Abstract
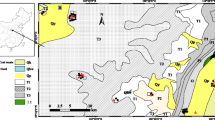
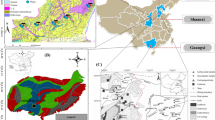
This study probe the human health risk of fluoride (F), arsenic (As), and selenium (Se) and their daily intake available quantity to human through different sources in different regions of Shaanxi, China. For this purpose, a number of samples, including coal and coal wastes, rocks, soil, and vegetables were collected from south Qinling Mountain stone-like coal (Geo type-I), Binxian-Jurassic (Geo type-II), Hancheng Permo-Carboniferous (Geo type-III), and countryside (Huanglong County) of Shaanxi province. All these samples were analyzed through atomic fluorescence spectroscopy and combustion hydrolysis methods. Results showed that Geo type-I was enriched with As, Se, and F, Geo type-II, III, and the countryside were slightly enriched with As and F and deficient in Se. The average daily intake (ADI) of Se in Geo type-I was 0.005–0.0045, Geo type-II 0.0005–0.0004, Geo type-III 0.0006–0.0005, and countryside 0.0002–0.001 in mg kg−1 day−1 adult–children, respectively, which was lower than the optimum level (0.06–0.075 mg kg−1day−1). ADI of As at Geo type-I was 0.0085–0.0075, Geo type-II 0.004–0.0037, Geo type-III 0.0008, and countryside 0.00022–0.00019 in mg kg−1 day−1 adult–children, respectively, which was above the acceptable range (10−6–10−4). ADI of F at Geo type-I was 0.0047–0.0041, Geo type-II 0.0098–0.0087, Geo type-III 0.002–0.0017 and countryside 0.0015–0.0013 in mg kg−1 day−1 adult–children, respectively. The toxicity level of Se and F at all the regions was lower than the NOAEL and LOAEL, while As was higher at Geo type-II and I. The extreme deficient of Se than the optimum range along with high F could deregulate the normal body growth especially causes bones and joint problems. However, the study found a rare patient with bone and joint disease (maybe Kashin–Beck disease) in the countryside. To find the exact cause of Kashin–Beck disease, the study needs further medical investigation in Se-deficient regions and their association with selenium deficiency and enriched fluoride.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ai, Z., Lu, W., Ton, S., Liu, H., Sou, T., & Shen, Z. (2007). Arsenic trioxide-mediated growth inhibition in gallbladder carcinoma cells via down-regulation of Cyclin D1 transcription mediated by Sp1 transcription factor. Biochemistry Biophysics Resource Communication, 360, 684–689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.06.123.
Bai, X., Li, W., Chen, Y., & Jiang, Y. (2007). The general distributions of trace elements in Chinese coals. Coal Quality Technology, 1, 1–4. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Baoshan, Z., Binbin, W., & Finkelman, R. B. (2010). Medical geology in China: Then and now. In O. Selinus, R. B. Finkelman, & J. A. Centeno (Eds.), Medical geology: A regional synthesis (pp. 303–327). Dordrecht: Springer.
Cai, H., Di, X., Chang, S. X., Wang, C., Shi, B., Geng, P., et al. (2016a). Carbon storage, net primary production, and net ecosystem production in four major temperate forest types in northeastern China. Canadian Journal of Forest Research/Revue Canadienne de Recherche Forestiere, 46, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjfr-2015-0038.
Cai, X., Wang, C., Yu, W., Fan, W., Wang, S., Shen, N., et al. (2016b). Selenium exposure and cancer Risk: An update meta-analysis and meta-regression. Scientific Reports, 6, 19213. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep19213.
Chen, J. (2012). An original discovery: Selenium deficiency and Keshan disease (an endemic heart disease). Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 21(3), 320–326.
Dai, S., Li, D., Chou, C.-L., Zhao, L., Zhang, Y., Ren, D., et al. (2008). Mineralogy and geochemistry of boehmite-rich coals: New insights from the Haerwusu Surface Mine, Jungar Coalfield, Inner Mongolia China. International Journal of Coal Geology, 74(3), 185–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2008.01.001.
Dai, S., Ren, D., Chou, C.-L., Finkelman, R. B., Seredin, V. V., & Zhou, Y. (2012). Geochemistry of trace elements in Chinese coals: A review of abundances, genetic types, impacts on human health, and industrial utilization. International Journal of Coal Geology, 94, 3–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2011.02.003.
Du, Y., Luo, K., Ni, R., & Hussain, R. (2018). Selenium and hazardous elements distribution in plant–soil–water system and human health risk assessment of Lower Cambrian, Southern Shaanxi, China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0082-3.
EQSS. (1991). Environmental Quality Standards for Soil Pollution (EQSS). Ministry of the Environment Government of Japan Godochosha No. 5, 1-2-2 Kasumigaseki, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 100-8975, Japan. https://www.env.go.jp/en/water/soil/sp.html.
Feng, H., Zilong, Z., Hongxu, L., Ping, L., & Yafeng, L. (2017). Palaeogeomorphic restoring of the Jurassic Zhiluo Formation and its effect on uranium mineralization in Binxian areas, southern Ordos Basin. Journal of Palaeogeography, 19(4), 692–702.
Finkelman, R. B. (1993). Trace and minor elements in coal. In M. H. Engel & S. A. Macko (Eds.), Organic Geochemistry (pp. 593–607). New York: Plenum press.
Franus, W., Wiatros-Motyka, M. M., & Wdowin, M. (2015). Coal fly ash as a resource for rare earth elements. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22(12), 9464–9474. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4111-9.
Fu, L. P., Zhang, Z. F., & Xie, C. R. (2004). Cyrtograptid zones near the lower boundary of the Silurian Wenlock Series in Ziyang Shaanxi. Geological Bulletin of China, 23(8), 795–798.
