Abstract
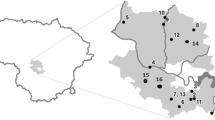
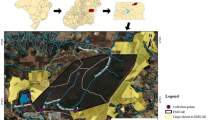
Pig farming is one of the human activities carried out to meet the increasing food demand by the increasing population. South Brazil is the region with most intensive pig farming in the country, exerting pressure on the water and soil environments by the relevant pollutant emissions. Therefore, the main objective of this work was to assess pig farming pollution by monitoring superficial water qualities of the Taquari-Antas Watershed in South Brazil. The study area is about 8062 km2 (south latitude 292,614, 282,624 and west longitude 520,802, 504,554). In 2014, there were 861 pig farmers and 739,858 animals were slaughtered. Samples were collected bimonthly from 13 spots during 2 years of monitoring. The main analysis included the determination of the water quality index (WQI)—a nine physicochemical and microbiological parameter index—and the trophic state index (TSI), which gives a trophic degree based on phosphorous and chlorophyll-α concentration to assess the impacts of the pig farming on superficial water of the region. The results suggest that the regions with high concentration of finishing stage farms present a higher risk to water quality. A distance of 4 km between different spots was enough to detect a significant decrease in the WQI. The WQI was found ranging from “regular” to “good” (62.77 and 78.95). The TSI were found to be mesotrophic at every spot during the entire period of the study.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Public Health Association – APHA (2012). Standard methods for the examination of water & wastewater (22 ed.). São Paulo: APHA. Pharmabooks.
Arbat, G., Roselló, A., Domingo Olivé, F., Puig-Bargués, J., Gozález Llinás, E., Duran-Ros, M., Pujol, J., & Ramírez de Cartagena, F. (2012). Soil water and nitrate distribution under drip irrigated corn receiving pig slurry. Agricultural Water Management, 120, 11–22.
Awad, Y. M., Kim, S. C., Abd El-Azeem, S. A. M., Kim, K. H., Kim, K. R., Kim, K., Jeon, C., Lee, S. S., & Ok, Y. S. (2014). Veterinary antibiotics contamination in water, sediment and soil near a swine manure composting facility. Environmental Earth Science, 71, 1433–1440.
Bernet, N., & Béline, F. (2009). Challenges and innovations on biological treatment of livestock effluents. Bioresource Technology, 100, 5431–5436.
Bonanno, G., & Giudice, R. L. (2010). Application of two quality indices as monitoring and management tools of rivers. Case study: the Imera Meridionale River, Italy. Environmental Management, 45, 856–867.
Brazil. Ministry of Environment. National Environment Council. (2005). Resolution 357. Provisions for the classification of environmental directives for the framing of superficial water bodies as well as for the establishment of conditions and standards related to releases into effluents. Brasília – DF.
Brazil. Ministry of Planning, Budget and Management. Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics. (2016). Indicadores de produção pecuária – Março/2016 [Livestock Production Index – March/2016].
Candelise, C., Speirs, J. F., & Gross, R. J. K. (2012). Materials availability for thin film (TF) PV technologies development: a real concern? Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 15, 4972–4981.
Carra, S. H. Z. (2015). Pegada hídrica da atividade suinícola na região do Corede Serra [Waterfootprint of pig farmers in Corede Serra region]. Dissertation (Master). Universidade de São Paulo (USP). Retrieved from:https://repositorio.ucs.br/xmlui/bitstream/handle/11338/1054/Dissertacao%20Sofia%20Helena%20Zanella%20Carra.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y. Acessed Aug 2016.
Cherubini, E., Zanghelini, G. M., Alvarenga, R. A. F., Franco, D., & Soares, S. R. (2015). Life cycle assesment of swine production in Brazil: a comparison of four manure management systems. Journal of Cleaner Production, 87, 68–77.
Fridrich, B., Krcmar, D., Dalmacija, B., Molnar, J., Pesic, V., Kragulj, M., & Varga, N. (2014). Impact of wastewater from pig farm lagoons on the quality of local groundwater. Agricultural Water Management, 135, 40–53.
Gallay, A., de Valk, H., Cournot, M., Ladeuil, B., Hemery, C., Castor, C., Bon, F., Mégraud, F., le Cann, P., & Desenclos, J. C. (2006). A large multi-pathogen waterborne community outbreak linked to faecal contamination of a groundwater system, France, 2000. Clinical Microbiology and Infection, 12, 561–570.
