of earth and clinographic component use by geoprocessment: the environment of Salto Grande—SP reservoir. Geography Bulletin, 32(3), 48–60.
Förstner, U. E., & Wittman, G. T. W. (1983). Metal pollution in aquatic environment (484p). Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
Frascareli, D., de Souza Beghelli, F. G., Da Silva, S. C., & Moschini-Carlos, V. (2015). Spatial and seasonal heterogeneity of limnological variables in Itupararanga reservoir associated with the land use in the Bacia do Alto Sorocaba-SP. Journal Enviromental & Water, 10, 771–781.
Gao, Q., Li, Y., Cheng, Q., Yu, M., Hu, B., Wang, Z., & Yu, Z. (2016). Analysis and assessment of the nutrients, biochemical indexes and heavy metals in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China, from 2008 to 2013. Water Research, 92, 262–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.12.055.
Hammer, Ø., Dat, H., & Ryan, P. D. (2001). PAST: paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol Electron, 4(1), 9.
He, Y., Men, B., Yang, X., Li, Y., Xu, H., & Wang, D. (2017). Investigation of heavy metals release from sediment with bioturbation/bioirrigation. Chemosphere.
Huszar, V. L. M., Silva, L. H. S., Marino, M., Domingos, P., Sant’Anna, C. L. (2000). Cyanoprokaryote assemblages in eight productive tropical Brazilian waters. In: The Trophic Spectrum Revisited (pp. 67–77). Netherlands: Dordrecht.
INAG, I.P 2009. Manual para a avaliação da qualidade biológica da água. Protocolo de amostragem e análise para o Fitoplâncton. Ministério do Ambiente, do Ordenamento do Território e do Desenvolvimento Regional. Instituto da Água, I.P.
Iqbal, J., Saleem, M., & Shah, M. H. (2016). Spatial distribution, environmental assessment and source identification of metals content in surface sediments of freshwater reservoir, Pakistan. Chemie der Erde, 76, 171–177.
Jain, C. K., Malik, D. S., & Yadav, R. (2007). Metal fractionation study on bed sediments of Lake Nainital, Uttaranchal, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 130(1-3), 129–139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-9383-6.
Kimmel, B.L., Lind, O.T., Paulson, L.J. (1990). Reservoir primary production In: Thornton, K.W., Kimmel, B.L. & Payne, F.E. (Eds.), Reservoir limnology: ecological perspectives. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Lamparelli, M. C. (2004). Trophic status in São Paulo state water bodies evaluation of monitoring methodologies. 238f. Doctoral thesis (phD in ecology apply)—São Paulo University, Institute of Biosciences, São Paulo.
Landajo, A., Arana, G., De Diego, A., Etxebarria, N., Zuloaga, O., & Amouroux, D. (2004). Analysis of heavy metal distribution in superficial estuarine sediments (estuary of Bilbao, Basque Country) by open-focused microwave-assisted extraction and ICP-OES. Chemosphere, 56(11), 1033–1041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.06.005.
Legendre, P., & Legendre, L. (1998). Numerical ecology (p. 853). Amsterdam: Elsevier Science.
Leite, M. A., Espindola, E. L. G., & Dornfeld, C. B. (2004). Quantification of metals in the water of the Salto Grande Reservoir (Americana, SP). In E. L. G. Espindola, M. A. Leite, & C. B. Dornfeld (Eds.), Salto Grande reservoir (Americana, SP): characterization, impacts and management proposals (pp. 55–70). São Carlos: Rima Editora.
Li, H., Song, C. L., Cao, X. Y., & Zhou, Y. Y. (2016). The phosphorus release pathways and their mechanisms driven by organic carbon and nitrogen in sediments of eutrophic shallow lakes. Science of the Total Environment, 572, 280–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.07.221.
Mariani, C. F., & Pompêo, M. (2008). Potentially bioavailable metals in sediment from a tropical polymictic environment, Rio Grande Reservoir, Brazil. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 8(5), 284–288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-008-0018-0.
Mayer, T., Rosa, F., Mayer, R., & Charlton, M. (2006). Relationship between the sediment geochemistry and phosphorus fluxes in a Great Lakes coastal marsh, Cootes Paradise, ON, Canada. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution: Focus, 6(5–6), 495–503. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11267-006-9033-6.
Meguro, M. (2000). Ecology methods. São Paulo. Methodology handbook for BIE discipline—321. Institute of Biosciences, USP, 117.
Moschini-Carlos, V., Bortolli, S., Pinto, E., Nishimura, P. Y., Freitas, L. G., Pompêo, M. L. M., & Dorr, F. (2009). Cyanobacteria and cyanotoxin in the Billings Reservoir (São Paulo, SP, Brazil). Limnetica, 28(2), 227–236.
Mozeto, A. A., Yamada, T. M., Morais, C. R., Nascimento, M. R. L., Fadini, P. S., Torres, R. J., Sueitt, A. P. E., & Faria, B. M. (2014). Assessment of organic and inorganic contaminants in sediments of an urban tropical eutrophic reservoir. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 186(2), 815–834. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3419-5.
