Abstract
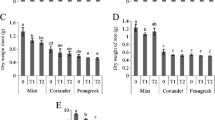
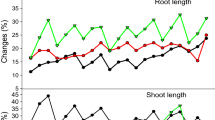
Increasing consciousness about future sustainable agriculture and hazard free food production has lead organic farming to be a globally emerging alternative farm practice. We investigated the accumulation of air-borne heavy metals in edible parts of vegetables and in cultivated soil horizon in organic farming system in a low rain fall tropical region of India. The factorial design of whole experiment consisted of six vegetable crops (tomato, egg plant, spinach, amaranthus, carrot and radish) × two treatments (organic farming in open field and organic farming in glasshouse (OFG)) × seven independent harvest of each crop. The results indicated that except for Pb, atmospheric deposition of heavy metals increased consistently on time scale. Concentrations of heavy metals in cultivated soil horizon and in edible parts of open field grown vegetables increased over time and were significantly higher than those recorded in OFG plots. Increased contents of heavy metals in open field altered soil porosity, bulk density, water holding capacity, microbial biomass carbon, substrate-induced respiration, alkaline phosphatase and fluorescein diacetate hydrolytic activities. Vegetable concentrations of heavy metal appeared in the order Zn > Pb > Cu > Ni > Cd and were maximum in leaves (spinach and amaranths) followed by fruits (tomato and egg plant) and minimum in roots (carrot and radish). Multiple regression analysis indicated that the major contribution of most heavy metals to vegetable leaves was from atmosphere. For roots however, soil appeared to be equally important. The study suggests that if the present trend of atmospheric deposition is continued, it will lead to a destabilizing effect on this sustainable agricultural practice and will increase the dietary intake of toxic metals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Khashman, O. A. (2004). Heavy metal distribution in dust and soils from the work place in Korak Industrial Estate, Jordan. Atmospheric Pollution, 38, 6803–6812.
Allen, S. E., Grimshaw, H. M., & Rowland, A. P. (1986). Chemical analysis. In P. D. Moore & S. B. Chapman (Eds.), Methods in plant ecology (pp. 285–344). Oxford, London: Blackwell.
Anderson, J. P. E., & Domsch, K. H. (1978). A physiologically active method for the quantitative measurement of microbial biomass in soils. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 10, 215–221.
Anderson, T. H., & Domsch, K. H. (1986). Carbon assimilation and microbial activity in soil. Zeifschrift fur pfanzenernahrung und Bodenkunde, 149, 457–468.
Awasthi, S. K. (2000). Prevention of food adulteration act no 37 of 1954: Central and State rules as amended for 1999. New Delhi: Ashoka.
Azimi, S., Chambier, P., Lecuyer, I., & Therenot, D. (2004). Heavy metal determination in atmospheric deposition and other fluxes in northern agrosystems. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 157, 295–313.
Azimi, S., Ludwig, A., Thevenot, D., & Colin, J. L. (2003). Trace metal determination in total atmospheric deposition in rural and urban areas. The Science of the Total Environment, 308, 247–256.
Bagatto, G., & Shorthouse, J. D. (1991). Accumulation of copper and nickel in plant tissues and in insect gall of low bush blueberry, Vaccinium angustifolium, near an ore smelter at Sudbury, Ontario, Canada. Canadian Journal of Botany, 69, 1483–1490.
Bartl, B., Hartl, W., & Horak, O. (2002). Long-term application of biowaste compost versus mineral fertilization: effects on the nutrient and heavy metal contents of soil and plants. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 165, 161–165.
Belay, A., Claassens, A. S., Wehner, F. C., & De Beer, J. M. (2001). Influence of residual manure on selected nutrient elements and microbial composition of soil under long-term crop rotation. South African Journal of Plant and Soil, 18, 1–6.
Cardelli, R., Levi–Minzi, R., Saviozzi, A., & Riffaldi, R. (2004). Organically and conventionally managed soils: biochemical characteristics. Journal of Sustainable Agriculture, 25, 63–74.
Chopin, E. I. B., & Alloway, B. J. (2007). Distribution and mobility of trace elements in soil and vegetation around the mining and smelting areas of Tharsis, Riotinto and Huelva, Iberian Pyrite Belt, S W Spain. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 182, 245–261.
Ciavatta, C., Govil, M., Antisari, V. L., & Sequi, P. (1991). Determination of organic carbon in aqueous extract of soil and fertilizers. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 22, 795–807.
Conway, G. (1997). The doubly green revolution. London: Penguin.
Cook, B. D., & Allen, D. L (1992). Dissolved organic carbon in old field soil: Total amount as a measure of available resources for soil mineralization. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 24, 585–594.
