Abstract
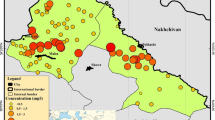
This study analyzes the concentrations and health risks of fluoride in 249 drinking water samples collected from different regions of Anhui Province in China. Results indicated that fluoride content in drinking water ranged from 0.12 to 1.94 mg L−1 (mean = 0.57 mg L−1) in the following order: Huaibei plain region > Jianghuai hill region ≈ Dabieshan mountainous region > plain along the Yangtze River region > southern Anhui mountainous region. The fluoride contents were less than 0.50 mg L−1 in 66.66 % of the drinking water samples, 0.51–1.0 mg L−1 in 23.29 %, and higher than 1.0 mg L−1 in 12.04 %. The fluoride levels in some samples were lower than the recommended values for controlling dental caries (0.50–1.0 mg L−1). The total fluoride intake from drinking water was between 0.14 and 2.33 mg per day in different regions of the province, supposing an individual consumes 1.2 L of water per day. Therefore, measures should be taken to increase fluoride intake in the Jianghuai hill region, Dabieshan mountainous region, plain along the Yangtze River, and southern Anhui mountainous region to control dental caries. On the other hand, the fluoride levels must be reduced in the Huaibei plain region to decrease endemic fluorosis. The results serve as crucial guidelines for managing fluoride safety in drinking water and controlling endemic fluorosis in different regions of Anhui Province.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao, J., Zhao, Y., Liu, J. W., Xirao, R. D., & Danzeng, S. B. (2000). Environmental fluoride contents in Tibet. Environmental Research Section A, 83, 333–337.
Chen, Y., Xie, Z. F., Yan, Q., Cai, G. Q., & Chen, J. Z. (2006). Preliminary investigation the contents of fluoride in the environmental water body and drinking water in Yulin of Guangxi Province, China. Journal of Yulin Teachers College, 27(3), 76–80 (in Chinese).
Dai, S., Ren, D., & Ma, S. (2004). The cause of endemic fluorosis in western Guizhou Province, Southwest China. Fuel, 83, 2095–2098.
Deng, Y. C. (2006). Reasons and distributions of high fluoride in underground water in Anhui Province, China. Jiang-huai Water Resource Science, 2, 22–24 (in Chinese).
Dey, S., Goswami, S., & Ghosh, U. C. (2004). Hydrous ferric oxide (HFO)-a scavenger for fluoride from contaminated water. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 158, 311–323.
Dhiman, S. D., & Keshari, A. K. (2006). Hydrogeochemical evaluation of high-fluoride ground water: a case study from Mehsana District, Gujarat, India. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 51(6), 1149–1162.
Dissanayake, C. B. (1991). The fluoride problem in the ground water of Sri Lanka—environmental management and health. International Journal of Environmental Studies, 38, 137–156.
Doull, J., Boekelheide, K., Farishian, B. G., Isaacson, R. L., Klotz, J. B., Kumar, J. V., Limeback, H., Poole, C., Puzas, J. E., Reed, N. M. R., Thiessen, K. M., Webster, T. F., & Committee on Fluoride in Drinking Water, Board on Environmental Studies and Toxicology, Division on Earth and Life Studies, National Research Council of the National Academies. (2006). Fluoride in drinking water: a scientific review of EPA’s standards. Washington, DC: The National Academies.
Fawell, J., Bailey, K., Chilton, J., Dahi, E., Fewtrell, L., & Magara, Y. (2006). Fluoride in drinking-water. Geneva: WHO.
Gao, H. J., Zhang, X. C., Cai, H. M., Zhang, Z. Z., & Wan, X. C. (2010). Comparison and optimization of total ionic strength adjustment buffer for determination fluoride in water. Environmental Chemistry, 29(4), 759–764 (in Chinese).
GB5749-2006 (2006). Sanitary standard for drinking water quality in China.
Gong, X. (2008). Assessment on fluoride pollution in farm soil and water samples in Nanchang city of Guangxi province. Jiangxi Chemical, 9, 111–113 (in Chinese).
Guo, Q. H., Wang, Y. X., Ma, T., & Ma, R. (2007). Geochemical processes controlling the elevated fluoride concentrations in ground waters of the Taiyuan Basin, Northern China. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 93, 1–12.
Hamilton, M. (1992). Water fluoridation: a risk assessment perspective. Journal of Environmental Health, 54(6), 27–32.
Harrison, P. T. C. (2005). Fluoride in water: a UK perspective. Journal of Fluorine Chemistry, 126, 1448–1456.
Helm, J. D. (1985). The study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water, 3rd edn. Alexandria, VA: U.S. Geological Survey Water-Supply Paper 2254.
Hileman, B. (1988). Fluoridation of water: questions about health risks and benefits remain after more than 40 years. Chemical & Engineering News, 1, 26–42.
Hu, X. S., Fang, B. H., Fang, H. P., & Zhang, Y. P. (2008). Investigation the fluoride concentrations in drinking water in Huangshan of Anhui Province, China. Shanghai Journal of Preventive Medicine, 20(11), 547–548 (in Chinese).
IPCS (International Program on Chemical Safety). (1984). Environmental Health Criteria 36: fluorine and fluoride. Geneva: World Health Organization.
Kaminsky, L. S., Mahoney, M. C., Leach, J., Melius, J., & Miller, J. M. (1990). Fluoride: benefits and risks of exposure. Critical Reviews in Oral Biology and Medicine, 1, 261–281.
