Abstract
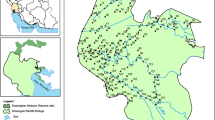
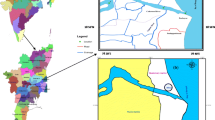
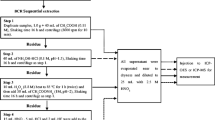
In this study, the chemical speciation of heavy metals and their distribution in surface sediments of Gowatr bay, southeast Iran, are investigated. Modified Bureau Commune de Reference of the European Commission (BCR) sequential extraction technique was applied to assess Cu, Pb, Zn, Mn, Ni, Co, Cr, V, and Fe in the four fractions of five surface sediment samples. Calculated contamination factors (C i f) indicate considerable to very high degree of contamination for Cu and Cr, and very high degree for Zn and Ni. Maximum contamination degree (C d) also suggests serious anthropogenic pollution at two sites. The dominance of average concentration of Cu, Pb, Zn, and Mn in non-residual fractions indicates higher ecological risk within Gowatr bay. Conversely, Ni, Co, Cr, Fe, and V mainly exist in residual phase and hence pose no immediate ecological risk. Calculated individual contamination factors (ICFs) indicate the highest risk of Cu, Pb, Zn, and Mn at two investigated sites. Global contamination factor (GCF) reveals that Pasabandar harbor is highly impacted by metal pollutants.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, M., Islam, S., Rahman, S., Haque, M., & Islam, M. (2010). Heavy metals in water, sediment and some fishes of Buriganga river, Bangladesh. International Journal of Environmental Research, 4(2), 321–332.
Alloway, B., & Ayres, D. C. (1997). Chemical principles of environmental pollution: CRC Press.
Amiard, J.-C., Geffard, A., Amiard-Triquet, C., & Crouzet, C. (2007). Relationship between the lability of sediment-bound metals (Cd, Cu, Zn) and their bioaccumulation in benthic invertebrates. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 72(3), 511–521.
Arain, M. B., Kazi, T. G., Jamali, M. K., Jalbani, N., Afridi, H. I., & Baig, J. A. (2008). Speciation of heavy metals in sediment by conventional, ultrasound and microwave assisted single extraction methods: a comparison with modified sequential extraction procedure. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 154(1), 998–1006.
Batley, G. E. (1989). Trace Element Speciation Analytical Methods and Problems: CRC Press.
Besser, J. M., Brumbaugh, W. G., May, T. W., & Ingersoll, C. G. (2003). Effects of organic amendments on the toxicity and bioavailability of cadmium and copper in spiked formulated sediments. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 22(4), 805–815.
Billon, G., Ouddane, B., Recourt, P., & Boughriet, A. (2002). Depth variability and some geochemical characteristics of Fe, Mn, Ca, Mg, Sr, S, P, Cd and Zn in anoxic sediments from Authie Bay (northern France). Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 55(2), 167–181.
Bloom, H., & Ayling, G. (1977). Heavy metals in the Derwent Estuary. Environmental Geology, 2(1), 3–22.
Caplat, C., Texier, H., Barillier, D., & Lelievre, C. (2005). Heavy metals mobility in harbour contaminated sediments: the case of Port-en-Bessin. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 50(5), 504–511.
Chibunda, R., Pereka, A., Phiri, E., & Tungaraza, C. (2010). Ecotoxicity of mercury contaminated sediment collected from mabubi river (geita district, Tanzania) to the early life stages of African catfish (Clarias gariepinus). International Journal of Environmental Research, 4(1), 49–56.
Choo, K.-H., & Kang, S.-K. (2003). Removal of residual organic matter from secondary effluent by iron oxides adsorption. Desalination, 154(2), 139–146.
Cuong, D. T., & Obbard, J. P. (2006). Metal speciation in coastal marine sediments from Singapore using a modified BCR-sequential extraction procedure. Applied Geochemistry, 21(8), 1335–1346.
Davidson, C. M., Thomas, R. P., McVey, S. E., Perala, R., Littlejohn, D., & Ure, A. M. (1994). Evaluation of a sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of heavy metals in sediments. Analytica Chimica Acta, 291(3), 277–286.
Davies, C. A., Tomlinson, K., & Stephenson, T. (1991). Heavy metals in river tees estuary sediments. Environmental Technology, 12(11), 961–972.
Esen, E., Kucuksezgin, F., & Uluturhan, E. (2010). Assessment of trace metal pollution in surface sediments of Nemrut Bay, Aegean Sea. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 160(1–4), 257–266.
Fan, W., Wang, W.-X., & Chen, J. (2002). Geochemistry of Cd, Cr, and Zn in highly contaminated sediments and its influences on assimilation by marine bivalves. Environmental Science and Technology, 36(23), 5164–5171.
