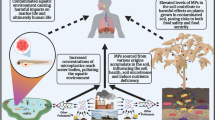
Abstract
Industrial horticulture can release pesticides and trace metals/metalloids to terrestrial and aquatic environments. To assess long-term and more recent land contamination from an expanding horticultural region, we sampled soils from chemical mixing, crop production, and drainage areas, as well as retention reservoirs (dam) sediments, from 3 blueberry farms with varying land-use history in subtropical Australia. Soils were analysed for 97 different pesticides and trace metal/metalloid contents. The most recent farm had fungicides propiconazole and cyprodinil contents that may compromise soil invertebrate survival and/or nutrient recycling (5–125 mg kg−1). A site previously used to cultivate bananas had 6 dam sediment subsamples with arsenic contents over sediment quality guidelines (SQG); however, the soil content values were just below Australian health investigation levels (100 mg kg−1). Arsenic is suspected to originate from pesticide application during previous banana cultivation in the region. Dam sediment cores at all sites had mercury contents over the SQG likely due to fungicides or fertiliser impurities. Mean contents of mercury from dam sediments (141 ± 15.5 µg kg−1) were greater than terrestrial soils (78 ± 6.5 µg kg−1), and sediment profiles suggest mercury retention in anoxic sediments. Soils in chemical mixing areas at two sites were contaminated with copper and zinc which were above the national soil ecological investigation levels. Based on toxicity data, distribution, persistence, and mobility, we identified the fungicide cyprodinil, mercury, and phosphorus as contaminants of the greatest concern in this intensive horticulture area of Australia. Additional sampling (spatial, chemical speciation, biotic) is required to support mitigation efforts of the emerging contamination in the rapidly expanding blueberry farms of this region of Australia.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Data are available in the manuscript or as supplementary material.
References
ABGA. (2018). Australian Blueberry Industry Strategic Investment Plan 2018–2022. In A. B. G. Association (Ed.), (pp. 1–16). Lindendale, NSW, Australia: Australian Blueberry Growers’ Association.
Agüera, A., Almansa, E., Tejedor, A., Fernández-Alba, A. R., Malato, S., & Maldonado, M. I. (2000). Photocatalytic pilot scale degradation study of pyrimethanil and of its main degradation products in waters by means of solid-phase extraction followed by gas and liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry detection. Environmental Science and Technology, 34(8), 1563–1571. https://doi.org/10.1021/es990112u.
Ahmad, K. S. (2018). Sorption-desorption characteristics of benzimidazole based fungicide benomyl on physicochemical properties of selected Pakistani soils and their minerals. Biological Sciences-PJSIR, 61(2), 59–67.
APVMA. (2012). Diuron final review report. In A. P. a. V. M. Authority (Ed.), (pp. 1–112). Canberra, ACT, Australia.
APVMA. (2020). AVPMA Gazette No. 12. In A. P. a. V. M. Authority (Ed.), (Vol. 25, p. 25). Sydney, NSW: Commonwealth of Australia.
Argent, N. (2002). From pillar to post? In search of the post-productivist countryside in Australia. Australian Geographer, 33(1), 97–114.
Arias, M., Torrente, A., López, E., Soto, B., & Simal-Gándara, J. (2005). Adsorption–desorption dynamics of cyprodinil and fludioxonil in vineyard soils. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 53(14), 5675–5681.
Arsic, M., Teasdale, P. R., Welsh, D. T., Johnston, S. G., Burton, E. D., Hockmann, K., et al. (2018). Diffusive gradients in thin films reveals differences in antimony and arsenic mobility in a contaminated wetland sediment during an oxic-anoxic transition. Environmental Science and Technology, 52(3), 1118–1127.
Authority, E. F. S., Arena, M., Auteri, D., Barmaz, S., Bellisai, G., Brancato, A., et al. (2017). Peer review of the pesticide risk assessment of the active substance propiconazole. Efsa Journal, 15(7), e04887.
Authority, E. F. S. (2006). Conclusion regarding the peer review of the pesticide risk assessment of the active substance cyprodinil. Efsa Journal, 4(1), 51r.
Azimonti, et al. (2015). Comparison of NOEC values to EC10/EC20 values, including confidence intervals, in aquatic and terrestrial ecotoxicological risk assessment. EFSA Supporting Publications, 12(12), 906E.
