Abstract
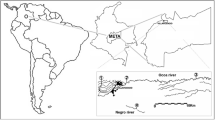
Aquatic environmental pollution may cause biodiversity loss. Thus, monitoring studies are very important because fish health reflects both quality and sustainability of the environment, as well as of the individuals that live there. In the present report, genetic biomarkers (piscine micronucleus test; comet assay with blood, liver, and kidney cells) were used in specimens of Astyanax sp. to analyze the contamination level of the Cangüiri Farm through biomonitoring. The Cangüiri Farm, the old school farm of the Federal University of Paraná, is inside the Iraí River Environment Preservation Area, created in 1996 to preserve the sources of public water supply in Curitiba and metropolitan area. We verified that the fishes collected within the Cangüiri Farm area presented high damage levels, showing more environment contamination when compared to the specimens collected in the Costa Ecologic Park, used as reference in the present report. The results indicate that the Cangüiri Farm, which is inside an environment protection area, created especially for the protection of the fountainhead for water supply, may be contaminated. These toxic residues, which were remarkably persistent in the environment, are possibly derived from agricultural activities in the wider area. Thus, we suggest the analysis of the area with other biomarkers and for a longer time period.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agostinho, A. A., & Gomes, L. C. (1997). Reservatório de Segredo: Bases ecológicas para o manejo. Maringá: EDUEM.
Andreoli, C. V., & Carneiro, C. (2005). Gestão Integrada de Mananciais de Abastecimento Eutrofizados. Finep: SANEPAR.
Andreoli, C. V., Dalarmi, O., Lara, A. I., & Andreoli, F. N. (1999). Limites ao desenvolvimento da região metropolitana de Curitiba impostos pela escassez de água. Sanare: Revista Técnica Da Sanepar, 12, 31–42.
ANVISA (2006) Rev. Saúde Pública. 40(2), 361–363.
Ayllon, F., & Garcia-Vazquez, E. (2000). Induction of micronuclei and other nuclear abnormalities in European minnow Phoxinus phoxinus and mollie Poecilia latipinna: An assessment of the fish micronucleus test. Mutation Research, 467, 177–186.
Batzias, F. A., & Siontorou, C. (2006). A knowledge-based approach to environmental biomonitoring. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 123, 167–197.
Belpaeme, K., Cooreman, K., & Kirsch-Volders, M. (1998). Development and validation of the in vivo alkaline comet assay for detecting genomic damage in marine flatfish. Mutation Research, 415(3), 167–184.
Bertotti, L.G., & Santos, A.F. (2004). Caracterização sócio-ambiental da área de proteção ambiental do Iraí/PR. Anais do Workshop Regional de Geografia e mudanças ambientais. Universidade Estadual do Centro-Oeste. Disponível em http://www.unicentro.br/editora/anais/workgeo/11º%20Artigo%20(103-112).pdf. Accessed 19 July 2012.
Carrasco, K. R., Tilbury, K. L., & Myers, M. S. (1990). Assessment of the piscine micronucleus test as in situ biological indicator of chemical contaminant effects. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 47, 2123–2136.
Collins, A., Dušinská, M., Franklin, M., Somorovská, M., Petrovská, H., Duthie, S., et al. (1997). Comet assay in human biomonitoring studies: Reliability, validation, and applications. Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, 30(2), 139–146.
Costa, J. R. M., Mela, M., Assis, H. C. S., Pelletier, É., Randi, M. A. F., & Oliveira-Ribeiro, C. A. (2007). Enzymatic inhibition and morphological changes in Hoplias malabaricus from dietary exposure to lead(II) or methylmercury. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 67, 82–88.
Dixon, D. R., Pruski, A. M., Dixon, L. R., & Jha, A. N. (2002). Marine invertebrate eco-genotoxicology: A methodological overview. Mutagenesis, 17, 495–507.
Everaarts, J. M., Sleiderink, H. M., den Besten, P. J., Halbrook, R. S., & Shugart, L. R. (1994). Molecular responses as indicators of marine pollution: DNA damage and enzyme induction in Limanda limanda and Asterias rubens. Environmental Health Perspective, 102(Suppl 12), 37–43.
Garutti, V., & Britski, H. A. (2000). Descrição de uma espécie nova de Astyanax (Teleostei: Characidae) da bacia do alto rio Paraná e considerações sobre as demais espécies do gênero na bacia. Comum Mus Ciênc Tecnol PUCRS Sér Zool, 13, 65–88.
Godoy, M. P. (1975). Peixes do Brasil. Subordem Characidade, Ed. Franciscana, São Paulo, 4. p. 847.
Goksoyr, A., Anderson, T., Buhler, D. R., Stegeman, J. J., Williams, D. E., & Forlin, L. (1991). Immunochemical cross-reactivity os β-naphthoflavone-inducible cytocrome P450 in liver microsomes from different fish species and rat. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 9, 1–13.
Grisolia, C. K., & Cordeiro, C. M. T. (2000). Variability in micronucleus induction with different mutagens applied to several species of fish. Genetics and Molecular Biology, 23, 235–239.
Hartmann, A., Elhajouji, A., Kiskinis, E., Poetter, F., Martus, H. J., Fjallman, A., et al. (2001). Use of the alkaline comet assay for industrial genotoxicity screening: Comparative investigation with the micronucleus test. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 39, 843–858.