Lennon, M. A., Whelton, H., O’Mullane, D., & Ekstrand, J. (2004). Rolling revision of the WHO guidelines for drinking-water quality—fluoride. Geneva: WHO.
Li, J., Wang, Z. H., Cheng, X. T., Jia, Q. Z., San, Z. P., Zhang, J., Han, L. L., Duan, H. S., Liang, B. F., & Wang, S. X. (2006). Endemic Fluorosis prevalence in the counties of severe disease areas of Shanxi province. Chinese Journal of Endemiol, 25(5), 541–543.
Liang, C. K., Sun, S. Z., & Wei, Z. D. (1996). Research progress of sanitation standard for people’s total absorbing fluoride. Journal of Medicine Hygiene Science Overseas, 23(5), 293–296 (in Chinese).
Meng, D. Q. (2001). Relationship between fluoride content in drinking water and incidence of decayed tooth of children in central district of Qiqihar City of Helongjiang Province, China. Helongjiang Environmental Journal, 25(2), 104–107 (in Chinese).
MMWR. (2001). Recommendation and report. Recommendations for using fluoride to prevent and control dental caries in the United States. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 17; 50(RR-14), 1–42.
Oruc, N. (2008). Occurrence and problems of high fluoride waters in Turkey: an overview. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 30, 315–323.
Ozsvath, D. L. (2009). Fluoride and environmental health: a review. Reviews in Environmental Science and Biotechnology, 8(1), 59–79.
Ren, Q. Q. (2002). Fluoride in drinking water and human health. Anhui Preventive Medicine, 8(2), 123–125 (in Chinese).
Shao, S. P., Zhao, X. M., Sun, A. F., & Sun, X. M. (2000). The distribution regularities of the fluoride content of drinking water over Zhengzhou District. Journal of Henan Education Institute, 9(3), 28–29 (in Chinese).
Shi, T. X., Sun, L., Shi, J., Fu, X. S., Huang, R. M., Liu, H., & Wang, D. D. (2008). Investigation on the quality of water resource in Guangzhou from 2005 to 2007. Journal of Tropical Medicine, 8(10), 1084–1086 (in Chinese).
Tahir Shah, M., & Danishwar, S. (2003). Potential fluoride contamination in the drinking water of Naranji area, northwest Frontier Province, Pakistan. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 25, 475–481.
Walna, B., Kurzyca, I., & Siepak, J. (2007). Variations in the fluoride level in precipitation in a region of human impact. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 7, 33–40.
Wang, L., & Huang, J. (1995). Outline of control practice of endemic fluorosis in China. Social Science & Medicine, 41(8), 1191–1195 (in Chinese).
WHO. (1984). Guidelines for drinking-water quality. Volume 2. Health criteria and other supporting information. Geneva: World Health Organization.
WHO. (1994). Fluorides and oral health: report of a WHO Expert Committee on oral health status and fluoride use. Technical report 846, Geneva: World Health Organization.
Wu, J. Q., Peng, J. W., Wu, H. Y., Li, B. L., & Miao, L. J. (2006). Investigation on the current water-related endemic fluorosis in Shaoguang City of Guangdong Province. Chinese Journal of Endemiol, 25(5), 535–536 (in Chinese).
Wu, Y. T., & Ye, D. Q. (2008). A survey of fluoride concentration in water and defluoridation in the country of Fuyang City of Anhui Province. Chinese Journal of Diseases Control and prevention, 12(6), 608–610 (in Chinese).
Xu, K. F. (2001). Investigation on the drinking water quality in Yongkang City of Zhejiang Province, China. Zhejiang Preventive Medicine, 13(6), 30–31 (in Chinese).
Yang, F. T., Lu, Q., Xu, Y. B., Gu, W. H., & Li, J. T. (2008). Investigation the fluoride contents in drinking water in Hefei City of Anhui Province in 2007. Anhui Journal of Preventive Medicine, 14(6), 461–462 (in Chinese).
Yao, P. J. (2005). Analysis of drinking water-born endemic fluorosis associated with drinking water in Xi’an in 2002. Chinese Journal of Endemiol, 24(1), 67–69 (in Chinese).
Yu, G. C. (2004). Investigating the distribution of fluoride in underground water in Zaozhuang City of Shandong Province, China. Chinese Journal of Endemiol, 23(2), 152 (in Chinese).
Zhang, U. N., & Zhang, W. (2005). Investigation the endemic fluorosis in Helongjiang Province in 2004, China. Chinese Journal of Endemiol, 24(4), 436 (in Chinese).
Zhao, H. L., Gao, J., Meng, K., & Pan, F. (2008). Hygienic evaluation of drinking water in Daxing District of Beijing. Capital Journal of Public Health, 2(2), 84–87 (in Chinese).
Zhu, M. X., Ding, K. Y., Jiang, X., & Wang, H. H. (2007). Investigation on co-sorption and desorption of fluoride and phosphate in a red soil of China. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 183, 455–465.
Acknowledgments
We thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41071158) and the Key Project of Chinese Ministry of Education (210097) for financially supporting this work. We also gratefully acknowledge the anonymous reviewers who provided valuable comments and suggestions for improving this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Hj., Jin, Yq. & Wei, Jl. Health risk assessment of fluoride in drinking water from Anhui Province in China. Environ Monit Assess 185, 3687–3695 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2820-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2820-9