Baude, F. J., Pease, H. L., & Holt, R. F. (1974). Fate of benomyl on field soil and turf. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 22(3), 413–418. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf60193a051.
Belzile, N., Lang, C.-Y., Chen, Y.-W., & Wang, M. (2008). The competitive role of organic carbon and dissolved sulfide in controlling the distribution of mercury in freshwater lake sediments. Science of the Total Environment, 405(1), 226–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.06.034.
Bennett, E. M., Carpenter, S. R., & Caraco, N. F. (2001). Human Impact on Erodable Phosphorus and Eutrophication: A Global Perspective: Increasing accumulation of phosphorus in soil threatens rivers, lakes, and coastal oceans with eutrophication. AIBS Bulletin, 51(3), 227–234.
Bermúdez-Couso, A., Arias-Estévez, M., Nóvoa-Muñoz, J., López-Periago, E., Soto-González, B., & Simal-Gándara, J. (2007). Seasonal distributions of fungicides in soils and sediments of a small river basin partially devoted to vineyards. Water Research, 41(19), 4515–4525.
Bisht, S., Chauhan, R., Kumari, B., & Singh, R. (2015). Fate of thiodicarb and its metabolite methomyl in sandy loam soil under laboratory conditions. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(7), 429. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4640-1.
Boesten, J. J. T. I., & Gottesbüren, B. (2000). Testing PESTLA using two modellers for bentazone and ethoprophos in a sandy soil. Agricultural Water Management, 44(1), 283–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-3774(99)00096-7.
Boesten, J. J. T. I., & van der Pas, L. J. T. (2000). Movement of water, bromide and the pesticides ethoprophos and bentazone in a sandy soil: The Vredepeel data set. Agricultural Water Management, 44(1), 21–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-3774(99)00082-7.
Bohn, W. (1964). The disappearance of dimethoate from soil. Journal of Economic Entomology, 57(6), 798–799.
Brazelton, C. (2013). World blueberry acreage & production. North American Blueberry Council. Available online: http://www.chilealimentos.com/2013/phocadownload/Aprocesados_congelados/nabc_2012-world-blueberry-acreage-production.pdf. Accessed 4 May 2015.
Brennan, R. (2001). Residual value of zinc fertiliser for production of wheat. Australian Journal of Experimental Agriculture, 41(4), 541–547.
Brodie, J. E., & Mitchell, A. W. (2005). Nutrients in Australian tropical rivers: Changes with agricultural development and implications for receiving environments. Marine & Freshwater Research, 56(3), 279–302. https://doi.org/10.1071/MF04081.
Browne, B. (2016). Storing pesticides safely on farm. In D. o. P. Industries (Ed.), (pp. 1–4). NSW, Australia: NSW DPI.
Budd, L. (1995). Toxic playground: Reducing the toxic chemica load on schools and childcare centres. In Children’s Health and Chemicals Total Environment Center Sydney, NSW, Australia, 1995 (Conference Proceedings ed., pp. 4–7).
Campiche, S., Becker-van Slooten, K., Ridreau, C., & Tarradellas, J. (2006). Effects of insect growth regulators on the nontarget soil arthropod Folsomia candida (Collembola). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 63(2), 216–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2005.07.004.
Carpenter, S. R. (2005). Eutrophication of aquatic ecosystems: Bistability and soil phosphorus. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 102(29), 10002–10005.
Collins, P. J., Treverrow, N. L., & Lambkin, T. M. (1991). Organophosphorus insecticide resistance and its management in the banana weevil borer, Cosmopolites sordidus (Germar) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae), Australia. Crop Protection, 10(3), 215–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/0261-2194(91)90046-T.
Conrad, S. R., Santos, I. R., Brown, D. R., Sanders, L. M., van Santen, M. L., & Sanders, C. J. (2017). Mangrove sediments reveal records of development during the previous century (Coffs Creek estuary, Australia). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 122(1–2), 441–445.
Conrad, S. R., Santos, I. R., White, S. A., Hessey, S., & Sanders, C. J. (2020). Elevated dissolved heavy metal discharge following rainfall downstream of intensive horticulture. Applied Geochemistry, 113, 104490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2019.104490.
