Abstract
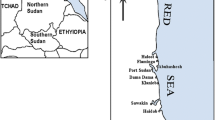
Concentrations of Cu, Zn, Cd, Pb, Ni, Co, Fe, Mn, and Hg were measured successively in water, sediments, and six macroalgal species belonging to three algal classes during 3 years (2008–2010) from Abu Qir Bay, Alexandria, Egypt: Chlorophyceae (Enteromorpha compressa, Ulva fasciata), Phaeophyceae (Padina boryana), and Rhodophyceae (Jania rubens, Hypnea musciformis, Pterocladia capillacea). The study aimed to assess the bioaccumulation potential of the seaweeds, as well as to evaluate the extent of heavy metal contamination in the selected study site. Metals were analyzed using atomic absorption spectrophotometry coupled with MH-10 hydride system. The obtained data showed that the highest mean concentrations of Cu, Zn, Fe, and Mn were recorded in E. compressa; Cd, Ni, and Hg exhibited their highest mean concentrations in P. boryana, while Pb and Co were found in J. rubens. Abundance of the heavy metals in the algal species was as follow: Fe > Mn > Zn > Pb > Ni > Co > Cu > Cd > Hg. E. compressa showed the maximum metal pollution index (MPI) which was 11.55. Bioconcentration factor (BCF) for the metals in algae was relatively high with a maximum value for Mn. The Tomlinson pollution load index (PLI) values for the recorded algal species were low, which ranged between 1.00 in P. boryana and 2.72 in E. compressa. Enrichment factors for sediments were low fluctuating between 0.43 for Hg to 2.33 for Mn. Accordingly, the green alga E. compressa, brown alga P. boryana, and red alga J. rubens can be nominated as bioindicators. Based on MPI and PLI indices, Abu Qir Bay in the present study is considered as low-contaminated area.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdallah, M. A. M. (2007). Chemical composition and trace element concentration of marine algae Enteromorpha spp as potential food source. In: Proceedings of the third Mediterranean symposium on marine vegetation (Marseilles, 27-29 March 2007). C. Pergent-Martini, S. El Asmi, C. Le Ravallec edits., RAC/SPA publ., Tunis: 225-228.
Abdallah, M. A. M., & Abdallah, A. M. A. (2008). Biomonitoring study of heavy metals in biota and sediments in the south eastern coast of Mediterranean Sea Egypt. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 146, 139–145.
Abdallah, M. A. M. (2008). Chemical composition, mineral content and heavy metals of some marine seaweeds from Alexandria coast. Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Research, 34(2), 84–94.
Abdallah, M. A. M. (2010). Heavy metal monitoring in marine seaweeds from the southeastern Mediterranean Sea off the Egyptian coast, 2006-2009. United Nations Environment Programme Mediterranean Action Plan, Regional Activity Centre for Specially Protected Areas. Proceedings of the 4th Mediterranean Symposium on marine vegetation, Yasmine-Hammamet, 2-4 December 2010, pp:11-16.
Abdel Ghani, S. A. H., El Naggar, M. F., El Zokm, G. M., Shakweer, L., & Okbah, M. A. (2010). Concentration level of some dissolved trace metals in Mediterranean coastal water NW-Egypt. Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Research, 36(4), 509–522.
Adeloju, S. B., Dhindsa, H. S., & Tandon, R. K. (1994). Evaluation of some wet decomposition methods for mercury determination in biological and environmental materials by cold vapour atomic absorption spectrometry. Analytical Chemistry Acta, 285, 359–364.
Ahdy, H. H., Mohammed, T. A., & Abdallah, A. M. A. (2006). Multi-elements content in some marine seaweeds from Egyptian Red Sea coast. Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Research, 32, 1–15. special issue.
Akcali, I., & Kucuksezgin, F. (2011). A biomonitoring study: heavy metals in macroalgae from eastern Aegean coastal areas. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 62, 637–645.
Aleem, A. A. (1993). The marine algae of Alexandria, Egypt.139 pp.
Anastasakis, K., Ross, A. B., & Jones, J. M. (2011). Pyrolysis behaviour of the main carbohydrates of brown macro-algae. Fuel, 90, 598–607.
Angelidis, M. O., & Aloupi, M. (2001). Geochemical study of coastal sediments influenced by river-transported pollution: southern Evoikos Gulf. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 40(1), 77–82.
