Abstract
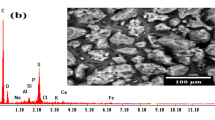
Mercury is a highly toxic substance that is a health hazard to humans. This study aims to investigate powders obtained from the peel of the fruit of Pachira aquatica Aubl, in its in natura and/or acidified form, as an adsorbent for the removal of mercury ions in aqueous solution. The materials were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and thermogravimetric analysis. The infrared spectra showed bands corresponding to the axial deformation of carbonyls from carboxylic acids, the most important functional group responsible for fixing the metal species to the adsorbent material. The thermograms displayed mass losses related to the decomposition of three major components, i.e., hemicellulose, cellulose, and lignin. The adsorption process was evaluated using cold-vapor atomic fluorescence spectrometry (CV AFS) and cold-vapor atomic absorption spectrometry (CV AAS). Three isotherm models were employed. The adsorption isotherm model, Langmuir-Freundlich, best represented the adsorption process, and the maximum adsorption capacity was predicted to be 0.71 and 0.58 mg g−1 at 25 °C in nature and acidified, respectively. Adsorption efficiencies were further tested on real aqueous wastewater samples, and removal of Hg(II) was recorded as 69.6 % for biomass acidified and 76.3 % for biomass in nature. Results obtained from sorption experiments on real aqueous wastewater samples revealed that recovery of the target metal ions was very satisfactory. The pseudo-second-order model showed the best correlation to the experimental data. The current findings showed that the investigated materials are potential adsorbents for mercury(II) ion removal in aqueous solution, with acidified P. aquatica Aubl being the most efficient adsorbent.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayrancy, E., & Hoda, N. (2005). Adsorption kinetics and isotherms of pesticides onto active carbon-cloth. Chemosphere, 60(11), 1600–1607.
Azevedo, C. C. (2008). Modificação química das proteínas de amêndoas da munguba (Pachira aquatica Aubl): propriedades funcionais. Master Thesis. João Pessoa, Brazil: Universidade Federal da Paraíba.
Badr, N., & Al-Qahtani, K. M. (2013). Treatment of wastewater containing arsenic using Rhazya stricta as a new adsorbent. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185(12), 9669–9681.
Barriada, J. L., Caridad, S., Lodeiro, P., Herrero, R., & Vicente, M. E. S. (2009). Physicochemical characterisation of the ubiquitous bracken fern as useful biomaterial for preconcentration of heavy metals. Bioresource Technology, 100, 1561–1567.
CONAMA. (2005). Resolution No 357, the Brazilian National Council for the Environment. http://www.mma.gov.br/port/conama/processos/61AA3835/CONAMA-ingles.pdf. Accessed 5 January 2013.
CONAMA. (2011). Resolution No 430, the Brazilian National Council for the Environment. http://www.mma.gov.br/port/conama/processos/61AA3835/CONAMA-ingles.pdf. Accessed 5 January 2013.
Cotton, F. A., & Wilkinson, G. (1980). Advanced inorganic chemistry: a comprehensive text. New York: Wiley.
Di Natale, F., Erto, A., Lancia, A., & Musmarra, D. (2011). Mercury adsorption on granular activated carbon in aqueous solutions containing nitrates and chlorides. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 192(3), 1842–1850.
Eom, Y., Won, J. H., Ryu, J. Y., & Lee, T. G. (2011). Biosorption of mercury(II) ions from aqueous solution by garlic (Allium sativum L.) powder. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 28(6), 1439–1443.
EPA-United States Environmental Protection Agency. (2008). Health services industry detailed study—dental amalgam, EPA-821-R-08-014.
Farinella, N. V., Matos, G. D., & Arruda, M. A. Z. (2007). Grape bagasse as a potential biosorbent of metals in effluent treatments. Bioresource Technology, 98(10), 1940–1946.
Febrianto, J., Kosasih, A. N., Sunarso, J., Ju, Y. H., Indraswati, N., & Ismadji, S. (2009). Equilibrium and kinetic studies in adsorption of heavy metals using biosorbent: a summary of recent studies. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 162(2-3), 616–645.
Ghodbane, I., & Hamdaoui, O. (2008). Removal of mercury(II) from aqueous media using eucalyptus bark: kinetic and equilibrium studies. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 160(2-3), 301–309.
Han, R., Zhang, J., Han, P., Wang, Y., Zhao, Z., & Tang, M. (2009). Study of equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic parameters about methylene blue adsorption onto natural zeolite. Chemical Engineering Journal, 145(3), 496–504.
Hassan, S. M., Nasser, S. A., & Awaad, H. A. A. (2008). Removal of mercury(II) from wastewater using camel bone charcoal. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 154(1-3), 992–997.
Henriques, B., Rocha, L. S., Lopes, C. B., Figueira, P., Monteiro, R. J. R., Duarte, A. C., Pardal, M. A., & Pereira, E. (2015). Study on bioaccumulation and biosorption of mercury by living marine macroalgae: prospecting for a new remediation biotechnology applied to saline waters. Chemical Engineering Journal, 281, 759–770.
Ho, Y. S. (2006). Review of second-order models for adsorption systems. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 136(3), 681–689.
Khaled, A., El Nemr, A., El-Sikaily, A., & Abdelwahab, O. (2009). Removal of Direct N Blue-106 from artificial textile dye effluent using activated carbon from orange peel: adsorption isotherm and kinetic studies. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 165(1-3), 100–110.
Lemos, V. A., Santos, M. S., Santos, E. S., Santos, M. J. S., Santos, W. N. L., Souza, A. S., et al. (2007). Application of polyurethane foam as a sorbent for a trace metal pre-concentration. Spectrochimica Acta Part B, 62(1), 4–12.