Conrad, S. R., Santos, I. R., White, S., & Sanders, C. J. (2019a). Nutrient and Trace Metal Fluxes into Estuarine Sediments Linked to Historical and Expanding Agricultural Activity (Hearnes Lake, Australia). Estuaries and Coasts, 42(4), 944–957. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-019-00541-1.
Conrad, S. R., Santos, I. R., White, S., & Sanders, C. J. (2019). Nutrient and trace metal fluxes into estuarine sediments linked to historical and expanding agricultural activity (Hearnes Lake, Australia). Estuaries and Coasts, 1–14.
Conrad, S. R., Santos, I. R., S.A., W., Woodrow, R., & Sanders, C. J. (2021). Cryptic night-time trace metal and metalloid contamination in an intensively cultivated coastal catchment. [Full Research Article]. Environmental Pollution, In Press (In Press).
Corkidi, L., Bohn, J., & Evans, M. (2009). Effects of bifenthrin on mycorrhizal colonization and growth of corn. HortTechnology, 19(4), 809–812.
Dibden, J., Potter, C., & Cocklin, C. (2009). Contesting the neoliberal project for agriculture: Productivist and multifunctional trajectories in the European Union and Australia. Journal of Rural Studies, 25(3), 299–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrurstud.2008.12.003.
Doughty, C. C., Adams, E. B., & Martin, L. W. (1988). Highbush blueberry production in Washington and Oregon. PNW-Pacific Northwest Extension Publication, Washington, Oregon, and Idaho State Universities, Cooperative Extension Service (USA).
Edwards, P. G., Murphy, T. M., & Lydy, M. J. (2016). Fate and transport of agriculturally applied fungicidal compounds, azoxystrobin and propiconazole. Chemosphere, 146, 450–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.11.116.
El Beit, I. O. D., Verner Wheelock, J., & Cotton, D. E. (1981). Factors affecting soil residues of dieldrin, endosulfan, γ-HCH, dimethoate, and pyrolan. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 5(2), 135–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/0147-6513(81)90030-0.
EPA, N. (1997). Guidelines for assessing banana plantation sites. In E. P. Authoritiy (Ed.), (Vol. 1–27). Sydney, NSW: NSW Environmental Protection Authority.
eSpade version 2.1. (2020). New South Wales Department of Planning, Industry and Environment. https://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/eSpade2WebApp#. Accessed September 2020.
Fang, W., Jiang, X., Bian, Y.-R., Yao, F.-X., Gao, H.-J., Yu, G.-F., et al. (2007). Organochlorine pesticides in soils under different land usage in the Taihu Lake region, China. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 19(5), 584–590.
Field, J. A., Reed, R. L., Sawyer, T. E., Griffith, S. M., & Wigington, P. (2003). Diuron occurrence and distribution in soil and surface and ground water associated with grass seed production. Journal of Environmental Quality, 32(1), 171–179.
Grigal, D. (2003). Mercury sequestration in forests and peatlands. Journal of Environmental Quality, 32(2), 393–405.
Harvey, J., Jr., & Pease, H. L. (1973). Decomposition of methomyl in soil. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 21(5), 784–786.
Haynes, R. J., & Naidu, R. (1998). Influence of lime, fertilizer and manure applications on soil organic matter content and soil physical conditions: A review. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 51(2), 123–137. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1009738307837.
He, Z. L., Yang, X. E., & Stoffella, P. J. (2005). Trace elements in agroecosystems and impacts on the environment. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, 19(2), 125–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2005.02.010.
Hedditch, R. (2014). Coffs Harbour 2014 Heritage Study.
Hernández, A., Gil, F., Pla, A., Gómez, A., Lozano, D., Parrón, T., et al. (2011). Emerging human health concerns from chronic exposure to pesticide mixtures. Toxicology Letters (205), S4–S5.
Holmes, G. (2014). Australia’s pesticide environmental risk assessment failure: The case of diuron and sugarcane. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 88(1), 7–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.08.007.
Hunt, J., Honeycutt, C., Starr, G., & Yarborough, D. (2009). Influence of Coastal Proximity on Evapotranspiration Rates and Crop Coefficients of Maine Lowbush Blueberry (Vaccinium angustifolium). International Journal of Fruit Science, 9(4), 323–343.