Godfray, H. C. J., Beddington, J. R., Crute, I. R., Haddad, L., Lawrence, D., Muir, J. F., Pretty, J., Robinson, S., Thomas, S. M., & Toulmin, C. (2010). Food security: the challenge of feeding 9 billion people. Science, 327(5967), 812–818.
Haberl, H., Erb, K., Krausmann, F., Running, S., Searchinger, T. D., & Kolby Smith, W. (2013). Bioenergy: how much can we expect for 2050? Environmental Research Letters, 8, 31004–31008.
Hayes-Labruto, L., Schillebeeckx, S. J. D., Workman, M., & Shah, N. (2013). Contrasting perspectives on China’s rare earths policies: reframing the debate through a stakeholder lens. Energy Policy, 63, 55–68.
Holman, I. P., Howden, N. J. K., Bellamy, P., Willby, N., Whelan, M. J., & Rivas-Casado, M. (2010). An assessment of the risk to surface water ecosystems of groundwater P in the UK and Ireland. Science of the Total Environment, 408, 1847–1857.
Jha, D. K., Devi, M. P., Vidyalakshmi, R., Brindha, B., Vinithkumar, N. V., & Kirubagaran, R. (2015). Water quality assessment using water quality index and geographical information system methods in the coastal waters of Andaman Sea, India. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 100(1), 555–561.
Kalavathy, S., Sharma, T. R., & Sureshkumar, P. (2011). Water quality index of river Cauvery in Tiruchirappalli district, Tamilnadu. Archives of Environmental Science, 5, 55–61.
Lamparelli, M. C. (2015). Graus de trofia em corpos d’agua do estado de São Paulo: avaliação dos métodos de monitoramento [Trophic Status in São Paulo State Water Bodies: Evaluation of Monitoring Methodologies]. Thesis (Doctoral). Universidade de São Paulo (USP). Retrieved from: http://www.teses.usp.br/teses/disponiveis/41/41134/tde–20032006–075813/pt-br.php. Accessed May 2015.
Lapworth, D. J., Baran, N., Stuart, M. E., & Ward, R. S. (2012). Emerging organic contaminants in groundwater: a review of sources, fate and occurrence. Environmental Pollution, 163, 287–303.
Martinez, J., Dabert, P., Barrington, S., & Burton, C. (2009). Livestock waste treatment systems for environmental quality, food safety, and sustainability. Bioresource Technology, 100, 5527–5536.
Martinez-Almeda, J., & Barrera, J. M. (2005). SELCO-Ecopurin pig slurry treatment system. Bioresource Technology, 96, 223–228.
Momblanch, A., Paredes-Arquiola, J., Munné, A., Manzano, A., Arnau, J., & Andreu, J. (2015). Managing water quality under drought conditions in the Llobregat River basin. Science of the Total Environment, 503–504, 300–318.
Nolan, T., Troy, S. H., Gilkinson, S., Frost, P., Xie, S., Zhan, X., Harrington, C., Healy, M. G., & Lawlor, P. G. (2012). Economic analysis of pig manure treatment options in Ireland. Bioresource Technology, 105, 15–23.
Noyola, A., Morgan-Sagastume, J. M., & Lopez-Hernandez, J. F. (2006). Treatment of biogas produced in anaerobic reactors from domestic wastewater: odor control and energy/resource recovery. Reviews in Environmental Science and Biotechnology, 5(1), 93–114.
Ogbuewu, I. P., Odoemenam, V. U., Omede, A. A., Durunna, C. S., Emenalom, O. O., Uchegbu, M. C., Okoli, I. C., & Iloeje, M. U. (2012). Livestock waste and its impact on the environment. Scientific Journal of Review, 1(2), 17–32.
Palhares, J. C. P. (2011). Water footprint of pigs slaughtered in the states of south-Central Brazil. Acta Scientarium Animal Science, 33, 309–314.
Payet, N., Nicolini, E., Rogers, K., Macary, H. S., & Vauclin, M. (2010). Evidence of soil pollution by nitrates derived from pig effluent using 18O and 15N isotope analyses. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 30, 743–751.
Pizzuti, L., Martins, C. A., & Lacava, P. T. (2016). Laminar burning velocity and flammability limits in biogas: a literature review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 62, 856–885.
Reckmann, K., Traulsen, I., & Krieter, J. (2013). Life cycle assessment of pork production: a data inventory for the case of Germany. Live Stock Science, 157, 586–596.