Lima, A. C. A., Nascimento, R. F., Sousa, F. F., Filho, J. M., & Oliveira, A. C. (2012). Modified coconut shell fibers: a green and economical sorbent for the removal of anions from aqueous solutions. Chemical Engineering Journal, 185–186, 274–284.
Liu, Y., & Liu, Y.-J. (2008). Biosorption isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics. Separation and Purification Technology, 61(3), 229–242.
Lv, J., Luo, L., Zhang, J., Christie, P., & Zhang, S. (2012). Adsorption of mercury on lignin: combined surface complexation modeling and X-ray absorption spectroscopy studies. Environmental Pollution, 162, 255–261.
Mishra, V. K., Tripathi, B. D., & Kim, K.-H. (2009). Removal and accumulation of mercury by aquatic macrophytes from an open cast coal mine effluent. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 172(2-3), 749–754.
Montanher, S. F. (2009). Utilização da biomassa de bagaço de laranja como material sorvente de íons metálicos presentes em soluções aquosas. Maringá, Brazil: Universidade Estadual de Maringá.
Nam, K. W., Gomez-Salazar, S., & Tavlarides, L. L. (2003). Mercury(II) adsorption from wastewater using a thiol functional adsorbent. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 42(9), 1955–1964.
O’Connell, D. W., Birkinshaw, C., & O’Dwyer, T. F. (2008). Heavy metal adsorbents prepared from the modification of cellulose: a review. Bioresource Technology, 99(15), 6709–6724.
Pavan, F. A., Lima, E. C., Dias, S. L. P., & Mazzocato, A. C. (2008). Methylene blue biosorption from aqueous solutions by yellow passion fruit waste. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 150(3), 703–712.
Pillay, K., Cukrowska, E. M., & Coville, N. J. (2013). Improved uptake of mercury by sulphur-containing carbon nanotubes. Microchemical Journal, 108, 24–130.
Polizelli, P. P., Facchini, F. D., Cabral, H., & Bonilla-Rodriguez, G. O. (2008). A new lipase isolated from oleaginous seeds from Pachira aquatica (Bombacaceae). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 150(3), 233–242.
Rao, M. M., Reddy, D. H. K. K., Venkateswarlu, P., & Seshaiah, K. (2009). Removal of mercury from aqueous solutions using activated carbon prepared from agricultural by-product/waste. Journal of Environmental Management, 90(1), 634–643.
Santos, W. N. L., Cavalcante, D. D., Silva, E. G. P., Virgens, C. F., & Dias, F. S. (2011). Biosorption of Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions by Agave sisalana (sisal fiber). Microchemical Journal, 97(2), 269–273.
Santos, V. C. G., Grassi, M. T., & Abate, G. (2015). Sorption of Hg(II) by modified K10 montmorillonite: influence of pH, ionic strength and the treatment with different cations. Geoderma, 237–238, 129–136.
Sharma, P., Kaur, H., Sharma, M., & Sahore, V. (2011). A review on applicability of naturally available adsorbents for the removal of hazardous dyes from aqueous waste. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 183(1-4), 151–195.
Silva, B. L. A. (2011). Análise físico-química lipídica e morfologia das Amêndoas das sementes da munguba (Pachira aquatica Aubl.). Revista UNI, 1, 63-74.
Srivasta, V. C., Mall, I. D., & Mishra, I. M. (2008). Adsorption of toxic metal ions onto active carbon: study of sorption behavior through characterization and kinetics. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification, 47(8), 1269–1280.
Toledo, I. B., Garcia, M. A. F., Utrilla, J. R., Castilla, C. M., & Fernadez, F. J. V. (2005). Bisphenol a removal from water by activated carbon. Effects of carbon characteristics and solution chemistry. Environmental Science & Technology, 39(16), 6246–6250.
Tuzen, M., Karaman, I., Citak, D., & Soylak, M. (2009a). Mercury(II) and methyl mercury determinations in water and fish samples by using solid phase extraction and cold vapour atomic absorption spectrometry combination. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 47(7), 1648–1652.
Tuzen, M., Sari, A., Mendil, D., & Soylak, M. (2009b). Biosorptive removal of mercury(II) from aqueous solution using lichen (Xanthoparmelia conspersa) biomass: kinetic and equilibrium studies. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 169(1-3), 263–270.
Tuzen, M., & Soylak, M. (2005). Mercury contamination in mushroom samples from Tokat, Turkey. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 74(5), 968–972.
Tuzen, M., Uluozlu, O. D., Karaman, I., Citak, D., & Soylak, M. (2009c). Mercury(II) and methyl mercury speciation on streptococcus pyogenes loaded Dowex Optipore SD-2. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 169(1-3), 345–350.
Velasquez, G., Herrera-Gomez, A., & Martin-Polo, M. O. (2003). Identification of bound water through infrared spectroscopy in methylcellulose. Journal of Food Engineering, 59(1), 79–84.
Yang, H. (2007). Characteristics of hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin pyrolysis. Fuel, 86(12-13), 1781–1788.
Zabihi, M., Ahmadpour, A., & Asl, H. A. (2009). Removal of mercury from water by carbonaceous sorbents derived from walnut shell. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 167(1-3), 230–236.
Acknowledgments
We thank CAPES for financial support and the UNEB. The authors wish to express their gratitude to MSc. Gefferson Silva dos Santos for the analysis in atomic fluorescence spectrometer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santana, A.J., dos Santos, W.N.L., Silva, L.O.B. et al. Removal of mercury(II) ions in aqueous solution using the peel biomass of Pachira aquatica Aubl: kinetics and adsorption equilibrium studies. Environ Monit Assess 188, 293 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5266-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5266-7