Jiang, C., Li, X. J., Wang, Y. R., Ma, L. Y., Wang, Y. K., Lu, Y. C., et al. (2017). Assessment of photodegradation of herbicide prometryn in soil. Water, Air, and Soil pollution, 228(4), 135.
Jinadasa, K., Milham, P., Hawkins, C., Cornish, P., Williams, P., Kaldor, C., et al. (1997). Survey of cadmium levels in vegetables and soils of Greater Sydney, Australia. Journal of Environmental Quality, 26(4), 924–933.
Kalam, A., Tah, J., & Mukherjee, A. K. (2004). Pesticide effects on microbial population and soil enzyme activities during vermicomposting of agricultural waste. Journal of Environmental Biology, 25(2), 201–208.
Kamble, S., & Saran, R. (2005). Effect of concentration on the adsorption of three termiticides in soil. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 75(6), 1077–1085.
Komárek, M., Čadková, E., Chrastný, V., Bordas, F., & Bollinger, J.-C. (2010). Contamination of vineyard soils with fungicides: A review of environmental and toxicological aspects. Environment International, 36(1), 138–151.
Kreuger, J., Peterson, M., & Lundgren, E. (1999). Agricultural inputs of pesticide residues to stream and pond sediments in a small catchment in southern Sweden. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 62(1), 55–62.
Langheinrich, U., Tischner, R., & Godbold, D. L. (1992). Influence of a high Mn supply on Norway spruce (Picea abies (L.) Karst.) seedlings in relation to the nitrogen source. Tree physiology, 10(3), 259–271.
Lawrence, G., Richards, C., & Lyons, K. (2013). Food security in Australia in an era of neoliberalism, productivism and climate change. Journal of Rural Studies, 29, 30–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrurstud.2011.12.005.
Leitão, S., Cerejeira, M. J., Van den Brink, P. J., & Sousa, J. P. (2014). Effects of azoxystrobin, chlorothalonil, and ethoprophos on the reproduction of three terrestrial invertebrates using a natural Mediterranean soil. Applied Soil Ecology, 76, 124–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2013.12.013.
Liu, Y., Xu, Z., Wu, X., Gui, W., & Zhu, G. (2010). Adsorption and desorption behavior of herbicide diuron on various Chinese cultivated soils. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 178(1–3), 462–468.
Lockhart, W., Macdonald, R., Outridge, P., Wilkinson, P., DeLaronde, J., & Rudd, J. (2000). Tests of the fidelity of lake sediment core records of mercury deposition to known histories of mercury contamination. Science of the Total Environment, 260(1–3), 171–180.
Lowry, D. B., Rockwood, R. C., & Willis, J. H. (2008). Ecological reproductive isolation of coast and inland races of Mimulus guttatus. Evolution: International Journal of Organic Evolution, 62(9), 2196–2214.
Malhat, F., Watanabe, H., & Youssef, A. (2015). Degradation profile and safety evaluation of methomyl residues in tomato and soil. Hellenic Plant Protection Journal, 8(2), 55–62.
Martikainen, E. (1996). Toxicity of dimethoate to some soil animal species in different soil types. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 33(2), 128–136. https://doi.org/10.1006/eesa.1996.0016.
McLaughlin, M. J., Palmer, L., Tiller, K., Beech, T. A., & Smart, M. (1994). Increased soil salinity causes elevated cadmium concentrations in field-grown potato tubers. Journal of Environmental Quality, 23(5), 1013–1018.
Millaleo, R., Alvear, M., Aguilera, P., González-Villagra, J., de la Luz Mora, M., Alberdi, M., et al. (2019). Mn toxicity differentially affects physiological and biochemical features in highbush blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum L.) cultivars. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 1–11.
Mishra, G., Debnath, S., & Rawat, D. (2017). Managing phosphorus in terrestrial ecosystem: A review. European Journal of Biological Research, 7(3), 255–270.
Moen, J., Cornet, J., & Evers, C. (1986). Soil protection and remedial actions: Criteria for decision making and standardization of requirements. In Contaminated soil (pp. 441–448): Springer.
Moncada, A. (2004). Environmental fate of diuron. Sacramento, CA: California Department of Pesticide Regulation.
Mortvedt, J., & Osborn, G. (1982). Studies on the chemical form of cadmium contaminants in phosphate fertilizers. Soil Science, 134(3), 185–192.
