Abstract
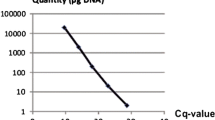
A method was developed for the specific detection, identification and quantification of Monosporascus cannonballus in infected melon roots based on real-time PCR (SYBR® Green chemistry) targeting the ITS1 region of the rDNA conserved between different strains of the pathogen. The specificity of the reaction was assessed using a number of fungi taxonomically and ecologically related to M. cannonballus. The method was highly sensitive and M. cannonballus was first detected in the roots of a susceptible Piel de Sapo cultivar 2 days after inoculation, before symptom appearance. Although conventional PCR methods could also provide such a specific and sensitive detection, real-time PCR was also able to produce reliable quantitative data over a range of 4 orders of magnitude (from 5 ng to 0.3 pg). The method allowed the quantitative monitoring of fungal growth from the very first stages of infection, and was successfully employed in the early screening of resistance. The assessment of disease progress and severity obtained with real-time PCR was more accurate than that obtained with the visual scoring of root lesions or root biomass losses. Therefore, there exists a great potential for its implementation in those steps of breeding programmes where high accuracy is required.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkins, S. D., & Clark, I. M. (2004). Fungal molecular diagnostics: a mini review. Journal of Applied Genetics, 45, 3–15.
Atkins, S. D., Clark, I. M., Hirsch, P. R., & Kerry, B. R. (2005). The use of real-time PCR and species-specific primers for the identification and monitoring of Paecilomyces lilacinus. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 51, 257–264.
Bruton, B. D., García-Jimémez, J., Armengol, J., & Popham, T. W. (2000). Assessment of virulence of Acremonium cucurbitacearum and Monosporascus cannonballus on Cucumis melo. Plant Disease, 84, 907–913.
Cohen, R., Pivonia, S., Burger, Y., Edelstein, M., Gamliel, A., & Katan, J. (2000). Toward integrated management of Monosporascus wilt of melons in Israel. Plant Disease, 84, 496–505.
Collado, J., González, A., Platas, G., Stechiguel, A. M., Guarro, J., & Pelaez, F. (2002). Monosporascus ibericus sp. nov., an entophytic ascomycete from plants on saline soils, with observations on the position of the genus based on sequence analysis of the 18 S rDNA. Mycological Research, 106, 118–127.
Crosby, K., Wolff, D., & Miller, M. (2000). Comparisons of root morphology in susceptible and tolerant melon cultivars before and after infection by Monosporascus cannonballus. HortScience, 35, 681–683.
Cullen, D. W., Lees, A. K., Toth, I. K., & Duncan, J. K. (2001). Conventional PCR and real-time quantitative PCR detection of Helminthosporium solani in soil and on potato tubers. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 107, 387–398.
Dias, R. C., Picó, B., Espinós, A., & Nuez, F. (2004). Resistance to melon vine decline derived from C. melo subsp. agrestis: genetic analysis of root structure and root response to the disease. Plant Breeding, 123, 1–7.
Dias, R. C., Picó, B., Herraiz, J., Espinós, A., & Nuez, F. (2002). Modifying root structure on cultivated muskmelon to improve vine decline resistance. HortScience, 37, 1092–1097.
Filion, M., St-Arnaud, M., & Jabaji-Hare, S. H. (2003). Direct quantification of fungal DNA from soil substrate using real-time PCR. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 53, 67–76.
Fita, A., Picó, B., & Nuez, F. (2006). Análisis de imagen como herramienta en la mejora del sistema radicular de melón. Actas de Horticultura, 45, 119–120.
Gao, X., Jackson, T. A., Lambert, K. N., Li, S., Hartman, G. L., & Niblack, T. L. (2004). Detection and quantification of Fusarium solani f. sp. glycines in soyabean roots with quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Plant Disease, 88, 1372–1380.
Iglesias, A., Picó, B., & Nuez, F. (2000). A temporal genetic analysis of disease resistance genes: resistance to melon vine decline derived from C. melo var agrestis. Plant Breeding, 119, 329–334.
Ippolito, A., Schena, L., Nigro, F., Ligorio, V., & Yassen, T. (2004). Real-time detection of Phytophtora nicotianae and P. citrophtora in citrus roots and soils. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 110, 833–843.
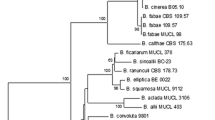
Lovic, B. R., Martyn, R. D., & Miller, R. D. (1995). Sequence analysis of the ITS regions of rDNA in Monosporascus spp. to evaluate its potential for PCR-mediated detection. Phytopathology, 85, 655–661.
Martyn, R. D., & Miller, M. E. (1996). Monosporascus root rot and vine decline. An emerging disease of melons worldwide. Plant Disease, 80, 716–725.
McCartney, H. A., Foster, S. J., Fraaije, B. A., & Ward, E. (2003). Molecular diagnostics for fungal plant pathogens. Pest Management Science, 59, 129–142.
Mertely, J. C., Martyn, R. D., Miller, M. E., & Bruton, B. D. (1993). An expanded host range for the muskmelon pathogen Monosporascus cannonballus. Plant Disease, 77, 667–673.
Stanghellini, M. E., Kim, D. H., Waugh, M. M., Ferrin, D. M., Alcantara, T., & Rasmussen, S. L. (2004). Infection and colonization of melon roots by Monosporascus cannonballus in two cropping seasons in Arizona and California. Plant Pathology, 53, 54–57.
van de Graaf, P., Lees, A. K., Cullen, D. W., & Duncan, J. M. (2003). Detection and quantification of Spongospora subterranea in soil, water and plant tissue samples using real-time PCR. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 109, 589–597.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Eva Ma Martínez (COMAV) for her technical assistance with the infected material, and to Dr. Jose Miguel Blanca and Dr. Alicia Sifres (COMAV) for their help with real-time PCR. This work was supported by MCT AGL2003-04817 and GEN2003-20237-C06-03. We would also like to thank the plant pathology group at the UPV, Dr. B.D. Bruton, and Dr M. Stanghellini for providing some fungal isolates.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Picó, B., Roig, C., Fita, A. et al. Quantitative detection of Monosporascus cannonballus in infected melon roots using real-time PCR. Eur J Plant Pathol 120, 147–156 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-007-9203-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-007-9203-z