Angula, E. (1996). The Tomlinson pollution index applied to heavy metal, Mussel-Watch data: a useful index to assess coastal pollution. Science of the Total Environment, 187, 19–56.
APHA. (1989). “AWWA and WPCF standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater” 17 th ed., APHA, Washington.
Birth, G. (2003). A scheme for assessing human impacts on coastal aquatic environments using sediments. In : Woodcoffe, C.D., Furnes, R.A. (Eds.). Coastal GIS, 2003. Wollongong University papers in Center for Maritime Policy, 14, Australia.
Bhowmik, D., Chiranjib, K. P., & Kumar, S. (2010). A potential medicinal importance of zinc in human health and chronic disease. Review article. International Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Sciences, 1(1), 5–11.
Black, W. A. P., & Mitchell, R. L. (1952). Trace elements in the common brown algae and in seawater. Journal of Marine Biology Assessment, UK, 30, 575–584.
Brewer, P. G., Spencer, D. W., & Smith, C. L. (1969). Determination of trace metals in seawater by atomic absorption spectroscopy. American Society for Testing Materials Tech. Publication, 443, 70–77.
Bryan, G. W. (1971). The effects of heavy metals (other than mercury) on marine and estuarine organisms. The Royal society, London, series B, 177:389 - 410.
Camargo, J. A. (2002). Contribution of Spanish-American silver mines (1570-1820) to the present high mercury concentrations in the global environment: a review. Chemosphere, 48, 51–57.
Carlson, L., & Erlandsson, B. (1991). Seasonal variation of radionuclides in Fucus vesiculosus L. from the oresund. Southern Sweden. Environmental Pollution, 73, 53–70.
Chaudhuri, A., Mitra, M., Havrilla, C., Waguespack, Y., & Schwarz, J. (2007). Heavy metal biomonitoring by seaweeds on the Delmarva, Peninsula, east coast of the USA. Botanica Marina, 50, 151–158.
Chen, C. W., Kao, C. M., Chen, C. F., & Dong, C. D. (2007). Distribution and accumulation of heavy metals in the sediments of Kaohsiung Harbor, Taiwan. Chemosphere, 66, 1431–1440.
Davis, T. A., Voleskya, B., & Mucci, A. (2003). A review of the biochemistry of heavy metal biosorption by brown algae. Water Research, 37, 4311–4330.
Denton, G. R. W.; Kelly, W. C.; Wood, H. R. & Wen, Y. (2006). Impact of metal enriched leachate from ordot dump on the heavy metal status of biotic and abiotic components of Pago Bay. Water and Environmental Research Institute (WERI) Technical Report No. 113, University of Guam, Mangilao, Guam, 63 pp.
EL-Deeb, M. K., & Aboul-Naga, W. M. (2002). Trace metals: Fe, Zn, Mn, Cu, Ni and Cr in macroalgae from Alexandria coast. Bulletin Facts Science, 42(1,2), 51–60. University of Alexandria.
El-Moselhy, Kh. M., & Gabal, M. N. (2004). Trace metals in water, sediments and marine organisms from the northern part of the Gulf of Suez, Red Sea. Journal of Marine Systems, 46, 39–46.
EL-Moselhy, Kh. M., & Abd El-Azim, H. (2005). Heavy metals content and grain size of sediments from Suez Bay, Red Sea, Egypt. Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Research, 31(2), 224–238.
EL-Moselhy, Kh. M.; Amer, A. M. & Shams El Din, N. G. (2006). Trace metals concentration in water, sediments and macroalgae species in the intertidal zone of Suez Bay, Red Sea, Egypt. International Journal Oce. and Oceano. 1 (3) in press.
EL-Moselhy, Kh. M., & Hamed, M. A. (2006). Impact of land-based activities on hydrographic conditions and levels of heavy metals in water and sediments along the Mediterranean coast of Egypt. Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Research, 32(2), 63–82.
El-Nady, F. E. (1996). Heavy metal pollution problems in the southeastern Mediterranean waters of Alexandria, Egypt. Proceeding of the 6th international conference on environmental protection is a must, NIOF, VEA, ISA and SFD, Alexandria, Egypt, 21-31 May: 364-381.
EL-Naggar, M. E. E. & Al-Amoudi, O. A. (1989). Heavy metal levels in several species of marine algae from the Red Sea of Saudi Arabia. J.K.A.U.: Science, 1:5-13.