Muukkonen, P., Hartikainen, H., Lahti, K., Särkelä, A., Puustinen, M., & Alakukku, L. (2007). Influence of no-tillage on the distribution and lability of phosphorus in Finnish clay soils. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 120(2–4), 299–306.
NEPC (2011a). National Environment Protection (Assessment of Site Contamination) Measure 2011 Schedule B7: Guideline on Health-Based Investigation Levels. In N. E. P. Council (Ed.), (pp. 1–60). Adelaide, Australia: Australian Commonwealth Government.
NEPC (2011b). National Environment Protection (Assessment of Soil Contamination) Measure 2011 Schedule B1: Guideline on Investigation Levels for Soil and Groundwater. In N. E. P. Council (Ed.), (pp. 1–61). Adelaide, Australia: Australian Commonwealth Government.
NEPC (2011c). National Environment Protection (Assessment of Soil Contamination) Measure 2011 Schedule B5a: Guideline on Ecological Risk Assessment. In N. E. P. Council (Ed.), (pp. 1–42). Adelaide, Australia: Australian Commonwealth Government.
NEPC (2011d). National Environment Protection (Assessment of Soil Contamination) Measure 2011 Schedule B5b: Methodology to Derive Ecological Investigation Levels in Contaminated Soils. In N. E. P. Council (Ed.), (Vol. Schedule B5b, pp. 1–87). Adelaide, Australia: Australian Commonwealth Government.
NEPC (2011e). National Environment Protection (Assessment of Soil Contamination) Measure 2011 Schedule B5c: Soil Quality guidelines for Arsenic, Chromium (III), Copper, DDT, Lead, Naphthalene, Nickel & Zinc. In N. E. P. Council (Ed.), (pp. 1–177). Adelaide, Australia: Australian Commonwealth Government.
NEPM. (1999). Investigation levels for soil and groundwater. Adelaide: National Environmental Protection Council Service Corporation.
Nicol, E., Chayata, H., Genty, C., Bouchonnet, S., & Bourcier, S. (2016). Photodegradation of cyprodinil under UV–visible irradiation–chemical and toxicological approaches. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 30(19), 2201–2211.
Nziguheba, G., & Smolders, E. (2008). Inputs of trace elements in agricultural soils via phosphate fertilizers in European countries. Science of the Total Environment, 390(1), 53–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.09.031.
Outridge, P. M., & Wang, F. (2015). The stability of metal profiles in freshwater and marine sediments. In Environmental contaminants (pp. 35–60): Springer.
Owojori, O. J., Ademosu, O. T., Jegede, O. O., Fajana, H. O., Kehinde, T. O., & Badejo, M. A. (2019). Tropical oribatid mites in soil toxicity testing: Optimization of test protocol and the effect of two model chemicals (cadmium and dimethoate) on Muliercula inexpectata. Chemosphere, 218, 948–954. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.11.173.
Paschke, M. W., Valdecantos, A., & Redente, E. F. (2005). Manganese toxicity thresholds for restoration grass species. Environmental Pollution, 135(2), 313–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2004.08.006.
Persaud, D., Jaagumagi, R., & Hayton, A. (1993). Guidelines for the protection and management of aquatic sediment quality in Ontario.
Rhodes, R. C., & Long, J. D. (1974). Run-off and mobility studies on benomyl in soils and turf. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 12(3), 385–393.
Rundgren, S., Rühling, Å., Schlüter, K., & Tyler, G. (1992). Mercury in soil: Distribution, speciation and biological effects. Nordic Council of Ministers.
Rydberg, J., Gälman, V., Renberg, I., Bindler, R., Lambertsson, L., & Martínez-Cortizas, A. (2008). Assessing the stability of mercury and methylmercury in a varied lake sediment deposit. Environmental Science and Technology, 42(12), 4391–4396.
Sakugawa, H., Tahara, K., Aoki, K., Arai, N., Nakatani, N., & Takeda, K. (2010). Studies on concentration, decomposition rate, half-life time and degradation products of herbicide diuron in river waters of Hiroshima Prefecture, Japan. Chikyukagaku (Geochemistry), 44(1), 1–15.
Sanderson, D., & Edson, E. (1964). Toxicological properties of the organophosphorus insecticide dimethoate. Occupational and Environmental Medicine, 21(1), 52–64.
