Abstract
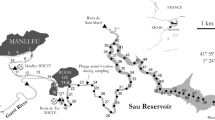
In contrast to extensive studies of dissolved organic matters (DOM) in natural lakes, the distributions and the characteristics of DOM in artificial dam reservoirs have not been well documented despite a growing demand for the construction worldwide. For this study, spatial variations in the concentrations and the characteristics of DOM in Lake Paldang, a large river-type dam reservoir, were investigated using the concentrations, the specific UV absorbance (SUVA), the synchronous fluorescence spectra and the molecular weight (MWw) values. In addition, environmental factors determining the DOM spatial distribution were examined based on a principal component analysis (PCA). Variations in the DOM characteristics were greater than those for the concentrations (1.1–2.4 mg C/L). In contrast to typical lakes, vertical variations with a depth were much smaller than those observed among horizontal sampling sites within the reservoir. Irrespective of the depth, four individual sampling locations were easily distinguished by comparison of some selected DOM characteristics. The protein-like fluorescence (PLF), MWw and SUVA values observed at the location near the dam exceeded the corresponding values for the sampling locations near major influent rivers, suggesting that, even for the river-type dam reservoir, the downstream DOM characteristics may be governed by in-lake DOM production processes such as the release from sediments and algal activities. The results of principal component analysis (PCA) revealed that approximately 61% of the variance in DOM distribution might be explained by allochthonous/autochthonous carbon sources and predominant presence of either total nitrogen or total phosphorous over the other.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (American Public Health Association), AWWA (American Water Works Association), & WEF (Water Environment Federation) (2005). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (20th ed.). Washington DC, USA.
Baker, A. (2001). Fluorescence excitation–emission matrix characterization of some sewage-impacted rivers. Environmental Science & Technology, 35(5), 948–953.
Chen, Y., & ZW, L. (2005). Analysis and evaluation of water environmental carrying capacity in Three Gorges Reservoir. Advances in Water Science, 16(5), 715–719.
Chen, J., LeBoef, E. J., Dai, S., & Gu, B. H. (2003). Fluorescence spectroscopic studies of natural organic matter fractions. Chemosphere, 50(5), 639–647.
Chen, Z. Q., Hu, C. M., Comny, R. N., Muller-Karger, F., & Swarzenski, P. (2007). Colored dissolved organic matter in Tampa Bay, Florida. Marine Chemistry, 104(1–2), 98–109.
Cortes, R. M. V., Ferreira, M. T., Oliveira, S. V., & Oliveira, D. (2002). Macroinvertebrate community structure in a regulated river segment with different flow conditions. River Research and Applications, 18(4), 367–382.
Dahl, M., & Wilson, D. I. (2004). Is Lake Vanern well mixed? A statistical procedure for selecting model structure and resolution. Journal of Great Lakes Research, 30(2), 267–276.
Fearnside, P. (2001). Environmental impacts of Brazil’s Tucuruí Dam, unlearned lessons for hydroelectric development in Amazonia. Environmental Management, 27(3), 377–396.
Fuentes, M., Gonzalez-Gaitano, G., & Garcia-Mina, J. M. (2006). The usefulness of UV–visible and fluorescence spectroscopies to study the chemical nature of humic substances from soils and composts. Organic Geochemistry, 37(12), 1949–1959.
Gandhi, N., Bhavsar, S. P., Diamond, M. L., & Kuwabara, J. S. (2007). Development of a mercury speciation, fate, and biotic uptake (biotranspec) model, application to lahontan reservoir (Nevada, USA). Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 26(11), 2260–2273.
Hedges, J. I., Keil, R. G., & Benner, R. (1997). What happens to terrestrial organic matter in the ocean? Organic Geochemistry, 27(5–6), 195–212.
Her, N., Amy, G., Park, H. R., & Song, M. (2004). Characterizing algogenic organic matter (AOM) and evaluating associated NF membrane fouling. Water Research, 38(6), 1427–1438.
Hur, J. (2010). Microbial changes in selected operational descriptors of dissolved organic matters from various sources in a watershed. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 215, 465–476.
