Abstract
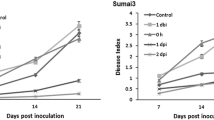
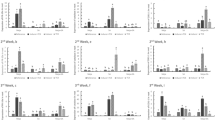
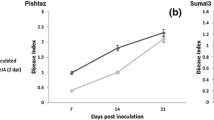
Maize is a socially and economically important crop in Africa (and worldwide) that is severely affected by many fungal pathogens. The pathogen Fusarium verticillioides can infect all maize tissue and causes Fusarium ear rot (FER), a disease that greatly reduces quantity and quality of annual maize yields. In response to fungal infection, maize produces kauralexins and zealexins, which are antimicrobial terpenoid phytoalexins that directly reduce the growth of many fungal pathogens including F. verticillioides. This research evaluates the induction of kauralexins and zealexins in F. verticillioides-inoculated sub-tropical maize lines. CML444 (moderately-resistant to FER) and CML144 (susceptible to FER) accumulated both phytoalexin types in seedling roots in response to seed inoculation with F. verticillioides. CML444 control roots also had higher kauralexin levels in comparison to CML144, suggesting that kauralexin accumulation may be primed for rapid up-regulation in CML444 following fungal infection. The an2 maize mutant, which displays reduced expression of the key kauralexin biosynthetic gene ZmAn2, accumulated decreased root levels of kauralexins and zealexins following F. verticillioides inoculation in comparison to wildtype line W22, confirming that both kauralexins and zealexins play a role in the resistance response to seedling disease caused by F. verticillioides.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldwin, T. T., Zitomer, N. C., Mitchell, T. R., Zimeri, A.-M., Bacon, C. W., Riley, R. T., & Glenn, A. E. (2014). Maize seedling blight induced by Fusarium verticillioides : Accumulation of Fumonisin B1 in leaves without colonization of the leaves. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 62(9), 2118–2125. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf5001106.
Christensen, S. A., Sims, J., Vaughan, M. M., Hunter, C., Block, A., Willett, D., Alborn, H. T., Huffaker, A., & Schmelz, E. A. (2018). Commercial hybrids and mutant genotypes reveal complex protective roles for inducible terpenoid defenses in maize. Journal of Experimental Botany, 69(7), 1693–1705. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erx495.
Christie, N., Myburg, A. A., Joubert, F., Murray, S. L., Carstens, M., Lin, Y.-C., Meyer, J., Crampton, B. G., Christensen, S. A., Ntuli, J. F., Wighard, S. S., van de Peer, Y., & Berger, D. K. (2017). Systems genetics reveals a transcriptional network associated with susceptibility in the maize-grey leaf spot pathosystem. The Plant Journal, 89(4), 746–763. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13419.
Degenhardt, J., Köllner, T. G., & Gershenzon, J. (2009). Monoterpene and sesquiterpene synthases and the origin of terpene skeletal diversity in plants. Phytochemistry, 70(15–16), 1621–1637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2009.07.030.
van der Linde, K., Kastner, C., Kumlehn, J., Kahmann, R., & Doehlemann, G. (2011). Systemic virus-induced gene silencing allows functional characterization of maize genes during biotrophic interaction with Ustilago maydis. New Phytologist, 189(2), 471–483. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03474.x.
Ejike, C. E. C. C., Gong, M., & Udenigwe, C. C. (2013). Phytoalexins from the Poaceae: Biosynthesis, function and prospects in food preservation. Food Research International, 52(1), 167–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2013.03.012.
Fandohan, P., Hell, K., Marasas, W. F. O., & Wingfield, M. J. (2003). Infection of maize by Fusarium species and contamination with fumonisin in Africa. African Journal of Biotechnology, 2(12), 570–579.
Fu, J., Ren, F., Lu, X., Mao, H., Xu, M., Degenhardt, J., Peters, R.J. & Wang, Q. (2016). A tandem array of ent-kaurene synthases in maize with roles in gibberellin and more specialized metabolism. Plant Physiology, 170(2):742–751. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.15.01727.
Gelderblom, W. C., Jaskiewicz, K., Marasas, W. F., Thiel, P. G., Horak, R. M., Vleggaar, R., & Kriek, N. P. (1988). Fumonisins–novel mycotoxins with cancer-promoting activity produced by Fusarium moniliforme. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 54(7), 1806–1811.
Harris, L. J., Saparno, A., Johnston, A., Prisic, S., Xu, M., Allard, S., Kathiresan, A., Ouellet, T., & Peters, R. J. (2005). The maize An2 gene is induced by Fusarium attack and encodes an ent-Copalyl diphosphate synthase. Plant Molecular Biology, 59(6), 881–894. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-005-1674-8.
Harrison, L. R., Colvin, B. M., Greene, J. T., Newman, L. E., & Cole Jr., J. R. (1990). Pulmonary edema and hydrothorax in swine produced by fumonisin B1, a toxic metabolite of Fusarium moniliforme. Journal of Veterinary Diagnostic Investigation, 2(3), 217–221.