Santos, I. R., De Weys, J., & Eyre, B. D. (2011). Groundwater or floodwater? Assessing the pathways of metal exports from a coastal acid sulfate soil catchment. Environmental Science and Technology, 45(22), 9641–9648.
Schäfer, R. B., Bundschuh, M., Rouch, D. A., Szöcs, E., von der Ohe, P. C., Pettigrove, V., et al. (2012). Effects of pesticide toxicity, salinity and other environmental variables on selected ecosystem functions in streams and the relevance for ecosystem services. Science of the Total Environment, 415, 69–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.05.063.
Shanley, J. B., & Bishop, K. (2012). Mercury cycling in terrestrial watersheds (Mercury in the environment: Pattern and process).
Short, K. (1994). Quick poison, slow poison: Pesticide risk in the lucky country. K. Short.
Simpson, M. (2019). Berry plant protection guide. In N. D. o. P. Industries (Ed.), Wollongbar Primary Industries Institute (pp. 1–100). Wollongbar, NSW: Department of Primary Industries.
Simpson, S., Batley, G., & Chariton, A. (2013). Revision of the ANZECC/ARMCANZ sediment quality guidelines. CSIRO Land and Water Report, 8(07), 128.
Sirtori, C., Zapata, A., Malato, S., & Agüera, A. (2012). Formation of chlorinated by-products during photo-Fenton degradation of pyrimethanil under saline conditions. Influence on toxicity and biodegradability. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 217–218, 217–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.03.017.
Smelt, J. H., Crum, S. J. H., Teunissen, W., & Leistra, M. (1987). Accelerated transformation of aldicarb, oxamyl and ethoprophos after repeated soil treatments. Crop Protection, 6(5), 295–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/0261-2194(87)90058-5.
Smith, E. R. G., Naidu, R., & Alston, A. (1998). Arsenic in the soil environment. Academic Press.
Smith, E., Smith, J., Smith, L., Biswas, T., Correll, R., & Naidu, R. (2003). Arsenic in Australian environment: An overview. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A, 38(1), 223–239.
Stork, P. R., Bennett, F. R., & Bell, M. J. (2008). The environmental fate of diuron under a conventional production regime in a sugarcane farm during the plant cane phase. Pest Management Science: Formerly Pesticide Science, 64(9), 954–963.
Sun, Q., Ding, S., Wang, Y., Xu, L., Wang, D., Chen, J., et al. (2016). In-situ characterization and assessment of arsenic mobility in lake sediments. Environmental Pollution, 214, 314–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.04.039.
Thorstensen, C. W., Lode, O., Eklo, O. M., & Christiansen, A. (2001). Sorption of bentazone, dichlorprop, MCPA, and propiconazole in reference soils from Norway. Journal of Environmental Quality, 30(6), 2046–2052.
Tilman, D. (1999). Global environmental impacts of agricultural expansion: The need for sustainable and efficient practices. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 96(11), 5995–6000.
USEPA. (1998). Pesticide fact sheet: Cyprodinil. In P. a. T. S. Office of Prevention (Ed.), Pesticide Fact Sheet (pp. https://nepis.epa.gov/Exe/ZyNET.exe/P100BIX107.TXT?ZyActionD=ZyDocument&Client=EPA&Index=1995+Thru+1999&Docs=&Query=&Time=&EndTime=&SearchMethod=1991&TocRestrict=n&Toc=&TocEntry=&QField=&QFieldYear=&QFieldMonth=&QFieldDay=&IntQFieldOp=1990&ExtQFieldOp=1990&XmlQuery=&File=D%1993A%1995Czyfiles%1995CIndex%1920Data%1995C1995thru1999%1995CTxt%1995C00000031%00000035CP00000100BIX00000037.txt&User=ANONYMOUS&Password=anonymous&SortMethod=h%00000037C-&MaximumDocuments=00000031&FuzzyDegree=00000030&ImageQuality=r00000075g00000038/r00000075g00000038/x00000150y00000150g00000016/i00000425&Display=hpfr&DefSeekPage=x&SearchBack=ZyActionL&Back=ZyActionS&BackDesc=Results%00000020page&MaximumPages=00000031&ZyEntry=00000031&SeekPage=x&ZyPURL). Greensboro, North Carolina, USA: US EPA.
