Abstract
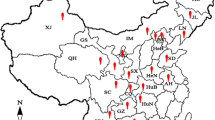
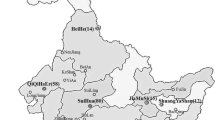
Between 2010 and 2015, 204 Rhizoctonia isolates were obtained from diseased sugar beet seedlings which collected from the sugar beet growing regions of China. On the basis of the morphological characteristics and sequence analysis of the internal transcribed spacers of the ribosomal DNA (rDNA ITS), 166 were identified as multinucleate Rhizoctonia (MNR), and 38 were binucleate Rhizoctonia (BNR), belonging to 15 species, anastomosis groups (AGs) or subgroups. The most prevalent was Rhizoctonia solani AG-4, with 49 isolates attributed to the subgroup HGIII, 47 to HGII, and 45 to HGI, followed by AG-K (31), AG-2-2IIIB (7), AG-A (6), AG-1-1C (4), AG-1-1B (3), AG-2-1 (3), AG-5 (3), AG-11 (2), AG-3 TB (1), Waitea circinata var. circinata (1), W. circinata var. zeae (1), and AG-C (1). Seventy-four representative isolates of all species, AGs or subgroups from different geographic origins were able to cause brown, dry lesions on roots of sugar beet seedlings or even seedling death with the disease incidence and the disease index ranging from 13.3 to 100% and from 1.9 to 97.1, respectively. The AG-4 isolates were the most aggressive on sugar beet seedlings. Moreover, the aggressiveness of the R. solani isolates was higher than that of the other isolates. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first detailed description of the AG composition of Rhizoctonia causing seedling damping-off on sugar beet in China.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahvenniemi, P., Wolf, M., Lehtonen, M. J., Wilson, P., German-kinnari, M., & Valkonen, J. P. (2009). Evolutionary diversification indicated by compensatory base changes in ITS2 secondary structures in a complex fungal species, Rhizoctonia solani. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 69(2), 150–163.
Ajayi-Oyetunde, O. O., & Bradley, C. A. (2017). Identification and characterization of Rhizoctonia species associated with soybean seedling disease. Plant Disease, 101(4), 520–533.
Bacharis, C., Gouziotis, A., Kalogeropoulou, P., Koutita, O., Tzavella-Klonari, K., & Karaoglanidis, G. (2010). Characterization of Rhizoctonia spp. isolates associated with damping-off disease in cotton and tobacco seedlings in Greece. Plant Disease, 94(11), 1314–1322.
Berdugo, C., Hillnhütter, C., Sikora, R., & Oerke, E. C. (2012). A resistance bioassay for Rhizoctonia root and crown rot and damping-off caused by the anastomosis groups AG-2-2IIIB and AG-4 in sugar beet. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, A2(3), 294–302.
Carling, D. E. (1996). Grouping in Rhizoctonia solani by the anastomosis reaction. In B. Sneh, S. Jabaji-Hare, S. Neate, & G. Dijst (Eds.), Rhizoctonia species: Taxonomy, molecularbiology, ecology, pathology and disease control (pp. 37–47). Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Carling, D., Kuninaga, S., & Brainard, K. (2002). Hyphal anastomosis reactions, rDNA-internal transcribed spacer sequences, and virulence levels among subsets of Rhizoctonia solani anastomosis group-2 (AG-2) and AG-BI. Phytopathology, 92(1), 43–50.
de la Cerda, K. A., Douhan, G. W., & Wong, F. P. (2007). Discovery and characterization of Waitea circinata var. circinata affecting annual bluegrass from the western United States. Plant Disease, 91(7), 791–797.
Dong, W. H., Li, Y. Q., Duan, C. F., Li, X. G., Naito, S., Conner, R. L., et al. (2017). Identification of AG-V, a new anastomosis group of binucleate Rhizoctonia spp. from taro and ginger in Yunnan province. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 148(4), 895–906.
Escande, A. R., & Echandi, E. (1991). Protection of potato from Rhizoctonia canker with binucleate Rhizoctonia fungi. Plant Pathology, 40(2), 197–202.
Fang, X., Finnegan, P. M., & Barbetti, M. J. (2013). Wide variation in virulence and genetic diversity of binucleate Rhizoctonia isolates associated with root rot of strawberry in Western Australia. PLoS One, 8(2), e55877.
García, V. G., Onco, M. P., & Susan, V. R. (2006). Biology and systematics of the form genus Rhizoctonia. Spanish Journal of Agricultural Research, 4(1), 55–79.