EL-Naggar, M. F. (2009). Heavy metals accumulation in the biotic environment of the Bitter to the Mediterranean Sea, west of Alexandria. Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Research, 31(special issue), 120–129.
El-Nemr, A., Khaled, A., & El-Sikaily, A. (2012). Heavy metal contamination in the seaweeds of Abu-Qir, Egypt. Journal of Blue Biotechnology, 1(2), 273–287.
EL-Sarraf, W. M. (1995). Heavy metal content in some marine algae from Alexandria, Egypt. Bulletin Facts Science, 35(2), 475–484. Alexandria University.
EL-Sayed, M. A., & Dorgham, M. M. (1994). Trace metals in macroalgae from the Qatari coastal water. Journal of King Abdulaziz University-Science, 5, 13–24.
El-Sherif, M. Z., & Mikhail, S. K. (2003). Phytoplankton dynamics in the southwestern part of Abu-Qir Bay Egypt. Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Biology and Fisheries, 7(1), 219–239.
El-Sikaily, A. (2008). Assessment of some heavy metals pollution in the sediments along the Egyptian Mediterranean coast. Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Research, 34(3), 58–71.
El-Tawil, B. A. H., & Khalil, A. N. (1983). Chemical constituents of some algal species from Abu-Qir Bay. Egyptian Journal Facts Marine Science, 3, 85–94.
Ergin, M., Saydam, C., Bastruk, O., Erdem, E., & Yoruk, R. (1991). Heavy metal concentrations in surface sediments from the two coastal inlets (Golden Horn Estuary and Izmit Bay) of the northeastern Sea of Marmara. Journal of Chemical Geology, 91, 269–285.
Evans, L. K., & Edwards, M. S. (2011). Bioaccumulation of copper and zinc by the giant kelp Macrocystis pyrifera. Algae, 26(3), 265–275.
Fityanos, K., Evgenidou, E., & Zachariadis, G. (1999). Use of macroalgae as biological indicators of heavy metal pollution in Thermaikos Gulf, Greece. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 62, 630–7.
Gunner, H. V.; Aysel, O.; Ozeisel, S. & Sukatar, A. (1987). Periodical variation of trace element accumulations in some algae found in the bay of Izmir. Review of International Oceanography of Mediterranean Tomes. LXXXV-LXXXVI: 52-55.
Güven, K.; Topcuoglu, S.; N. Balkis, N.; Ergul H. & Aksu, A. (2007). Heavy metals concentrations in marine algae from the Turkish coast of the Black Sea. Rapp. Comm. int. Mer Medit., 38, p.66.
Hamed, M. A. & El-Moselhy, Kh., M. (2000). Levels of some metals in the coastal water and sediments of the Red Sea, Egypt, A.M.S.E. vol.61 (1, 2):43-57.
Hardisson, A., Frı’as, I., Lozano, G., & Ba’ez, A. (1998). Mercury in algae of the Canary Islands littoral. Environment International, 24(8).
Haritonidis, S., & Malea, P. (1995). Seasonal and local variation of Cr, Ni, and Co concentrations in Ulva rigida C.Agardh and Enteromorpha linza (Linnaeus) from Thermaikos Gulf, Greece. Journal of Environmental Pollution, 89(1), 319–327.
Higgins, H. W., & Mackey, D. J. (1978). Role of Ecklonia radiate (C. Ag.) J. Agardh in determining trace metal availability in coastal waters. I. Total trace metals. Australian Journal of Marine and Fresh water Research, 38, 307–315.
Holan, Z. R., & Volesky, B. (1994). Biosorption of lead and nickel by biomass of marine algae. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 43, 1001–1009.
Jothinayagi, N., & Anbazhagan, C. (2009). Heavy metal monitoring of Rameswaram Coast by some Sargassum species. American - European Journal of Scientific Research, 4(2), 73–80.
Khairy, H. M., & Omar, H. H. (2008). Effect of heavy metals on some metabolic activities of Jania rubens and Ulva lactuca from Eastern harbor and Abu-Qir bay of Alexandria Egypt. Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Research, 34(2), 114–129.
Khalil, M. K., & Rifaat, A. E. (2010). Enrichment of zinc, copper, lead and nickel in bottom sediments from three environmentally different regions off Alexandria. Egypt. Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Research, 36(3), 379–394.
