Abstract
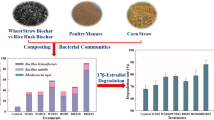
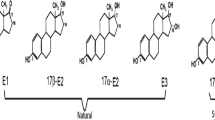
The presence of natural estrogen hormones as trace concentrations in the environment has been reported by many researchers and is of growing concern due to its possible adverse effects on the ecosystem. In this study, municipal biosolids, poultry manure (PM) and cow manure (CM), and spent mushroom compost (SMC) were analyzed for the presence of seven estrogen hormones. 17α-estradiol, 17β-estradiol, 17α-dihydroequilin, and estrone were detected in the sampled biosolids and manures at concentrations ranging from 6 to 462 ng/g of dry solids. 17α-estradiol, 17β-estradiol, and estrone were also detected in SMC at concentrations ranging from 4 to 28 ng/g of dry solids. Desorption experiments were simulated in the laboratory using deionized water (milli-Q), and the aqueous phase was examined for the presence of estrogen hormones to determine their desorption potential. Very low desorption of 0.4% and 0.2% estrogen hormones was observed from municipal biosolids and SMC, respectively. An estimate of total estrogen contribution from different solid waste sources is reported. Animal manures (PM and CM) contribute to a significant load of estrogen hormones in the natural environment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Mushroom Institute (2006). Applying mushroom compost to corn crops. In American Mushroom Institute. www.mushroomcompost.org/corn.pdf.
Andrew, D. E., & Mary Ann, H. F. (1995). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (19th ed.). American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation.
Baronti, C., Curini, R., D’Ascenzo, G., Di Corcia, A., Gentili, A., & Samperi, R. (2000). Monitoring natural and synthetic estrogens at activated sludge sewage treatment plants and in a receiving river water. Environmental Science & Technology, 34(24), 5059–5066.
Batziaka, V., Fytianos, K., & Voudrias, E. (2008). Leaching of nitrogen, phosphorus, TOC and COD from the biosolids of the municipal wastewater treatment plant of Thessaloniki. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 140(1–3), 331–338.
Chimchirian, R. F., Suri, R. P., & Fu, H. (2007). Free synthetic and natural estrogen hormones in influent and effluent of three municipal wastewater treatment plants. Water Environment Research, 79(9), 969–974.
Cromwell, G. L., Stahly, T. S., Coffey, R. D., Monegue, H. J., & Randolph, J. H. (1993). Efficacy of phytase in improving the bioavailability of phosphorus in soybean-meal and corn-soybean meal diets for pigs. Journal of Animal Science, 71(7), 1831–1840.
D’ascenzo, G., Di Corcia, A., Gentili, A., Mancini, R., Mastropasqua, R., Nazzari, M., et al. (2003). Fate of natural estrogen conjugates in municipal sewage transport and treatment facilities. Science of the Total Environment, 302(1–3), 199–209.
Desbrow, C., Routledge, E. J., Brighty, G. C., Sumpter, J. P., & Waldock, M. (1998). Identification of estrogenic chemicals in STW effluent. 1. Chemical fractionation and in vitro biological screening. Environmental Science & Technology, 32(11), 1549–1558.
Donald, D. D., Larry, J. K., Kristen, A., & Harpster, T. L. (2004). Artillery Fungus Sporulation on 27 different Mulches—A field study. Departments of Plant Pathology and Horticulture, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA.
Esperanza, M., Suidan, M. T., Nishimura, F., Wang, Z. M., & Sorial, G. A. (2004). Determination of sex hormones and nonylphenol ethoxylates in the aqueous matrixes of two pilot-scale municipal wastewater treatment plants. Environmental Science & Technology, 38(11), 3028–3035.
Finlay-Moore, O., Hartel, P. G., & Cabrera, M. L. (2000). 17ß-estradiol and testosterone in soil and runoff from grasslands amended with broiler litter. Journal of Environmental Quality, 29(5), 1604–1611.