Van Derveer, W. D., & Canton, S. P. (1997). Selenium sediment toxicity thresholds and derivation of water quality criteria for freshwater biota of western streams. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 16(6), 1260–1268.
van Herk, W. G., Vernon, R. S., & McGinnis, S. (2013). Response of the dusky wireworm, Agriotes obscurus (Coleoptera: Elateridae), to residual levels of bifenthrin in field soil. Journal of Pest Science, 86(1), 125–136.
Van Scoy, A., Pennell, A., & Zhang, X. (2016). Environmental fate and toxicology of dimethoate. In Reviews of environmental contamination and toxicology volume 237 (pp. 53–70). Springer.
Van Scoy, A. R., Yue, M., Deng, X., & Tjeerdema, R. S. (2013). Environmental fate and toxicology of methomyl. In Reviews of environmental contamination and toxicology (pp. 93–109). Springer.
Vašíčková, J., Hvězdová, M., Kosubová, P., & Hofman, J. (2019). Ecological risk assessment of pesticide residues in arable soils of the Czech Republic. Chemosphere, 216, 479–487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.10.158.
Warne, M. S. J., Heemsbergen, D., Stevens, D., McLaughlin, M., Cozens, G., Whatmuff, M., et al. (2008). Modeling the toxicity of copper and zinc salts to wheat in 14 soils. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry: An International Journal, 27(4), 786–792.
Waters, E. K., Scagel, C. F., & McLean, C. (2008). A survey of Vaccinium cultural practices in Australia emphasizing implications for mycorrhizal infection. International Journal of Fruit Science, 8(1–2), 109–124.
White, S., Conrad, S., Woodrow, R., Tucker, J., Wong, W., Cook, P., et al. (2020). Nutrient transport and sources in headwater streams surrounded by intensive horticulture. National Marine Science Centre: Southern Cross University, Coffs Harbour, NSW.
White, S., Santos, I., Conrad, S., & Sanders, C. (2018a). Investigating water quality in Coffs coastal estuaries and the relationship to adjacent land use. Part 2: Water Quality. National Marine Science Centre, Southern Cross University, Coffs Harbour. NSW.
White, S., Santos, I., & Hessey, S. (2018b). Effect of intensive horticulture practices on surrounding headwater stream nitrate concentrations. Environmental Pollution, 243, 1036–1046. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.08.074.
Wilk, P., & Ireland, G. (2008). Natural resource management guidelines for NSW Blueberry Growers. In N. DPI (Ed.), (pp. 1–16). Lismore, NSW: Graphiti-Design.
Yang, Y., Sheng, G., & Huang, M. (2006). Bioavailability of diuron in soil containing wheat-straw-derived char. Science of the Total Environment, 354(2), 170–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.01.026.
Zhang, J., & Liu, C. (2002). Riverine composition and estuarine geochemistry of particulate metals in China—weathering features, anthropogenic impact and chemical fluxes. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 54(6), 1051–1070.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the Gumbaynggirr people, traditional owners of the land on which this work took place. This project was funded by the Coffs Harbour City Council’s Environmental Levy program. We would like to acknowledge the contributions of Coffs Harbour City Council’s Samantha Hessey, Project Officer for the Orara River Rehabilitation Project & Regional State of the Environment Reporting for inspiring and supporting this project. We wish to thank the landowners who were kind enough to let us conduct sampling on their property and the efforts of Dylan Brown, Carolina Bueno, and Ceylena Holloway in both the laboratory and the field. Simon Proust provided insight in selecting sampling locations. Funding was provided by Australian Research Council (Grant Nos. FT170100327 and DE160100443).
Funding
Funding was provided by Coffs Harbour City Council’s Environmental Levy Grant Program. IRS and CJS receive funding from the Australian Research Council (FT170100327 and DE160100443).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SC, CS, and SW collected and prepared samples for analysis. SC wrote the introduction, methods, results, discussion, and conclusions sections of the manuscript. SW assisted in sampling design and wrote the study site section of the manuscript. CS and IS critically revised the intellectual content and edited multiple drafts of the manuscript before submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Conrad, S.R., White, S.A., Santos, I.R. et al. Assessing pesticide, trace metal, and arsenic contamination in soils and dam sediments in a rapidly expanding horticultural area in Australia. Environ Geochem Health 43, 3189–3211 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00803-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00803-z