Hur, J., & Schlautman, M. A. (2003). Molecular weight fractionation of humic substances by adsorption onto minerals. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 264(2), 313–321.
Hur, J., Jung, N. C., & Shin, J. K. (2007). Spectroscopic distribution of dissolved organic matter in a dam reservoir impacted by turbid storm runoff. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 133(1–3), 53–67.
Hur, J., Lee, D. H., & Shin, H. S. (2009). Comparison of the structural, spectroscopic and phenanthrene binding characteristics of humic acids from soils and lake sediments. Organic Geochemistry, 40(10), 1091–1099.
Hwang, S.-J., Kwun, S.-K., & Yoon, C.-G. (2003). Water quality and limnology of Korean reservoirs. Paddy and Water Environment, 1(1), 43–52.
Imai, A., Fukushima, T., Matsushige, K., & Hwan, K. Y. (2001). Fractionation and characterization of dissolved organic matter in a shallow eutrophic lake, its inflowing rivers, and other organic matter sources. Water Research, 35(17), 4019–4028.
Jaffé, R., Boyer, J. N., Lu, X., Maie, N., Yang, C., Scully, N. M., et al. (2004). Source characterization of dissolved organic matter in a subtropical mangrove-dominated estuary by fluorescence analysis. Marine Chemistry, 84(3–4), 195–210.
Kalbitz, K., Schwesig, D., Schmerwitz, J., Kaiser, K., Haumaier, L., Glaser, B., et al. (2003). Changes in properties of soil-derived dissolved organic matter induced by biodegradation. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 35(8), 1129–1142.
Kaplan, L. A., & Newbold, J. D. (1993). Biogeochemistry of dissolved organic carbon entering streams. In T. E. Ford (Ed.), Aquatic microbiology, an ecological approach (pp. 139–165). Blackwell.
Kendall, C., Silva, S. R., & Kelly, V. J. (2001). Carbon and nitrogen isotopic compositions of particulate organic matter in four large river systems across the United States. Hydrological Processes, 15(7), 1301–1346.
Kim, T., Heo, J. H., & Jeong, C. S. (2006). Multireservoir system optimization in the Han River basin using multi-objective genetic algorithms. Hydrological Processes, 20(9), 2057–2075.
Kalff, J. (2001). Limnology (pp. 1–592). Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall.
Lee, K.-S., Bong, Y.-S., Lee, D., Kim, Y., & Kim, K. (2008). Tracing the sources of nitrate in the Han River watershed in Korea, using δ15N-NO\(_{3}^{\,\,-}\) and δ18O-NO\(_{3}^{\,\,-}\) values. Science of the Total Environment, 395(2–3), 117–124.
Li, W., Wu, F. C., Liu, C. Q., Fu, P. Q., Wang, J., Mei, Y., et al. (2008). Temporal and spatial distributions of dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen in two small lakes on the Southwestern China Plateau. Limnology, 9(2), 163–171.
Lieberman, D. M., Horn, M. J., & Duffy, S. (2001). Effects of a temperature control device on nutrients, POM and plankton in the tailwaters below Shasta Lake, California. Hydrobiologia, 452(1–3), 191–202.
Na, E. H., & Park, S. S. (2006). A hydrodynamic and water quality modeling study of spatial and temporal patterns of phytoplankton growth in a stratified lake with buoyant incoming flow. Ecological Modelling, 199(3), 298–314.
Nguyen, H. V.-M., Hur, J., & Shin, H.-S. (2010). Changes in spectroscopic and molecular weight characteristics of dissolved organic matter in a river during a storm event. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 212, 395–406.
Park, H. K., Byeon, M. S., Shin, Y. N., & Jung, D. I. (2009). Sources and spatial and temporal characteristics of organic carbon in two large reservoirs with contrasting hydrologic characteristics. Water Resources Research, 45, W11418.
Sharp, E. L., Parsons, S. A., & Jefferson, B. (2004). The effects of changing NOM composition and characteristics on coagulation performance, optimisation and control. Water Science and Technology, Water Supply, 4(4), 95–102.
