Abstract
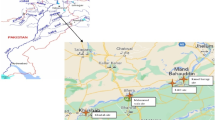
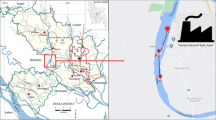
The untreated industrial and sewage wastes arising from industries and metropolitan activities make their passage to the River Ravi, Pakistan, where Balloki Headworks is one of the major sites of effluent concentration. This study was designed to evaluate the concentration of various toxic elements in fishes of that area compared to a nearby fish farm. The concentrations of heavy metals, such as As, Cd, Cu, Pb, Hg, and Zn, and electrolytes Ca, K, and Na were determined in different edible and non-edible fresh water fish varieties. Fish samples were collected from two selected sites and were analyzed for aforementioned elements. Higher levels of As (35.74–45.33 ppm), Cd (0.35–0.45 ppm), Pb (2.1–3.0 ppm), Hg (83.03–92.35 ppm) while normal levels of Zn (37.85–40.74 ppm) and Cu (1.39–2.93 ppm) were observed. Mercury, higher levels of which trigger cough, impairment of pulmonary function, and psychotic reactions, was significantly higher in all studied categories. At the sites under study, there has been observed alarming levels of toxic metals which are needed to be monitored regularly.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altindag, A., & Yigit, S. (2005). Assessment of heavy metal concentrations in the food web of lake Beysehir, Turkey. Chemosphere, 60(4), 552–556.
Arain, M. B., Kazi, T. G., Jamali, M. K., Jalbani, N., Afridi, H. I., Sarfraz, R. A., et al. (2007). Determination of toxic elements in muscle tissues of five fish species using ultrasound-assisted pseudodigestion by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrophotometry: Optimization study. Spectroscopy Letters, 40(6), 861–878.
Ashraf, M., & Jaffar, M. (1988). Correlation between some selected trace metal concentrations in six species of fish from the Arabian Sea. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 41(1), 86–93.
Ashraf, W., Seddigi, Z., Abulkibash, A., & Khalid, M. (2006). Levels of selected metals in canned fish consumed in Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 117(1), 271–279.
Boncompagni, E., Muhammad, A., Jabeen, R., Orvini, E., Gandini, C., Sanpera, C., et al. (2003). Egrets as monitors of trace-metal contamination in Wetlands of Pakistan. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 45(3), 399–406.
Canli, M., Kalay, M., & Ay, Ö. (2001). Metal (Cd, Pb, Cu, Zn, Fe, Cr, Ni) concentrations in tissues of a fish Sardina pilchardus and a prawn Peaenus japonicus from three stations on the Mediterranean Sea. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 67(1), 75–82.
Cohen, T., Que Hee, S. S., & Ambrose, R. F. (2001). Trace metals in fish and invertebrates of three California Coastal Wetlands. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 42(3), 224–232.
Farooqi, A., Masuda, H., & Firdous, N. (2007). Toxic fluoride and arsenic contaminated groundwater in the Lahore and Kasur districts, Punjab, Pakistan and possible contaminant sources. Environmental Pollution, 145, 839–849.
Farooqi, A., Masuda, H., Siddiqui, R., & Naseem, M. (2009). Sources of arsenic and fluoride in highly contaminated soils causing groundwater contamination in Punjab, Pakistan. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 56, 693–706.
Farkas, A., Salanki, J., & Varanka, I. (2000). Heavy metal concentrations in fish of Lake Balaton. Lakes & Reservoirs: Research & Management, 5(4), 271–279.
Fidan, A. F., Ciğerci, İ. H., Konuk, M., Küçükkurt, İ., Aslan, R., & Dündar, Y. (2008). Determination of some heavy metal levels and oxidative status in Carassius carassius L., 1758 from Eber Lake. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 147(1), 35–41.
Gale, N., Adams, C., Wixson, B., Loftin, K. & Huang, Y.-W. (2004). Lead, zinc, copper, and cadmium in fish and sediments from the big river and flat river creek of Missouri’s old lead belt. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 26(1), 37–49.
Heiny, J. S., & Tate, C. M. (1997). Concentration, distribution, and comparison of selected trace elements in bed sediment and fish tissue in the South Platte River Basin, U.S.A., 1992–1993. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 32(3), 246–259.
Javed, M. (2005). Heavy metal contamination of freshwater fish and bed sediments in the River Ravi Stretch and related tributaries. Pakistan Journal of Biological Sciences, 8(10), 1337–1341.
Leal, M. C. F., Vasconcelos, M. T., Sousa-Pinto, I., & Cabral, J. P. S. (1997). Biomonitoring with benthic macroalgae and direct assay of heavy metals in seawater of the Oporto coast (northwest Portugal). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 34(12), 1006–1015.
Murphy, B. R., Atchison, G. J., McIntosh, A. W., & Kolar, D. J. (1978). Cadmium and zinc content of fish from an industrially contaminated lake. Journal of Fish Biology, 13(3), 327–335.
Rashed, M. N. (2001). Cadmium and lead levels in fish (Tilapia nilotica) tissues as biological indicator for lake water pollution. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 68(1), 75–89.
Storelli, M. M., & Marcotrigiano, G. O. (2000). Organic and inorganic arsenic and lead in fish from the South Adriatic Sea, Italy. Food Additives and Contaminants, 17(9), 763–768.
Storelli, M. M., Ceci, E., Storelli, A., & Marcotrigiano, G. O. (2003). Polychlorinated biphenyl, heavy metal and methylmercury residues in hammerhead sharks: Contaminant status and assessment. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 46(8), 1035–1039.
Storelli, M. M., Giacominelli-Stuffler, R., Storelli, A., & Marcotrigiano, G. O. (2005). Accumulation of mercury, cadmium, lead and arsenic in swordfish and bluefin tuna from the Mediterranean Sea: A comparative study. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 50(9), 1004–1007.
Swaibuh Lwanga, M., Kansiime, F., Denny, P., & Scullion, J. (2003). Heavy metals in Lake George, Uganda, with relation to metal concentrations in tissues of common fish species. Hydrobiologia, 499(1), 83–93.
Tariq, J., & Jaffar, M. (1993). Selected trace metals in fish, sediments and water from freshwater Tarbella reservoir, Pakistan. Toxicology and Environmental Chemistry, 39, 201–205.
Tuzen, M. (2003). Determination of heavy metals in fish samples of the middle Black Sea (Turkey) by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Chemistry, 80(1), 119–123.
Vives, A. E. S., Moreira, S., Brienza, S. M. B., Zucchi, O. L. A. D., & Nascimento Filho, V. F. (2006). Analysis of fish samples for environmental monitoring and food safety assessment by synchrotron radiation total reflection X-ray fluorescence. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 270(1), 231–236.
Voegborlo, R. B., El-Methnani, A. M., & Abedin, M. Z. (1999). Mercury, cadmium and lead content of canned tuna fish. Food Chemistry, 67(4), 341–345.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-1175-3
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nawaz, S., Nagra, S.A., Saleem, Y. et al. Determination of heavy metals in fresh water fish species of the River Ravi, Pakistan compared to farmed fish varieties. Environ Monit Assess 167, 461–471 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-1064-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-1064-9