Emmerling, C., Udelhoven, T., & Schroder, D. (2001). Response of soil microbial biomass and activity of agricultural de-intensification over a 10 year period. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 33, 2105–2114.
Fowler, D., Cape, N., Coyle, M., Flechard, C., Kuylenstierna, J., Hicks, K., et al. (1999). The global exposure of forests to air pollutants. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 116, 5–32.
Gianfreda, L., & Bollag, J. M. (1996). Influence of natural and anthropogenic factors on enzyme activity in soil. In G. Stotzky & J. M. Bollag (Eds.), Soil biochemistry (pp. 123–193). New York: Marcel Dekker.
Gopalan, C., Ram Sastri, B. V., & Balasubramanian, S. C. (1991). Nutritive value of Indian foods. Hyderabad: NIN.
Goyal, S., Mishra, M. M., Hooda, I. S., & Singh, R. (1992). Organic matter–microbial biomass relationship in field experiments under tropical conditions: effects of inorganic fertilization and organic amendments. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 24, 1081–1084.
Gregorich, E. G., Caster, M. R., Angers, D. A., Monreal, C. M., & Ellert, B. H. (1994). Towards a minimum data set to assess soil organic matter quality in agricultural soils. Canadian Journal of Soil Science, 74, 367–385.
Harrison, R. M., & Chirgawi, M. B. (1989). The assessment of air and soil as contributors of some trace metals to vegetable plants. I. Use of a filtered growth cabinet. The Science of the Total Environment, 83, 13–34.
Hovmand, M. F., Tjell, J. C., & Mosback, H. (1983). Plant uptake of air borne cadmium. Environmental Pollution, 30, 27–38.
Jain, M., Kulshrestha, U. C., Sarkar, A. K., & Parashar, D. C. (2000). Influence of crustal aerosols on wet deposition at urban and rural sites in India. Atmospheric Environment, 34, 5129–5137.
Johnson, D., & Hale, B. (2004). White birch (Petula papyrifera Marshall) foliar litter decomposition in relation to trace element atmospheric inputs at metal contaminated and uncontaminated sites near Sudbury, Ontario and Rouyn Noranda, Quebec, Canada. Environmental Pollution, 127, 65–72.
Johnson, D., Leake, J. R., Lee, J. A., & Campbell, C. D. (1998). Changes in soil microbial biomass and microbial activities in response to 7 years simulated pollutant nitrogen deposition on a heathland and two grasslands. Environmental Pollution, 103, 239–250.
Kabata–Pendias, A., & Pendias, H. (1984). Trace elements in soils and plants. Boca Raton: CRC.
Kaur, R., & Rani, R. (2006). Spatial characterization and prioritization of heavy metal contaminated soil—water resources in periurban areas of national capital territory (NCT), Delhi. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 123, 233–247.
Kezyztof, L., Danutta, W., & Irena, K. (2004). Metal contamination of farming soils affected by industry. Environment International, 30, 159–165.
Kim, G., Scudlark, J. R., & Church, T. M. (2000). Atmospheric wet deposition of trace elements to Chesapeake and Delaware Bays. Atmospheric Environment, 34, 3437–3444.
Lawlor, A. J., & Tipping, E. (2003). Metals in bulk deposition and surface waters at two upland locations in Northern England. Environmental Pollution, 121, 153–167.
Liu, W. X., Li, H. H., Li, S. R., & Wang, Y. W. (2006). Heavy metal accumulation in edible vegetables cultivated in agricultural soil in the suburb of Zhengzhou city, People’s Republic of China. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 76, 163–170.
Moolennaar, S. W., Vander Zee, S. E. A. T. M., & Lexmond, Th. M. (1997). Indicators of the sustainability and heavy metal management in agro-ecosystem. The Science of the Total Environment, 201, 155–196.
Moseholm, L., Larsen, E. H., Andersen, B., & Nielsen, M. M. (1992). Atmospheric deposition of trace elements around point sources and human health risk assessment. I: impact zones near a source of lead emissions. The Science of the Total Environmemt, 126, 243–262.
Nannipieri, P., Greco, S., & Ceccanti, B. (1990). Ecological significance of the biological activity in soil. In G. Stotzky & J. M. Bollag (Eds.), Soil biochemistry (pp. 293–355). New York: Marcel Dekker.
Pandey, J. (2005). Evaluation of air pollution phytotoxicity down wind of a phosphate fertilizer factory in India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 100, 249–266.
Pandey, J., & Agrawal, M. (1994). Evaluation of air pollution phytotoxicity in a seasonally dry tropical urban environment using three woody perennials. The New Phytologist, 126, 53–61.
Pandey, J., Agrawal, M., Khanam, N., Narayan, D., & Rao, D. N. (1992). Air pollutants concentrations in Varanasi, India. Atmospheric Environment, 26B, 91–98.