Kimbrough, K. L.; Johnson, W. E.; Lauenstein, G. G.; Christensen, J. D. & Apeti, D. A. (2008). An assessment of two decades of contaminant monitoring in the Nation’s Coastal Zone. NOAA Technical Memorandum NOS NCCOS 74. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Centers for Coastal Ocean Science, Center for Coastal Monitoring and Assessment, Silver Spring, MD, 105 pp.
Kontas, A. (2008). Trace metals (Cu, Mn, Ni, Zn, Fe) contamination in marine sediment and zooplankton samples from Izmior bay. (Aegean Sea, Turkey). J. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 188, 323–333.
Laib, E. & Leghouchi, E. (2011). Cd, Cr, Cu, Pb, and Zn concentrations in Ulva lactuca, Codium fragile, Jania rubens, and Dictyota dichotoma from Rabta Bay, Jijel (Algeria) Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. DOI 10.1007/s10661-011-2072-2080.
Leal, M. C. F., Vasconcelos, M. T., Sousa-Pinto, I., & Cabral, J. P. S. (1997). Biomonitoring with benthic macroalgae and direct assay of heavy metals in seawater of the Oporto coast (Northwest Portugal). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 34(12), 1006–1015.
Long, E. R., MacDonald, D. D., Smith, S. L., & Calder, F. D. (1995). Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. Journal of Environmental Management, 19, 81–97.
Mohamed, L. A., & Khaled, A. (2005). Comparative study of heavy metal distribution in some coastal seaweeds of Alexandria, Egypt. Chemistry and Ecology, 21(3), 181–189.
Moore, J. W. (1991). Inorganic contaminants of surface water: Research and monitoring priorities, Springer-Verlag New York Inc.
Munda, I. M. (1984). Salinity dependent accumulation of Zn, Co and Mn in Scytosiphon lomentaria (Lyngb.) Link and Enteromorpha intestinalis (L.) Link from the Adriatic Sea. Botanica Marina, 27, 371–376.
OECD, (2003). Environmental indicators, development, measurement and use, Reference Paper, OECD, Paris.
Pawlik-Skowrońsk, B., Pirsze, J., & Brown, M. T. (2007). Concentrations of phytochelatins and glutathione found in natural assemblage of seaweeds depend on species and metal concentrations of the habitat. Aquatic Toxicology, 83(3), 190–199.
Philips, D. J. H. (1976). The common mussel Mytilus edulis as an indicator of pollution by zinc, cadmium, lead and copper. I. Effects of environmental variables on uptake of metals. Marine Biology, 38, 59–69.
Phillips, D. J. H. (1990). Use of macroalgae and invertebrates as monitors of metal levels in estuaries and coastal waters. In R. W. Furness & P. S. Rainbow (Eds.), Heavy metals in the marine environment (pp. 81–99). Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Rainbow, P. S. (1995). Biomonitoring of heavy metal availability in the marine environment. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 31, 183–192.
Rajfur, M., Klos, A., & Waclawek, M. (2010). Sorption properties of algae Spirogyra sp. and their use for determination of heavy metal ions concentrations in surface water. Bioelectrochemistry, 80, 81–86.
Riedel, R. (1970). Fauna und Flora der Adria (p. 702). Hamburg und Berlin: Verlag Paul Parey.
Riley, J. P. & Skirrow, G. (1965). Chemical Oceanography, Academic press, London, vol. 1, II, 411 pp.
Romera, E., González, F., Ballester, A., Blázquez, M. L., & Munoz, J. A. (2007). Comparative study of biosorption of heavy metals using different types of algae. Bioresource Technology, 98, 3344–3353.
Santamaria-Fernandez, R., Cave, M. R., & Hill, S. J. (2005). Trace metal distribution in the Arosa estuary (N.W. Spain): the application of a recently developed sequential extraction procedure for metal partitioning. Analytical chemistry Acta, 557(1–2), 344–352.
Sari, E., & Catagay, M. N. (2001). Distribution of heavy metals in the surface sediments of the Gulf of Saros, NE Agean Sea. Environment International, 26, 169–173.
Say, P. J., Burrows, I. G., & Whitton, B. A. (1990). Enteromorpha as a monitor of heavy metals in estuaries. Hydrobiologia, 195, 119–126.