Huffaker, A., Kaplan, F., Vaughan, M. M., Dafoe, N. J., Ni, X., Rocca, J. R., Alborn, H. T., Teal, P. E. A., & Schmelz, E. A. (2011). Novel acidic Sesquiterpenoids constitute a dominant class of pathogen-induced Phytoalexins in maize. Plant Physiology, 156(4), 2082–2097. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.111.179457.
Köllner, T. G., Schnee, C., Li, S., Svatoš, A., Schneider, B., Gershenzon, J., & Degenhardt, J. (2008). Protonation of a neutral (S)-β-Bisabolene intermediate is involved in (S)-β-Macrocarpene formation by the maize Sesquiterpene synthases TPS6 and TPS11. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 283(30), 20779–20788. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M802682200.
Korsman, J., Meisel, B., Kloppers, F. J., Crampton, B. G., & Berger, D. K. (2012). Quantitative phenotyping of grey leaf spot disease in maize using real-time PCR. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 133(2), 461–471. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-011-9920-1.
Lambarey, H. (2017). An investigation of Fusarium verticillioides infection in maize using physiological and molecular approaches (master of science thesis). University of Cape Town.
Lanubile, A., Ferrarini, A., Maschietto, V., Delledonne, M., Marocco, A., & Bellin, D. (2014). Functional genomic analysis of constitutive and inducible defense responses to Fusarium verticillioides infection in maize genotypes with contrasting ear rot resistance. BMC Genomics, 15(1), 1.
Logrieco, A., Mule, G., Moretti, A., & Bottalico, A. (2002). Toxigenic Fusarium species and mycotoxins associated with maize ear rot in Europe. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 108, 597–609. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020679029993.
Ma, J., Morrow, D. J., Fernandes, J., & Walbot, V. (2006). Comparative profiling of the sense and antisense transcriptome of maize lines. Genome Biology, 7(3), R22.
Manoli, A., Sturaro, A., Trevisan, S., Quaggiotti, S., & Nonis, A. (2012). Evaluation of candidate reference genes for qPCR in maize. Journal of Plant Physiology, 169(8), 807–815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2012.01.019.
Mao, H., Liu, J., Ren, F., Peters, R. J., & Wang, Q. (2016). Characterization of CYP71Z18 indicates a role in maize zealexin biosynthesis. Phytochemistry, 121, 4–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2015.10.003.
Marasas, W. F., Riley, R. T., Hendricks, K. A., Stevens, V. L., Sadler, T. W., Gelineau-van Waes, J., et al. (2004). Fumonisins disrupt sphingolipid metabolism, folate transport, and neural tube development in embryo culture and in vivo: A potential risk factor for human neural tube defects among populations consuming fumonisin-contaminated maize. The Journal of Nutrition, 134(4), 711–716.
Maschietto, V., Colombi, C., Pirona, R., Pea, G., Strozzi, F., Marocco, A., Rossini, L., & Lanubile, A. (2017). QTL mapping and candidate genes for resistance to fusarium ear rot and fumonisin contamination in maize. BMC Plant Biology, 17(1), 20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-017-0970-1.
Meyer, J., Murray, S. L., & Berger, D. K. (2015). Signals that stop the rot: Regulation of secondary metabolite defences in cereals. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology, 94, 156–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmpp.2015.05.011.
Meyer, J., Berger, D. K., Christensen, S. A., & Murray, S. L. (2017). RNA-Seq analysis of resistant and susceptible sub-tropical maize lines reveals a role for kauralexins in resistance to grey leaf spot disease, caused by Cercospora zeina. BMC Plant Biology, 17(1), 197. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-017-1137-9.
Moola, N. (2016). An analysis of the terpenoid defence response to Fusarium verticillioides infection in an African maize line (bachelor of science (Honours) thesis). Cape Town: University of Cape Town.
Munkvold, G. P. (2003). Epidemiology of Fusarium diseases and their mycotoxins in maize ears. In Epidemiology of Mycotoxin Producing Fungi (pp. 705–713). Springer. http://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-94-017-1452-5_5. Accessed 30 June 2017.
Murillo-Williams, A., & Munkvold, G. P. (2008). Systemic infection by Fusarium verticillioides in maize plants grown under three temperature regimes. Plant Disease, 92(12), 1695–1700.
Navi, S. S., & Yang, X. B. (2008). Foliar symptom expression in association with early infection and xylem colonisation by Fusarium virguliforme (formerly F. solani f. sp. glycines), the causal agent of soybean sudden death syndrome. Plant Health Progress. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHP-2008-0222-01-RS.
Nicolaisen, M., Supronienė, S., Nielsen, L. K., Lazzaro, I., Spliid, N. H., & Justesen, A. F. (2009). Real-time PCR for quantification of eleven individual Fusarium species in cereals. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 76(3), 234–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2008.10.016.
Okello, D. K., Manna, R., Imanywoha, J., Pixley, K., & Edema, R. (2006). Agronomic performance and breeding potential of selected inbred lines for improvement of protein quality of adapted Ugandan maize germplasm. African Crop Science Journal, 14(1), 37–47.