Navarro, E., Bacardit, M., Caputo, L., Palau, T., & Armengol, J. (2006). Limnological characterization and flow patterns of a three-coupled reservoir system and their influence on Dreissena polymorpha populations and settlement during the stratification period. Lake and Reservoir Management, 22(4), 293–302. https://doi.org/10.1080/07438140609354363.
Oksanen, J., F. Guillaume Blanchet, Roeland Kindt, Pierre Legendre, R. B. O'hara, G.L. Simpson, P. Solymos, M. H. H. Stevens, Helene Wagner. (2011). vegan: Community ecology package. R package version 1.17–6. http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan.
Piper, C. S. (1947). Soil and plant analysis. New York: Interscience Publishers.
Pompêo, M. L. M., & Moschini-Carlos, V. (2003). Aquatic macrophytes and periphyton: ecological and methodological aspects. São Carlos: RiMa.
Pompêo, M., Padial, P. R., Mariani, C. F., Cardoso-Silva, S., Moschini-Carlos, V., da Silva, D. C. V. R., Paiva, T. C., Brazil, D. E., & Brandimarte, A. L. (2013). Bioavailability of metals in the sediment of an urban tropical reservoir (Guarapiranga reservoir—São Paulo, Brazil): is there potential toxicity and spatial heterogeneity? Geochimica Brasiliensis., 27(2), 104–119. https://doi.org/10.5327/Z0102-9800201300020003.
Pompêo, M., Gonçalves, P. K., Moschini-Carlos, V., Cardoso-Silva, S., de Lucia Lobo, F., do Amaral Meirinho, P., Bitencourt, M. D., & Meirelles, S. T. (2015a). Spatial horizontal heterogeneity of quality water in Rio Grande reservoir, Billings Complex, São Paulo, Brasil. In M. Pompêo, V. Moschini-Carlos, P. Y. Nishimura, S. Cardoso-Silva, & J. C. López-Doval (Eds.), Ecology of reservoir and interfaces (Vol. 1, 1ed ed., pp. 82–95). São Paulo: Institute of Biosciences.
Pompêo, M.; Ruiz, J.P.C.; Moschini-Carlos, V.; Marcé, R.; Nishimura, P.Y.; Armengol, J.; López, P. (2015b). Chemical elements in superficial sediments of five reservoirs in the catalonia and aragon regions (Spain): is there an anthropogenic contribution? In: Pompêo, M., Moschini-Carlos, V., Nishimura, P.Y., Cardoso-Silva, S., López-Dorval, J. (Eds.), Ecologia de reservatórios e interfaces.
Rodgher, S., Espíndola, E. L. G., Rocha, O., Fracácio, R., Pereira, R. H. G., & Rodrigues, M. H. S. (2005). Limnological and ecotoxicological studies in the cascade of reservoirs in the Tietê river (São Paulo, Brazil). Brazilian Journal of Biology, 65(4), 697–710. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1519-69842005000400017.
Sauvé, S., Cook, N., Hendershot, W. H., & Mcbride, M. B. (1996). Linking plant tissue concentrations and soil copper pools in urban contaminated soils. Environmental Pollution, 94(2), 153–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(96)00081-4.
Sevindik, T. O., Çelik, K., & Naselli-Flores, L. (2017). Spatial heterogeneity and seasonal succession of phytoplankton functional groups along the vertical gradient in a mesotrophic reservoir. Annales de Limnologie-International Journal of Limnology, 53, 129–141 EDP Sciences.
Sisinno, C. L., & Moreira, J. C. (1996). Evaluation of contamination and environmental pollution in the area of influence of the controlled landfill of Morro do Céu, Niterói, Brazil. Handbook Public Health, 12(4), 515–523.
Smith, W. S., Espindola, E. L. G., & Rocha, O. (2014). Environmental gradient in reservoirs of the medium and low Tietê River: limnological differences through the habitat sequence. Acta Limnological Brasiliensia Rio Claro, 26, 73–88.
SNIS - Sistema Nacional de Informação sobre Saneamento (2016) Diagnóstico dos serviços de água e esgoto de 2016. Available in: http://www.snis.gov.br/diagnostico-agua-e-esgotos/154-diagnostico-ae-2016 Accessed 15 Feb 2016 .
Soares, M. C. S., Marinho, M. M., Huszar, V. L., Branco, C. W., & Azevedo, S. M. (2008). The effects of water retention time and watershed features on the limnology of two tropical reservoirs in Brazil. Lakes & Reservoirs: Research & Management, 13(4), 257–269. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1770.2008.00379.x.
Søndergaard, M., Jensen, J. P., & Jeppesen, E. (1999). Internal phosphorus loading in shallow Danish lakes. In: Hydrobiologia, 408(409), 145–152.