Riano, B., & Garcia-Gonzalez, M. C. (2014). On-farm treatment of swine manure based on solid-liquid separation and biological nitrification-denitrification of the liquid fraction. Journal of Environmental Management, 132, 87–93.
Santos, I. (2001). Hidrometria aplicada, 1edn. Curitiba, Paraná. 372p. ISBN 8588519011. Lactec.
Sao Paulo (2009). Retrieved at: http://aguasinteriores.cetesb.sp.gov.br/wp-content/uploads/sites/32/2013/11/Ap%C3%AAndice-C-%C3%8Dndices-de-Qualidade-das-%C3%81guas-.pdf Environmental company of Sao Paulo state. São Paulo: Quality of Superficial Waters of Sao Paulo State – Appendix C.
Sasada, Y., Win, K., Nonaka, R., Win, A., Toyota, K., Motobayashi, T., Hosomi, M., Dingjiang, C., & Lu, J. (2011). Methane and N2O emissions, nitrate concentrations of drainage water, and zinc and copper uptake by rice fertilized with anaerobically digested cattle or pig slurry. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 47(8), 949–956.
Schneider, R., Nadvorny, A., & Schmidt, V. (2009). Antibiotic resistance patterns of Escherichia coli strains isolated from surface water and groundwater samples in a pig production area. Biotemas, 22(3), 11–17.
Sharma, P., Meher, P. K., Kumar, A., Gautam, Y. P., & Mishra, K. P. (2014). Changes in water quality index of Ganges river at different locations in Allahabad. Sustainability of Water Quality and Ecology, 3–4, 67–76.
Speirs, J., McGlade, C., & Slade, R. (2015). Uncertainty in the availability of natural resources: fossil fuels, critical metals and biomass. Energy Policy, 87, 654–664.
Su, J., & Chen, Y. (2015). Monitoring of sulfur dioxide emission resulting from biogas utilization on commercial pig farms in Taiwan. Environmental Monitoring Assessment, 187, 4109. doi:10.1007/s10661-014-4109-7.
Tavares, J. M. R., Belli Filho, P., Coldebella, A., & Oliveira, P. A. V. (2014). The water disappearance and manure production at commercial growing-finishing pig farms. Livestock Science, 169, 146–154.
United States Department of Agriculture – USDA. (2015). Livestock and poultry: world markets and trade. Foreign Agricultural Service.
Vanotti, M. B., Millner, P. D., Hunt, P. G., & Ellison, A. Q. (2005). Removal of pathogen and indicator microorganisms from liquid swine manure in multi-step biological and chemical treatment. Bioresource Techonology, 96, 209–214.
Viancelli, A., Kunz, A., Steinmetz, R. L. R., Kich, J. D., Souza, C. K., Canal, C. W., Coldebella, A., Esteves, P. A., & Barardi, C. R. M. (2013). Performance of two swine manure treatment systems on chemical composition and on the reduction of pathogens. Chemosphere, 90(4), 1539–1544.
Von Sperling, M. (2007). Basic principles of wastewater treatment . London: International Water Association Publishing.200p. eISBN: 9781780402093
Walczak, J. J., & Xu, S. (2011). Manure as a source of antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli and enterococci: a case study of a Wisconsin, USA family dairy farm. Water, Soil and Air Pollution, 219, 579–589.
Xu, J., Vujic, T., & Deshusses, M. A. (2014). Nitrification of anaerobic digester effluent for nitrogen management at swine farms. Chemosphere, 117, 708–714.
Zang, B., Li, S., Michel Jr., F., Li, G., Luo, Y., Zhang, D., & Li, Y. (2016). Effects of mix ratio, moisture content and aeration rate on sulfur odor emissions during pig manure composting. Waste Management, 56, 498–505.
Zhang, X., Li, Y., Liu, B., Wang, J., Feng, C., Gao, M., & Wang, L. (2014). Prevalence of veterinary antibiotics and antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli in the surface water of a livestock production region in Northern China. Public Library of Science One., 9(11), 1–11. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0111026.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Rio Grande do Sul State Research Foundation (FAPERGS—from Portuguese) and the Coordination for Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES—from Portuguese) for their financial support to this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 59 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schneider, V.E., Marques, R.V., Bortolin, T.A. et al. Monitoring and assessment of surface water quality in Taquari-Antas Watershed, South Brazil—region with intensive pig farming. Environ Monit Assess 188, 617 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5635-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5635-2