Farhoudi, G., & Karig, D. (1977). Makran of Iran and Pakistan as an active arc system. Geology, 5(11), 664–668.
Fu, F., & Wang, Q. (2011). Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: a review. Journal of Environmental Management, 92(3), 407–418.
Fukue, M., Nakamura, T., Kato, Y., & Yamasaki, S. (1999). Degree of pollution for marine sediments. Engineering Geology, 53(2), 131–137.
Gallon, C., Tessier, A., Gobeil, C., & Alfaro-De La Torre, M. C. (2004). Modeling diagenesis of lead in sediments of a Canadian Shield lake. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 68(17), 3531–3545.
Gao, X., Arthur Chen, C.-T., Wang, G., Xue, Q., Tang, C., & Chen, S. (2010). Environmental status of Daya Bay surface sediments inferred from a sequential extraction technique. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 86(3), 369–378.
Geetha, R., Chandramohanakumar, N., & Mathews, L. (2008). Geochemical reactivity of surficial and core sediment of a tropical mangrove ecosystem. International Journal of Environmental Research, 2(4), 329–342.
Gomez Ariza, J., Giraldez, I., Sanchez-Rodas, D., & Morales, E. (2000). Metal sequential extraction procedure optimized for heavily polluted and iron oxide rich sediments. Analytica Chimica Acta, 414(1), 151–164.
Griscom, S. B., Fisher, N. S., & Luoma, S. N. (2000). Geochemical influences on assimilation of sediment-bound metals in clams and mussels. Environmental Science and Technology, 34(1), 91–99.
Guevara-Riba, A., Sahuquillo, A., Rubio, R., & Rauret, G. (2004). Assessment of metal mobility in dredged harbour sediments from Barcelona, Spain. Science of the Total Environment, 321(1), 241–255.
Hakanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Research, 14(8), 975–1001.
Heiri, O., Lotter, A. F., & Lemcke, G. (2001). Loss on ignition as a method for estimating organic and carbonate content in sediments: reproducibility and comparability of results. Journal of Paleolimnology, 25(1), 101–110.
Holm, N. G. (1988). Arsenic regeneration from estuarine sediments of the Bothnian Bay, Sweden. Chemical Geology, 68(1), 89–98.
Hong, Y., & Förstner, U. (1984). Chemical forms of some heavy metals in Huanghe River sediments (China) and comparison with data from Rhine River sediments (West Germany). Geophysical Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society, 3(1), 37–44.
Höss, S., Henschel, T., Haitzer, M., Traunspurger, W., & Steinberg, C. E. (2001). Toxicity of cadmium to Caenorhabditis elegans (Nematoda) in whole sediment and pore water—the ambiguous role of organic matter. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 20(12), 2794–2801.
Huheey, J. E. (1983). Inorganic chemistry (3rd ed.). New York: Harper and Row.
Ikem, A., Egiebor, N., & Nyavor, K. (2003). Trace elements in water, fish and sediment from Tuskegee Lake, Southeastern USA. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 149(1–4), 51–75.
Kabata, A., & Pendias, H. (2001). Trace elements in soils and plants. New York: CRC.
Kersten, M., & Förstner, U. (1986). Chemical fractionation of heavy metals in anoxic estuarine and coastal sediments. Water Science & Technology, 18(4–5), 121–130.
Korfali, S. I., & Davies, B. E. (2004). Speciation of metals in sediment and water in a river underlain by limestone: role of carbonate species for purification capacity of rivers. Advances in Environmental Research, 8(3), 599–612.
Li, X., Shen, Z., Wai, O. W., & Li, Y.-S. (2001). Chemical forms of Pb, Zn and Cu in the sediment profiles of the Pearl River Estuary. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 42(3), 215–223.
Luoma, S. N., Rainbow, P. S., & Luoma, S. (2008). Metal contamination in aquatic environments: science and lateral management: Cambridge University Press.
Malferrari, D., Brigatti, M. F., Laurora, A., & Pini, S. (2009). Heavy metals in sediments from canals for water supplying and drainage: mobilization and control strategies. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 161(2), 723–729.
Marguı, E., Salvadó, V., Queralt, I., & Hidalgo, M. (2004). Comparison of three-stage sequential extraction and toxicity characteristic leaching tests to evaluate metal mobility in mining wastes. Analytica Chimica Acta, 524(1), 151–159.
Moore, F., Nematollahi, M. J., Keshavarzi, B., & Hamzeh, M. A. (2014). Surficial and vertical distribution of heavy metals in marine and intertidal sediments in the Iranian sector of Gowatr bay. Journal of Khoramshahr Marine Science and Technology, In Press.