Souza, V. A., & Wasserman, J. C. (2015). Distribution of heavy metals in sediments of a tropical reservoir in Brazil: sources and fate. Journal of South American Earth Sciences, 63, 208–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsames.2015.07.014.
Sundaray, S. K., Nayak, B. B., Lin, S., & Bhatta, D. (2011). Geochemical speciation and risk assessment of heavy metals in the river estuarine sediments—a case study: Mahanadi basin, India. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 186(2-3), 1837–1846. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.12.081.
Superville, P. J., Prygiel, E., Mikkelsen, O., & Billon, G. (2015). Dynamic behaviour of trace metals in the Deûle River impacted by recurrent polluted sediment resuspensions: from diel to seasonal evolutions. Science of the Total Environment, 506, 585–593.
Sutherland, R. A. (2000). Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu. Hawaii. Enviromental Geology, 39(6), 611–627. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002540050473.
Thornton, K. W., Kimmel, B. L., & Payne, F. E. (1990). Perspectives on reservoir limnology. In K. W. Thornton, B. L. Kimmel, & F. E. Payne (Eds.), Reservoir limnology: ecological perspectives. New York: Wiley-Interscience.
Tomlinson, D. L., Wilson, J. G., Harris, C. R., & Jeffrey, D. W. (1980). Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgoländer Meeresuntersuchungen, 33(1), 566–575. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02414780.
Tundisi, J. G., Matsumura-Tundisi, T., Tundisi, J. E. M., Blanco, F. P., Abe, D. S., Contri Campanelli, L., Sidagis-Galli, G. A., Silva, V., & Lima, C. P. P. (2015). A bloom of cyanobacteria (Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii) in UHE Carlos Botelho (Lobo/Broa) reservoir: a consequence of global change? Brazilian Journal of Biology, 75(2), 507–508. https://doi.org/10.1590/1519-6984.24914.
Tzoraki, O., Karaouzas, I., Patrolecco, L., Skoulikidis, N., & Nikolaidis, N. P. (2015). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and heavy metal occurrence in bed sediments of a temporary river. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 226(12), 1–19.
US EPA (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency) (2016). Table of Regulated Drinking Water Contaminants. Regulated drinking water contaminants. Dados online, 2016. Acessado em: 01 de setembro de 2016. Disponível em: https://www.epa.gov/ground-water-and-drinking-water/table-regulated-drinking-water-contaminants#Inorganic.
US EPA, United States Environmental Protection Agency (2005). Procedure for the derivation of Equilibrium Partitioning Sediment Benchmarks (ESBs) for the protection of benthic organisms: metal mixtures (cadmium, cooper, lead, nickel, silver and zinc. Office of Research and Development. Washington, D. C.: (EPA-600-R-02-011).121.
US EPA United States Environmental Protection Agency. Method 3050B (1996). Acid digestion of sediments, sludges and soil. Revision 2. December.
Wang, G., Yinglan, A., Jiang, H., Fu, Q., & Zheng, B. (2015). Modeling the source contribution of heavy metals in surficial sediment and analysis of their historical changes in the vertical sediments of a drinking water reservoir. Journal of Hydrology, 520, 37–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.11.034.
Wei, G., Yang, Z., Cui, B., Li, B., Chen, H., Bai, J., & Dong, S. (2009). Impact of dam construction on water quality and water self-purification capacity of the Lancang River, China. Water Resources Management, 23(9), 1763–1780. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-008-9351-8.
Wengrat, S., Bicudo, D., & De, C. (2011). Spatial evaluation of water quality in an urban reservoir (Billings Complex, southeastern Brazil). Acta Limnological. Brasiliensia, Rio Claro, 23(2), 200–216.
Wetzel, R. G. (2001). Limnology: lake and river ecosystems, 3rd ed. San Diego: Gulf professional publishing, Academic Press.
Wetzel, R. G., & Likens, G. E. (1991). Limnological analyses. New York: Springer-Verlag. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4757-4098-1.
Zahra, A., Hashmi, M. Z., Malik, R. N., & Ahmed, Z. (2014). Enrichment and geo-accumulation of heavy metals and risk assessment of sediments of the Kurang Nallah—feeding tributary of the Rawal Lake reservoir, Pakistan. Science of the Total Environment, 470-471, 925–933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.10.017.
Zhang, Z., Juying, L., & Mamat, Z. (2016). Sources identification and pollution evaluation of heavy metals in the surface sediments of Bortala River, Northwest China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 126, 94–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.12.025.
Zhu, L., Liu, J., Xu, S., & Xie, Z. (2017). Deposition behavior, risk assessment and source identification of heavy metals in reservoir sediments of Northeast China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 142, 454–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.04.039.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 338 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frascareli, D., Cardoso-Silva, S., de Oliveira Soares-Silva Mizael, J. et al. Spatial distribution, bioavailability, and toxicity of metals in surface sediments of tropical reservoirs, Brazil. Environ Monit Assess 190, 199 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6515-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6515-8