Abstract
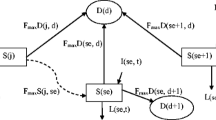
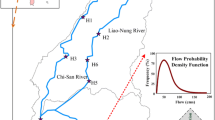
Selection procedure of the optimum station combination for decreasing the station number from 33 to 14 in water quality monitoring network of Gediz river basin was applied using an optimization method. Gediz basin is one of the important basins and it covers 2.3% of the total surface area of Turkey. The technique includes two stages as the data preparation and the optimization. In the data preparation stage, firstly, alternative station combinations decreased and then station combination scores obtained from assigned selection criteria for point and nonpoint pollution management objectives. Finally, genetic algorithm applied to select the best combination. The results were compared with a prior solution that used dynamic programming as the optimization technique.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gibbons, J. D. and Chakraborti, S.: 1992, Nonparametric Statistical Inference, 3rd edn, Marcel Dekker, New York.
Goldberg, D. E.: 1989, Genetic Algorithms in Search, Optimization, and Machine Learning, Addison Wesley Longman, U.S.A., p. 412.
Halhal, D., Walters, G. A., Ouazar, D. and Savic, D. A.: 1997, ‘Water network rehabilitation with structured messy genetic algorithm’, J. Water Resource Plan. Manag. (May –June), pp. 137–146.
Icaga, Y.: 1998, ‘Spatial Optimization of Hydrometric Data Networks by System Analysis Techniques’, PhD Thesis, 9 Eylul University, Izmir, p. 228.
Karpouzos, D. K., Delay, F. Katsifarakis, K. L. and de Marsily, G.: 2001, ‘A multipopulation genetic algorithm to solve the inverse problem in hydrogeology’, Water Resource Res. 37(9), 2291–2302.
Lettenmaier, D. P., Anderson, D. E. and Brenner, R. N.: 1984, ‘Consolidation of a stream quality monitoring network’, Water Resource Bull. 20(4), 473–481.
McMahon, T. A. and Mein, R. G.: 1986, River and Reservoir Yield, Monash University, Australia, p. 368.
Mitchell, M.: 1998, An Introduction to Genetic Algorithms, A Bradford Book, The MIT Press, Massachusetts, p. 209.
Mulligan, A. E. and Brown, L. C.: 1998, ‘Genetic algorithms for calibrating water quality models’, J. Environ. Engin. (March) 202–211.
Osyczka, A.: 2002, Evolutionary Algorithms for Single and Multicriteria Design Optimization, Physica-Verlag Heidelberg, New York, p. 218.
Sharp, W. E.: 1970, ‘Stream order as a measure of sample uncertainty’, Water Resource Res. 6(3), 919–926.
Sharp, W. E.: 1971, ‘A topologically optimum water –sampling plan for rivers and streams’, Water Resource Res. 7(6), 1641–1646.
Vasquez, J. A., Maier, H. R., Lence, B. J., Tolson, B. A. and Foschi, R. O.: 2000, ‘Achieving water quality system reliability using genetic algorithms’, J. Environ. Engin. (October), 954–962.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Icaga, Y. Genetic Algorithm Usage in Water Quality Monitoring Networks Optimization in Gediz (Turkey) River Basin. Environ Monit Assess 108, 261–277 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-005-4328-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-005-4328-z