Nádaská, G., Polčová, K., & Lesný, J. (2009). Manganese fractionation analysis in specific soil and sediment samples. Nova Biotechnological, 9(3), 295–301.
Okoro, H. K., Fatoki, O. S., Adekola, F. A., Ximba, B. J., & Snyman, R. G. (2012). A review of sequential extraction procedures for heavy metals speciation in soil and sediments. Open Access Scientific Reports, 181(1)
Qiu, Y.-W., Lin, D., Liu, J.-Q., & Zeng, E. Y. (2011). Bioaccumulation of trace metals in farmed fish from South China and potential risk assessment. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 74(3), 284–293.
Quevauviller, P., Rauret, G., Muntau, H., Ure, A., Rubio, R., López-Sánchez, J., et al. (1994). Evaluation of a sequential extraction procedure for the determination of extractable trace metal contents in sediments. Fresenius Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 349(12), 808–814.
Rauret, G., López-Sánchez, J.-F., Sahuquillo, A., Barahona, E., Lachica, M., Ure, A., et al. (2000). Application of a modified BCR sequential extraction (three-step) procedure for the determination of extractable trace metal contents in a sewage sludge amended soil reference material (CRM 483), complemented by a three-year stability study of acetic acid and EDTA extractable metal content. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 2(3), 228–233.
Root, R. A., Dixit, S., Campbell, K. M., Jew, A. D., Hering, J. G., & O’Day, P. A. (2007). Arsenic sequestration by sorption processes in high-iron sediments. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71(23), 5782–5803.
Salomons, W., & Förstner, U. (1984). Metals in the Hydrocycle: Springer-Verlag.
Shriadah, M. (1999). Heavy metals in mangrove sediments of the United Arab Emirates shoreline (Arabian Gulf). Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 116(3–4), 523–534.
Szefer, P., Glasby, G., Pempkowiak, J., & Kaliszan, R. (1995). Extraction studies of heavy-metal pollutants in surficial sediments from the southern Baltic Sea off Poland. Chemical Geology, 120(1), 111–126.
Tam, N., & Wong, Y. (1995). Spatial and temporal variations of heavy metal contamination in sediments of a mangrove swamp in Hong Kong. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 31(4), 254–261.
Tessier, A., Campbell, P. G., & Bisson, M. (1979). Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Analytical Chemistry, 51(7), 844–851.
Turner, A. (2000). Trace metal contamination in sediments from UK estuaries: an empirical evaluation of the role of hydrous iron and manganese oxides. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 50(3), 355–371.
Uluturhan, E. (2010). Heavy metal concentrations in surface sediments from two regions (Saros and Gökova Gulfs) of the Eastern Aegean Sea. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 165(1–4), 675–684.
Ure, A., Quevauviller, P., Muntau, H., & Griepink, B. (1993). Speciation of heavy metals in soils and sediments. An account of the improvement and harmonization of extraction techniques undertaken under the auspices of the BCR of the Commission of the European Communities. International Journal of Environmental and Analytical Chemistry, 51(1–4), 135–151.
Wang, L., Chin, Y.-P., & Traina, S. J. (1997). Adsorption of (poly) maleic acid and an aquatic fulvic acid by geothite. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 61(24), 5313–5324.
Wang, S., Jia, Y., Wang, S., Wang, X., Wang, H., Zhao, Z., et al. (2010). Fractionation of heavy metals in shallow marine sediments from Jinzhou Bay, China. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 22(1), 23–31.
Yan, C., Li, Q., Zhang, X., & Li, G. (2010). Mobility and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Xiamen Bay and its adjacent areas, China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 60(7), 1469–1479.
Yap, C. K., Ismail, A., Tan, S. G., & Omar, H. (2002). Correlations between speciation of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn in sediment and their concentrations in total soft tissue of green-lipped mussel Perna viridis from the west coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Environment International, 28(1–2), 117–126. doi:10.1016/S0160-4120(02)00015-6.
Yuan, C. G., Shi, J. B., He, B., Liu, J. F., Liang, L.-N., & Jiang, G.-B. (2004). Speciation of heavy metals in marine sediments from the East China Sea by ICP-MS with sequential extraction. Environment International, 30(6), 769–783.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their special thanks to agents of Iranian National Institute for Oceanography and Atmospheric Science (INIOAS)–Chabahar research station, and medical geology research center of Shiraz University for financial and experimental supports.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moore, F., Nematollahi, M.J. & Keshavarzi, B. Heavy metals fractionation in surface sediments of Gowatr bay-Iran. Environ Monit Assess 187, 4117 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-4117-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-4117-7