Schuhmacher, M., & Domingo, J. L. (1996). Concentrations of selected elements in oyster Crassostra angulata from the Spanish coast. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 56, 106–113.
Shakweer, L., Shiridah, M., Fahmi, M., & Fattah, L. A. (2006). Distribution and concentrations of trace elements along the Mediterranean coastal water of Egypt. Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Research, 32(2), 95–127.
Shams El-Din, N. G., & Dorgham, M. M. (2007). Phytoplankton community in Abu-Qir as a hot spot on the southeaster Mediterranean coast. Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Research, 33(1), 163–182.
Shobier, A. H., Abdel Ghani, S. A., & Shreadah, M. A. (2011). Distribution of total mercury in sediments of four semi-enclosed basins along the Mediterranean coast of Alexandria. Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Research, 37(1), 1–11.
Shriadah, M. A. & Emara, H. I. (1991). The distribution of chromium, copper, cadmium and lead in areas in multi-polluting factors of Alexandria. Proceeding of Symposium of Marine Chemistry in the Arab region, Suez, April, 39-50.
Steffens, J. C. (1990). The heavy metal-binding peptides of plants. Annual of Review Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology, 41, 553–575.
Stenner, R. D., & Nickless, G. (1975). Heavy metal in organisms of the Atlantic coast of SW. Spain and Portugal. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 6, 89–92.
Svete, P., Milacic, R., & Pihlar, B. (2001). Partitioning of Zn, Pb, and Cd in river sediments from a lead and zinc mining area using the BCR three-step sequential extraction procedure. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 3, 586–590.
Tomlinson, D. L., Wilson, J. G., Harris, C. R., & Jeffrey, D. W. (1980). Problems in the assessment of heavy metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgol Meeresunters, 33, 566–575.
Topcuoǧlu, S., Güven, K. C., Balkıs, N., & Kirbașoǧlu, Ҫ. (2003). Heavy metal monitoring of marine algae from the Turkish Coast of the Black Sea, 1998–2000. Chemosphere, 52, 1683–1688.
Torres, M. A., Barros, M. P., Campos, S. C. G., Pinto, E., Rajamani, S., Sayre, R. T., & Colepicolo, P. (2008). Biochemical biomarkers in algae and marine pollution: a review. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 71, 1–15.
Tropin, I. V. (1995). Distribution of metals in thalluses of red alga with special reference to their taxonomy and ecology. Oceanology, 35(1), 92–98.
Usero, J., Morillo, J., & Gracia, I. (2005). Heavy metal contamination in mollusks from the Atlantic coast of southern Spain. Chemosphere, 59, 1175–1181.
Vald’es, J., Vargas, G., Sifeddine, A., Ortlieb, L., & Guinez, M. (2005). Distribution and enrichment evaluation of heavy metals in Mejillones Bay (23-S), Northern Chile: geochemical and statistical approach. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 50, 1558–1568.
Volterra, L., & Conti, M. E. (2000). Algae as biomarkers, bioaccumulators and toxin producers. International Journal of Environment and Pollution, 13, 92–125.
Waldichut, M. (1974). Some biological concern in heavy metals pollution. In F. J. Vernberg & W. B. Vernerberg (Eds.), Pollution and Physiology of marine organisms (pp. 1–54). New York: Academic Press.
Warnau, M., & Bustamante, P. (2007). Editorial: Radiotracer techniques: a unique tool in marine ecotoxicological studies. Environmental Bioindicators, 2(4), 217–218.
WQC, (1972). A report of the committee on water quality criteria. NAS. Washington. DC. 593pp.
Zauke, G. P., Ritterhoff, J. & Rinderhagen, M. (1998). Concepts and applications in aquatic biomonitoring – internal review paper. Aquatic Ecology Group, ICBM, CvO Universitat, Oldenburg, Germany, pp. 38.
Żbikowski, R., Szefer, P., & Latała, A. (2007). Comparison of green algae Cladophora sp. and Enteromorpha sp. As potential biomonitors of chemical elements in the southern Baltic. Science of the Total Environment, 387, 320–332.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shams El-Din, N.G., Mohamedein, L.I. & El-Moselhy, K.M. Seaweeds as bioindicators of heavy metals off a hot spot area on the Egyptian Mediterranean Coast during 2008–2010. Environ Monit Assess 186, 5865–5881 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3825-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3825-3