Servais, P., Barillier, A., & Garnier, J. (1995). Determination of the biodegradable fraction of dissolved and particulate organic carbon in waters. Annales de Limnologie, 31(1), 75–80.
Sodré, F. F., dos Anjos, V. E., Prestes, E. C., & Grassi, M. T. (2005). Identification of copper sources in urban surface waters using the principal component analysis based on aquatic parameters. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 7(6), 581–585.
Sommaruga, R., & Augustin, G. (2006). Seasonality in UV transparency of an alpine lake is associated to changes in phytoplankton biomass. Aquatic Sciences, 68(2), 129–141.
Sugiyama, Y., Anegawa, A., Kumagai, T., Harita, Y., Hori, T., & Sugiyama, M. (2004). Distribution of dissolved organic carbon in lakes of different trophic types. Limnology, 5(3), 165–176.
Sugiyama, Y., Anegawa, A., Inokuchi, H., & Kumagai, T. (2005). Distribution of dissolved organic carbon and dissolved fulvic acid in mesotrophic Lake Biwa, Japan. Limnology, 6(3), 161–168.
Sullivan, B. E., Prahl, F. G., Small, L. F., & Covert, P. A. (2001). Seasonality of phytoplankton production in the Columbia River, a natural or anthropogenic pattern? Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 65(7), 1125–1139.
Tan, Y. R., Kilduff, J. E., Kitis, M., & Karanfil, T. (2005). Dissolved organic matter removal and disinfection byproduct formation control using ion exchange. Desalination, 176(1–3), 189–200.
Wang, Z., Wu, Z., & Tang, S. (2009). Characterization of dissolved organic matter in a submerged membrane bioreactor by using three-dimensional excitation and emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopy. Water Research, 43(6), 1533–1540.
Wei, G. L., Yang, Z. F., Cui, B. S., Li, B., Chen, H., Bai, J. H., et al. (2009). Impact of dam construction on water quality and water self-purification capacity of the Lancang River, China. Water Resources Management, 23(9), 1763–1780.
Weishaar, J. L., Aiken, G. R., Bergamaschi, B. A., Fram, M. S., Fujii, R., & Mopper, K. (2003). Evaluation of specific ultraviolet absorbance as an indicator of the chemical composition and reactivity of dissolved organic carbon. Environmental Science & Technology, 37(20), 4702–4708.
Wetzel, R. (2001). Limnology, lake and river ecosystems. New York: Academic.
World Commission on Dams (2000). Dams and development, a new framework for decision-making (pp. 8–10, 75–293). Earthscan. London, UK: Earthscan.
Yoshioka, T., Ueda, S., Khodzher, T., Bashenkhaeva, N., Korovyakova, I., Sorokovikova, L., et al. (2002). Distribution of dissolved organic carbon in Lake Baikal and its watershed. Limnology, 3(3), 159–168.
Zelano, V., Zambrotta, M., Defilippi, A., & Torazzo, A. (2005). Water quality of two glacial alpine Italian lakes. Annali di chimica, 95(11–12), 845–856.
Zhou, Q. H., Cabaniss, S. E., & Maurice, P. A. (2000). Considerations in the use of high-pressure size exclusion chromatography (HPSEC) for determining molecular weights of aquatic humic substances. Water Research, 34(14), 3505–3514.
Zhuo, P. J., & Zhao, W. H. (2009). Fluorescence characterization of dissolved organic matter in the east China Sea after diatom red tide dispersion. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 29(5), 1349–1353.
Zsolnay, A., Baigar, E., Jimenez, M., Steinweg, B., & Saccomandi, F. (1999). Differentiating with fluorescence spectroscopy the sources of dissolved organic matter in soils subjected to drying. Chemosphere, 38(1), 45–50.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, H.VM., Shin, JK. & Hur, J. Multivariate analysis for spatial distribution of dissolved organic matters in a large river-type dam reservoir. Environ Monit Assess 183, 425–436 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-1930-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-1930-0