Hanselman, T. A., Graetz, D. A., & Wilkie, A. C. (2003). Manure-borne estrogens as potential environmental contaminants: A review. Environmental Science & Technology, 37(24), 5471–5478.
Holbrook, R. D., Novak, J. T., Grizzard, T. J., & Love, N. G. (2002). Estrogen receptor agonist fate during wastewater and biosolids treatment processes: A mass balance analysis. Environmental Science & Technology, 36(21), 4533–4539.
Kjaer, J., Olsen, P., Bach, K., Barlebo, H. C., Ingerslev, F., Hansen, M., et al. (2007). Leaching of estrogenic hormones from manure-treated structured soils. Environmental Science & Technology, 41(11), 3911–3917.
Kolok, A. S., Snow, D. D., Kohno, S., Sellin, M. K., & Guillette, L. J. (2007). Occurrence and biological effect of exogenous steroids in the Elkhorn River, Nebraska, USA. Science of the Total Environment, 388(1–3), 104–115.
Kolpin, D. W., Furlong, E. T., Meyer, M. T., Thurman, E. M., Zaugg, S. D., Barber, L. B., et al. (2002). Pharmaceuticals, hormones, and other organic wastewater contaminants in U.S. streams, A national reconnaissance. Environmental Science & Technology, 36(6), 1202–1211.
Labadie, P., & Hill, E. M. (2007). Analysis of estrogens in river sediments by liquid chromatography - electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry — Comparison of tandem mass spectrometry and time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A, 1141(2), 174–181.
Lai, K. M., Johnson, K. L., Scrimshaw, M. D., & Lester, J. N. (2000). Binding of waterborne steroid estrogens to solid phases in river and estuarine systems. Environmental Science & Technology, 34(18), 3890–3894.
Lai, K. M., Scrimshaw, M. D., and Lester, J. N. (2002). Prediction of the bioaccumulation factors and body burden of natural and synthetic estrogens in aquatic organisms in the river systems. Science of the Total Environment, 289(1–3), 159–168.
Lange, I. G., Daxenberger, A., Schiffer, B., Witters, H., Ibarreta, D., & Meyer, H. H. D. (2002). Sex hormones originating from different livestock production systems: fate and potential disrupting activity in the environment. Analytica Chimica Acta, 473(1–2), 27–37.
Larsson, D. G. J., Adolfsson-Erici, M., Parkkonen, J., Pettersson, M., Berg, A. H., Olsson, P. E., et al. (1999). Ethinyloestradiol—an undesired fish contraceptive? Aquatic Toxicology, 45(2–3), 91–97.
Lorenzen, A., Hendel, J. G., Conn, K. L., Bittman, S., Kwabiah, A. B., Lazarovitz, G., et al. (2004). Survey of hormone activities in municipal biosolids and animal manures. Environmental Toxicology, 19(3), 216–225.
Lucas, S. D., & Jones, D. L. (2009). Urine enhances the leaching and persistence of estrogens in soil. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 41, 236–242.
Matejicek, D., Houserova, P., & Kuban, V. (2007). Combined isolation and purification procedures prior to the high-performance liquid chromatographic-ion-trap tandem mass spectrometric determination of estrogens and their conjugates in river sediments. Journal of Chromatography A, 1171(1–2), 80–89.
Raman, D. R., Williams, E. L., Layton, A. C., Burns, R. T., Easter, J. P., Daugherty, A. S., et al. (2004). Estrogen content of dairy and swine wastes. Environmental Science & Technology, 38(13), 3567–3573.
Robert, L. K., Charles, H. L., David, C. M., & Noel, G. (2000). Manure nutrients relative to the capacity of cropland and pastureland to assimilate nutrients: Spatial and temporal trends for the US. USDA Census of Agriculture.