Hall, G. (1986). A species of Rhizoctonia, with uninucleate hyphae isolated from roots of winter wheat. Transactions of the British Mycological Society, 87(3), 466–471.
Hanson, L. E., & McGrath, J. M. (2010). Sugar beet seedling damping-off in Michigan. Phytopathology, 100(6S), S47.
Hanson, L. E., & McGrath, J. M. (2011). Rhizoctonia seedling disease on sugar beet. International Sugar Journal, 113(8), 584–589.
Harris, A. (2000). Solid formulations of binucleate Rhizoctonia isolates suppress Rhizoctonia solani and Pythium ultimum in potting medium. Microbiological Research, 154(4), 333–337.
Harveson, R. M., Hanson, L. E., & Hein, G. L. (2009). Compendium of beet diseases and pests. Ed. 2. American Phytopathological society. (APS press) 21–24.
Hayakawa, T., Toda, T., Ping, Q., Mghalu, J. M., Yaguchi, S., & Hyakumachi, M. (2006). A new subgroup of Rhizoctonia AG-D, AG-D III, obtained from Japanese zoysia grass exhibiting symptoms of a new disease. Plant Disease, 90(11), 1389–1394.
Hietala, A. M. (1995). Uni-and binucleate Rhizoctonia spp. co-existing on the roots of Norway-spruce seedlings suffering from root dieback. Forest Pathology, 25(3), 136–144.
Hietala, A. M., Vahala, J., & Hantula, J. (2001). Molecular evidence suggests that Ceratobasidium bicorne has an anamorph known as a conifer pathogen. Mycological Research, 105(5), 555–562.
Kuramae, E. E., Buzeto, A. L., Ciampi, M. B., & Souza, N. L. (2003). Identification of Rhizoctonia solani AG 1-IB in lettuce, AG 4 HG-I in tomato and melon, and AG 4 HG-III in broccoli and spinach, in Brazil. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 109(4), 391–395.
Kuznia, R., & Windels, C. (1994). Rhizoctonia zeae pathogenic to spring wheat and sugar beet seedlings. Phytopathology, 84(10), 1159.
Li, J., Xia, H. B., & Yu, J. F. (2011). The anastomosis groups of the corn sheath blight pathogen Rhizoctonia spp. in northeastern China. Mycosystema, 30(3), 392–399 (in Chinese).
Lilja, A., Hietala, A. M., & Karjalainen, R. (1996). Identification of a uninucleate Rhizoctonia spp. by pathogenicity, hyphal anastomosis and RAPD analysis. Plant Pathology, 45(5), 997–1006.
Nagendran, S., Hammerschmidt, R., & McGrath, J. M. (2009). Identification of sugar beet germplasm EL51 as a source of resistance to post-emergence Rhizoctonia damping-off. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 123(4), 461–471.
Nelson, B., Helms, T., Christianson, T., & Kural, I. (1996). Characterization and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia from soybean. Plant Disease, 80(1), 74–80.
Ogoshi, A. (1987). Ecology and pathogenicity of anastomosis and intraspecific groups of Rhizoctonia solani Kuhn. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 25(1), 125–143.
O'sullivan, E., & Kavanagh, J. (1991). Characteristics and pathogenicity of isolates of Rhizoctonia spp. associated with damping-off of sugar beet. Plant Pathology, 40(1), 128–135.
Otero, J. T., Ackerman, J. D., & Bayman, P. (2002). Diversity and host specificity of endophytic Rhizoctonia-like fungi from tropical orchids. American Journal of Botany, 89(11), 1853–1858.
Priyatmojo, A., Yamauchi, R., Kageyama, K., & Hyakumachi, M. (2001). Grouping of binucleate Rhizoctonia anastomosis group D (AG-D) isolates into subgroups I and II based on whole-cell fatty acid compositions. Journal of Phytopathology, 149(7–8), 421–426.
Sharon, M., Freeman, S., Kuninaga, S., & Sneh, B. (2007). Genetic diversity, anastomosis groups and virulence of Rhizoctonia spp. from strawberry. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 117(3), 247–265.
Sharon, M., Sneh, B., Kuninaga, S., Hyakumachi, M., & Naito, S. (2008). Classification of Rhizoctonia spp. using rDNA ITS sequence analysis supports the genetic basis of the classical anastomosis grouping. Mycoscience, 49(2), 93–114.