Pandey, J., & Pandey, U. (1994). Evaluation of air pollution phytotoxicity in a seasonally dry tropical urban environment. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 33, 195–213.
Pandey, J., & Pandey, U. (2001). The influence of catchment on ecosystem properties of a tropical fresh water lake. Biotronics, 30, 85–92.
Powell, J. M. (1986). Manure for cropping: a case study from central Nigeria. Experimental Agriculture, 22, 15–24.
Romesh, P., Singh, M., & Subba rao, A. (2005). Organic farming: its relevance to the Indian context. Current Science, 88, 561–568.
Rosegrant, M. W., & Cline, S. A. (2004). Global food security: challenges and policy. Science, 302, 1907–1919.
Sanchez–Camazano, M., Sanchez–Martin, M. J., & Lorenzo, L. F. (1994). Lead and cadmium in soils and vegetables from urban gardens of Salamanka (Spain). The Science of the Total Envuironment, 146/147, 163–168.
Schnurer, J., & Rosswall, T. (1982). Fluorescein diacetate hydrolysis as a measure of total microbial activity in the soil and litter. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 43, 1256–1261.
Sharma, R. K., Agrawal, M., & Marshall, F. (2006). Heavy metal contamination of soil and vegetables in suburban areas of Varanasi, India. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 66, 258–266.
Sharma, K., Chaturvedi, R. K., Bharadwaj, S. M., & Sharma, K. P. (2001). Heavy metals in vegetables and cereals growing around Sanganer town, Jaipur, Rajasthan (India). Journal of Indian Botanical Society, 80, 103–108.
Singh, R. K., & Agrawal, M. (2005). Atmospheric deposition around a heavily industrialized area in a seasonally dry tropical environment of India. Environmental Pollution, 138, 142–152.
Sweet, C. W., Weiss, A., & Vermette, S. J. (1998). Atmospheric deposition of trace elements at three sites near the Great Lakes. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 103, 423–439.
Tabatabai, M. A., & Bremner, J. M. (1969). Use of p-nitrophenyl phosphate for assay of soil phosphatase activity. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 1, 301–307.
Tate, K. R., Ross, D. J., & Filtham, C. W. (1988). A direct method to estimate soil microbial biomass C: effects of experimental variables on some different calibration procedure. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 20, 329–335.
Thripathi, R. M., Raghunath, R., & Krishnamoorthy, T. M. (1997). Dietary intake of heavy metals in Bombay city, India. The Science of the Total Environment, 208, 149–159.
Tilman, D., Fargione, J., Wolff, B., D’Antonio, C., Dobson, A., Howarth, R., et al. (2001). Forecasting agriculturally driven global environmental change. Science, 292, 281–284.
Tjell, J. C., Hovmand, M. F., & Mossback, H. (1979). Atmospheric lead pollution of grass grown in a background area of Denmark. Nature, 280, 425–426.
Verloo, M., & Eeckhout, M. (1990). Metals species transportation in soil: an analytical approach. International Journal of Environmental and Analytical Chemistry, 39, 179–186.
Voutsa, D., Grimanis, A., & Samara, C. (1996). Trace elements in vegetables grown in an industrial area in relation to soil and air particulate matter. Environtal Pollution, 94, 325–335.
Voutsa, D., & Samara, C. (1998). Dietary intake of trace elements and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons via vegetables grown in an industrial Greek area. The Science of the Total Environment, 218, 203–216.
Wardle, D. A. (1998). Control of temporal variability of the soil microbial biomass: a global scale synthesis. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 30, 1627–1637.
Wardle, D. A., Yeates, G. W., Nicholson, K. S., Bonner, K. I., & Watson, R. N. (1999). Response of soil microbial biomass dynamics, activity and plant litter decomposition to agricultural intensification over a seven year period. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 31, 1707–1720.
Wardle, D. A., Yeates, G. W., Watson, R. N., & Nicholson, K. S. (1993). Response of soil microbial biomass and plant litter decomposition in maize and asparagus cropping systems. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 25, 857–868.
Weiss, D., Shotyk, W., Appleby, P. G., Kramers, J. D., & Cheburkin, A. K. (1999). Atmospheric Pb deposition since the industrial revolution recorded by five Swiss peat profile: environment factors, fluxes, isotopic composition and sources. Environmental Science and Technology, 33, 1340–1352.
Witter, E. (1996). Towards zero accumulation of heavy metals in soil: an imperative or a fad. Fertility Research, 43, 225–233.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pandey, J., Pandey, U. Accumulation of heavy metals in dietary vegetables and cultivated soil horizon in organic farming system in relation to atmospheric deposition in a seasonally dry tropical region of India. Environ Monit Assess 148, 61–74 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-0139-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-0139-8