Roefer, P., Snyder, S., Zegers, R. E., Rexing, D. J., & Fronk, J. L. (2000). Endocrine-disrupting chemicals in a source water. Journal American Water Works Association, 92(8), 52–58.
Routledge, E. J., Sheahan, D., Desbrow, C., Brighty, G. C., Waldock, M., & Sumpter, J. P. (1998). Identification of estrogenic chemicals in STW effluent. 2. In vivo responses in trout and roach. Environmental Science & Technology, 32(11), 1559–1565.
Shore, L., & Shemesh, M. (1993). Analysis of testosterone levels in chicken manure. Israel Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 48, 35–37.
Shore, L. S., & Shemesh, M. (2003). Naturally produced steroid hormones and their release into the environment*. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 75(11–12), 1859–1871.
Spiro, E. S. (2006). Economic Impact of the mushroom industry in Chester county, PA. Mushroom Farm Community. http://www.mushroomfarmcommunity.org/truimg/EconomicImpactReport.pdf.
Suri, R. P. S., Singh, T. S., & Abburi, S. (2010). Influence of alkalinity and salinity on the sonochemical degradation of estrogen hormones in aqueous solution. Environmental Science & Technology, 44(4), 1373–1379.
Swartz, C. H., Reddy, S., Benotti, M. J., Yin, H. F., Barber, L. B., Brownawell, B. J., et al. (2006). Steroid estrogens, nonylphenol ethoxylate metabolites, and other wastewater contaminants in groundwater affected by a residential septic system on Cape Cod, MA. Environmental Science & Technology, 40(16), 4894–4902.
Ternes, T. A., Stumpf, M., Mueller, J., Haberer, K., Wilken, R. D., & Servos, M. (1999). Behavior and occurrence of estrogens in municipal sewage treatment plants—I. Investigations in Germany, Canada and Brazil. Science of the Total Environment, 225(1–2), 81–90.
Ternes, T. A., Andersen, H., Gilberg, D., & Bonerz, M. (2002). Determination of estrogens in sludge and sediments by liquid extraction and GC/MS/MS. Analytical Chemistry, 74(14), 3498–3504.
US-EPA (1999). National Sewage Sludge Survey (NSSS): Biosolids Generation, Use, and Disposal in the US. Office of Solid Waste, EPA530-R-99-009.
US-EPA (2009). Targeted National Sewage Sludge Survey Sampling and Analysis Technical Report. Office of Water, Washington, D.C., EPA-822-R-08-016.
US-FDA (2002). The use of steroid hormones for growth promotion in food producing animals. Center for Veterinary Medicine, U.S. Food and Drug Administration. http://www.fda.gov/AnimalVeterinary/SafetyHealth/ProductSafetyInformation/ucm055436.htm.
Velicu, M., & Suri, R. (2009). Presence of steroid hormones and antibiotics in surface water of agricultural, suburban and mixed-use areas. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 154(1–4), 349–359.
Wenzel, A., Kuechler, T., & Mueller, J. (1998). Konzentrationen Oestrogen Wirksamer Substanzen in Um weltmedien. 216 02 011/11, German Environmental Protection Agency, Project No 216 02 011/11.
Wicks, C., Kelley, C., & Peterson, E. (2004). Estrogen in a karstic aquifer. Ground Water, 42(3), 384–389.
Wuest, P. J., Fahy, h. K., & Fahy, J. (1994). Use of spent mushroom substrate for corn production and its effect on surface water quality.” Spent Mushroom Substrate Symposium. American Mushroom Institute, Philadelphia, PA.
Xia, K., Bhandari, A., Das, K., & Pillar, G. (2005). Occurrence and fate of pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) in biosolids. Journal of Environmental Quality, 34, 91–104.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andaluri, G., Suri, R.P.S. & Kumar, K. Occurrence of estrogen hormones in biosolids, animal manure and mushroom compost. Environ Monit Assess 184, 1197–1205 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2032-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2032-8