Smiley, R., & Uddin, W. (1993). Influence of soil temperature on Rhizoctonia root rot (R. solani AG-8 and R. oryzae) of winter wheat. Phytopathology, 83(9), 777–785.
Soltaninezhad, S., Mahmoudi, S. B., & Farokhi, N. R. (2008). Characterization of sugar beet Rhizoctonia isolates in Iran. Journal of Sugar Beet, 23(2), 135–150.
Strausbaugh, C. A., Eujayl, I. A., Panella, L. W., & Hanson, L. E. (2011). Virulence, distribution and diversity of Rhizoctonia solani from sugar beet in Idaho and Oregon. Canadian Journal of Plant Pathology, 33(2), 210–226.
Taheri, P., & Tarighi, S. (2012). Genetic and virulence analysis of Rhizoctonia spp. associated with sugar beet root and crown rot in the northeast region of Iran. Plant Disease, 96(3), 398–408.
Taheri, P., Gnanamanickam, S., & Höfte, M. (2007). Characterization, genetic structure, and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia spp. associated with rice sheath diseases in India. Phytopathology, 97(3), 373–383.
Toda, T., Mushika, T., Hayakawa, T., Tanaka, A., Tani, T., & Hyakumachi, M. (2005). Brown ring patch: A new disease on bentgrass caused by Waitea circinata var. circinata. Plant Disease, 89(6), 536–542.
Wang, P. P., & Wu, X. H. (2012). First report of sugar beet seedling damping-off caused by binucleate Rhizoctonia AG-A in China. Plant Disease, 96(11), 1696.
Webb, K. M., Hill, A. L., Laufman, J., Hanson, L. E., & Panella, L. (2011). Long-term preservation of a collection of Rhizoctonia solani using cryogenic storage. Annals of Applied Biology, 158(3), 297–304.
White, T. J., Bruns, T., Lee, S., & Taylor, J. W. (1990). Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In M. A. Innis, D. H. Gelfand, J. J. Sninsky, & T. J. White (Eds.), PCR protocols: A guide to methods and applications (pp. 315–322). San Diego: Academic Press.
Windeis, С., & Nabben, D. J. (1989). Characterization and pathogenicity of anastomosis groups of Rhizoctonia solani isolated from Beta vulgaris. Phytopathology, 79(1), 83–88.
Yang, G. H., Chen, H. R., Naito, S. Y., Ogoshi, A., & Deng, Y. L. (2005). First report of AG-A of binucleate Rhizoctonia in China, pathogenic to soya bean, pea, snap bean and pak choy. Journal of Phytopathology, 153(6), 333–336.
Yang, Y. G., Zhao, C., Guo, Z. J., & Wu, X. H. (2014). Anastomosis groups and pathogenicity of binucleate Rhizoctonia isolates associated with stem canker of potato in China. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 139(3), 535–544.
Yang, Y. G., Zhao, C., Guo, Z. J., & Wu, X. H. (2015a). Anastomosis group and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia solani associated with stem canker and black scurf of potato in China. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 143(1), 99–111.
Yang, Y. G., Zhao, C., Guo, Z. J., & Wu, X. H. (2015b). Characterization of a new anastomosis group (AG-W) of binucleate Rhizoctonia, causal agent for potato stem canker. Plant Disease, 99(12), 1757–1763.
Zhao, C., & Wu, X. H. (2014). First report of sugar beet Rhizoctonia crown and root rot caused by Rhizoctonia solani AG-2-2IIIB in Shanxi province of China. Plant Disease, 98(3), 419.
Zhao, S. F., Li, G. Y., Li, H., & Wang, Q. Y. (2002). Identification of pathogen population of sugar beet root rot disease in Xinjiang. Sugar Crops of China, 1, 3–8 (in Chinese).
Zhou, S. Y., Zhang, M., Liu, Y., Zhen, J., Liang, W. X., Chen, X. J., et al. (2015). A uninucleate Rhizoctonia sp. from maize plant with ITS heterogeneity and hypersensitive to abiotic stresses. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 142(2), 397–401.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the earmarked fund for China Agriculture Research System (CARS-170304). Mention of trade names or commercial products in this report is solely for the purpose of providing specific information and does not imply recommendation or endorsement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and animal studies
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 269 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, C., Li, Y., Wu, S. et al. Anastomosis group and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia spp. associated with seedling damping-off of sugar beet in China. Eur J Plant Pathol 153, 869–878 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-018-1603-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-018-1603-8