Oren, L., Ezrati, S., Cohen, D., & Sharon, A. (2003). Early events in the Fusarium verticillioides-maize interaction characterized by using a green fluorescent protein-expressing transgenic isolate. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 69(3), 1695–1701. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.69.3.1695-1701.2003.
Peters, R. J. (2006). Uncovering the complex metabolic network underlying diterpenoid phytoalexin biosynthesis in rice and other cereal crop plants. Phytochemistry, 67(21), 2307–2317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2006.08.009.
Rose, L. J., Mouton, M., Beukes, I., Flett, B. C., van der Vyver, C., & Viljoen, A. (2016). Multi-environment evaluation of maize inbred lines for resistance to fusarium ear rot and fumonisins. Plant Disease, 100(10), 2134–2144.
Schmelz, E. A., Kaplan, F., Huffaker, A., Dafoe, N. J., Vaughan, M. M., Ni, X., Rocca, J. R., Alborn, H. T., & Teal, P. E. (2011). Identity, regulation, and activity of inducible diterpenoid phytoalexins in maize. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 108(13), 5455–5460. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1014714108.
Schmelz, E. A., Huffaker, A., Sims, J. W., Christensen, S. A., Lu, X., Okada, K., & Peters, R. J. (2014). Biosynthesis, elicitation and roles of monocot terpenoid phytoalexins. The Plant Journal, 79(4), 659–678. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12436.
Sikhakolli, U. R., López-Giráldez, F., Li, N., Common, R., Townsend, J. P., & Trail, F. (2012). Transcriptome analyses during fruiting body formation in Fusarium graminearum and fusarium verticillioides reflect species life history and ecology. Fungal Genetics and Biology, 49(8), 663–673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2012.05.009.
Small, I. M., Flett, B. C., Marasas, W. F. O., McLeod, A., Stander, M. A., & Viljoen, A. (2012). Resistance in maize inbred lines to Fusarium verticillioides and fumonisin accumulation in South Africa. Plant Disease, 96(6), 881–888.
Sun, G., Wang, S., Hu, X., Su, J., Huang, T., Yu, J., Tang, L., Gao, W., & Wang, J. S. (2007). Fumonisin B1 contamination of home-grown corn in high-risk areas for esophageal and liver cancer in China. Food Additives and Contaminants, 24(2), 181–185. https://doi.org/10.1080/02652030601013471.
Sydenham, E. W., Thiel, P. G., Marasas, W. F., Shephard, G. S., Van Schalkwyk, D. J., & Koch, K. R. (1990). Natural occurrence of some Fusarium mycotoxins in corn from low and high esophageal cancer prevalence areas of the Transkei, southern Africa. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 38(10), 1900–1903.
Thiel, P. G., Marasas, W. F., Sydenham, E. W., Shephard, G. S., & Gelderblom, W. C. (1992). The implications of naturally occurring levels of fumonisins in corn for human and animal health. Mycopathologia, 117(1–2), 3–9.
Vaughan, M. M., Huffaker, A., Schmelz, E. A., Dafoe, N. J., Christensen, S., Sims, J., et al. (2014). Effects of elevated [CO2] on maize defence against mycotoxigenic Fusarium verticillioides: Elevated [CO2] compromises maize defences. Plant, Cell & Environment, 37(12), 2691–2706. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12337.
Vaughan, M. M., Christensen, S., Schmelz, E. A., Huffaker, A., Mcauslane, H. J., Alborn, H. T., Romero, M., Allen, L. H., & Teal, P. E. A. (2015). Accumulation of terpenoid phytoalexins in maize roots is associated with drought tolerance: Maize root phytoalexins play a role in drought tolerance. Plant, Cell & Environment, 38(11), 2195–2207. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12482.
Vollbrecht, E., Duvick, J., Schares, J. P., Ahern, K. R., Deewatthanawong, P., Xu, L., Conrad, L. J., Kikuchi, K., Kubinec, T. A., Hall, B. D., Weeks, R., Unger-Wallace, E., Muszynski, M., Brendel, V. P., & Brutnell, T. P. (2010). Genome-wide distribution of transposed Dissociation elements in maize. The Plant Cell, 22(6), 1667–1685. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.109.073452.
Vranová, E., Coman, D., & Gruissem, W. (2013). Network analysis of the MVA and MEP pathways for isoprenoid synthesis. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 64(1), 665–700. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-050312-120116.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded in South Africa by The Maize Trust and the National Research Foundation. We would like to thank Bridget Crampton for seeds, and Bradley Flett and Lindy Rose for advice regarding experiments with F. verticillioides. Thank you to Humaira Lambarey for assistance with F. verticillioides inoculation and plant growth. We gratefully acknowledge Eric Schmelz for the establishment of the GC/MS phytoalexin analysis protocol and two unknown reviewers for helpful suggestions to the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
This research did not involve human participants and/or animals. The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Veenstra, A., Moola, N., Wighard, S. et al. Kauralexins and zealexins accumulate in sub-tropical maize lines and play a role in seedling resistance to Fusarium verticillioides. Eur J Plant Pathol 153, 223–237 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-018-1557-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-018-1557-x