Heddle, J. A. (1973). A rapid in vivo test for chromosome damage. Mutation Research, 18, 187–192.
Hernando, M. D., Ferrer, I., Agüera, A., & Fernandez-Alba, A. R. (2005). Evaluation of pesticides in wastewaters, a combined (chemical and biological) analytical approach. The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry, 5(Part O), 53–77. doi:10.1007/b98607.
IAP. (2010). Instituto Ambiental do Paraná. Relatório da qualidade das águas dos rios da RMC—2005–2009. IAP; Curitiba, Disponível em: http://www.iap.pr.gov.br/arquivos/File/boletins/RELATORIO_AGUA/relatorio_RIOS_2005_2009.pdf. Accessed 19 July 2012.
Kim, I. Y., & Hyun, C. K. (2006). Comparative evaluation of the alkaline comet assay with the micronucleus test for genotoxicity monitoring using aquatic organisms. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 64, 288–297.
Klobucar, G. I. V., Pavlica, M., Erben, R., & Papes, D. (2003). Application of the micronucleus and comet assays to mussel Dreissena polymorpha haemocytes for genotoxicity monitoring of freshwater environments. Aquatic Toxicology, 64, 15–23.
Lemos, N. G., Dias, A. L., Silva-Souza, A. T., & Mantovani, M. S. (2005). Evaluation of environmental waters using the comet assay in Tilapia rendalli. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 19, 197–201.
Livingstone, D. R. (1993). Biotechnology and pollution monitoring: Use of molecular biomarker in the aquatic environment. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 57, 195–211.
Misra, V., & Pandey, S. D. (2005). Hazardous waste, impact on health and environment and strategies for management: An Indian perspective. Environment International, 31, 417–431.
Mitchelmore, C. L., & Chipman, J. K. (1998). DNA strand breakage in aquatic organisms and the potential value of the comet assay in environmental monitoring. Mutation Research: Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis, 399, 135–147.
Nacci, D. E., Cayula, S., & Jackim, E. (1996). Detection of DNA damage in individual cells from marine organisms using the single cell gel assay. Aquatic Toxicology, 35, 197–210.
Nascimento, L.A., Lingnau, C., & Stolle, L. (2007). Diagnóstico da Reserva Legal e Área de Preservação Permanente em uma propriedade rural Estação Experimental Cangüiri da Universidade Federal do Paraná, 2007, Anais XIII Simpósio Brasileiro de Sensoriamento Remoto, Florianópolis, Brasil, INPE, p. 4081–4087. Disponível em: http://marte.dpi.inpe.br/col/dpi.inpe.br/sbsr@80/2006/11.15.22.38/doc/4081-4087.pdf. Accessed 19 July 2012.
Porto, J. I. R., Araújo, C. S. O., & Feldberg, E. (2005). Mutagenic effects of mercury pollution as revealed by micronucleus test on three Amazonian fish species. Environmental Research, 97, 287–292.
Rodriguez-Cea, A., Ayllon, F., & Garcia-Vazquez, E. (2003). Micronucleus test in freshwater fish species: An evaluation of its sensitivity for application in field surveys. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 56, 442–448.
Sanchez-Galan, S., Linde, A. R., & Garcia-Vazquez, E. (1999). Brown trout and European minnow as target species for genotoxicity tests: Differential sensitivity to heavy metals. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 43, 301–304.
Santos, E. (1981). Peixes de água doce, Ed. Itatiaia, Belo Horizonte.
Schmid, W. (1975). The micronucleus test. Mutation Research, 31, 9–15.
Setti, A. A. (1998). Diagnóstico sobre a situação dos mananciais dos 20 municípios selecionados dos Estados do Acre, Pará, Ceará, Pernambuco, Minas Gerais, Rio de Janeiro, Paraná, Rio Grande do Sul, Mato Grosso do Sul e Goiás e Proposta de Estruturação do Programa de Preservação e Conservação de Mananciais. Relatório Técnico: PNMA, Contrato n° 96/9596.
Speit, G., & Hartmann, A. (1999). The comet assay (single-cell gel test). In D. S. Henderson (Ed.), Methods in molecular biology (DNA repair protocols: Eukaryotic systems, Vol. 113, pp. 203–212). Totowa: Human Press.
Thompson, H. M., Langton, S. D., & Hart, A. D. M. (1995). Prediction of inter-species differences in the toxicity of organophosphorus pesticides to wildlife—A biochemical approach. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, 111C, 1–12.
Van Der Oost, R., Beyer, J., & Vermeulen, N. P. E. (2003). Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in environmental risk assessment: A review. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 13, 57–149.
von Sperling, E. (1999). Morfologia de lagos e represas. Belo Horizonte: DESA/UFMG.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank CNPq, CAPES, and the Aquatóxi group.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramsdorf, W.A., Vicari, T., de Almeida, M.I.M. et al. Handling of Astyanax sp. for biomonitoring in Cangüiri Farm within a fountainhead (Iraí River Environment Preservation Area) through the use of genetic biomarkers. Environ Monit Assess 184, 5841–5849 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2752-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2752-4