GB. (2005). Maximum levels of contaminants in food. National Food Safety Standard Guobiao (GB 2762-2005). Issued by Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China, Issued on January 25, 2005. https://www.chinesestandard.net/PDF/English.aspx/GB2762-2005.
GB. (2011). National Food Safety Standard General Principle for Prepackaged Food Label, Guobiao (GB 7718-2011). Issued by National Health and Family Planning Commission, Issued on: 2011-04-20. file:///C:/Users/Rahib%20Turi/Downloads/appendix-a2.pdf.
GB. (2012). National Food Safety Standard Maximum Levels of Contaminants in Food. Guobiao (GB 2762-2012). Issued by Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China, Issued on 13–11–2012.
Guo, Z. Q., Pan, L. H., Liu, X. Y., & Wang, J. (2001). Formation condition and distribution rule of Jurassic ancient landform oil field in Ordos Basin. China Petroleum Exploration, 6(4), 20–27.
Han, D. X., Ren, D. Y., Wang, Y. B., Jin, K., Mao, H. L., & Qin, Y. (1996). Coal petrology of China. (Chinese with English abstract) (pp. 98–168). Xuzhou: Publishing House of China University of Mining and Technology.
Hanjie, W., & Yuzhuo, Q. (1999). Geological setting of some classical selenium-bearing formations in China. Chinese Bulletin, 44, 185–186.
Hartikainen, H. (2005). Biogeochemistry of selenium and its impact on food chain quality and human health. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, 18(4), 309–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2005.02.009.
He, B., Liang, L., & Jiang, G. (2002). Distributions of arsenic and selenium in selected Chinese coal mines. Science of the Total Environment, 296(1), 19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(01)01136-6.
Hurst, R., Armah, C., & Dainty, J. (2010). Establishing optimal selenium status: results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 91(4), 923–931. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.2009.28169.
Hussain, R., Khattak, S. A., Shah, M. T., & Ali, L. (2015). Multistatistical approaches for environmental geochemical assessment of pollutants in soils of Gadoon Amazai Industrial Estate, Pakistan. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 15, 1119–1129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1075-9.
Hussain, R., Luo, K., Chao, Z., & Xiaofeng, Z. (2018). Trace elements concentration and distributions in coal and coal mining wastes and their environmental and health impacts in Shaanxi, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2148-2.
IRIS. (1987). Fluorine (soluble fluoride); CASRN 7782-41-4. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Chemical Assessment Summary National Center for Environmental Assessment. https://cfpub.epa.gov/ncea/iris/iris_documents/documents/subst/0053_summary.pdf. Accessed 31 Jan 1987.
IRIS. (1991). Selenium and Compounds; CASRN 7782-49-2 U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Chemical Assessment Summary National Center for Environmental Assessment. https://cfpub.epa.gov/ncea/iris/iris_documents/documents/subst/0472_summary.pdf. Accessed 1 June 1991.
IRIS. (1995). Integrated Risk Information System (Arsenic, inorganic; CASRN 7440-38-2. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Chemical Assessment Summary National Center for Environmental Assessment. https://cfpub.epa.gov/ncea/iris/iris_documents/documents/subst/0278_summary.pdf. Accessed 1 Mar 1994.
Jack, C. N., Wang, J., & Shraim, A. (2003). A global health problem caused by arsenic from natural sources. Chemosphere, 52(9), 1353–1359. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(03)00470-3.
JeffersonLab. (2007). It’s elemental -the periodic table of elements. Archived from the original on 29 April. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Abundance_of_elements_in_Earth%27s_crust. Accessed 14 Apr 2007.
Ketris, M. P., & Yudovich, Y. E. (2009). Estimations of Clarkes for Carbonaceous biolithes: World averages for trace element contents in black shales and coals. International Journal of Coal Geology, 78(2), 135–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2009.01.002.
Li, L., Luo, K.-L., Liu, Y.-L., & Xu, Y.-X. (2012a). The pollution control of fluorine and arsenic in roasted corn in “coal-burning” fluorosis area Yunnan, China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 229–230(Supplement C), 57–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.05.067.
Li, S., Xiao, T., & Zheng, B. (2012b). Medical geology of arsenic, selenium and thallium in China. Science of the Total Environment, 421(Supplement C), 31–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.02.040.
Li, X. C., Liu, W. S., Jia, L. C., & Zhang, C. W. (2014). Prognosis of sandstones hosted uranium deposit in southern Ordos Basin. Uranium Geology, 30(6), 321–327.
Liu, X., Song, Q., Tang, Y., Li, W., Xu, J., Wu, J., et al. (2013a). Human health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil-vegetable system: a multi-medium analysis. Science of the Total Environment, 463–464, 530–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.06.064.
Liu, Y., Luo, K., Li, L., & Shahid, M. Z. (2013b). Fluoride and sulfur dioxide indoor pollution situation and control in coal-burning endemic area in Zhaotong, Yunnan, China. Atmospheric Environment, 77, 725–737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2013.05.043.
Lu, Y., Sun, Z. R., Wu, L. N., Wang, X., Lu, W., & Liu, S. S. (2000). Effect of high-fluoride water on intelligence in children. Fluoride, 33(2), 74–78.
Luo, K. (2005). Arsenic content and distribution pattern in Chinese coals. Toxicological and Environmental Chemistry, 87(4), 427–438. https://doi.org/10.1080/02772240500286418.
Luo, K. (2011). Arsenic and fluorine contents and distribution patterns of early paleozoic stonelike coal in the Daba Fold Zone and Yangtze plate, China. Energy and Fuels, 25, 4479–4487. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef200737s.
Luo, K., Li, L., & Zhang, S. X. (2011). Coal-burning roasted corn and chili as the cause of dental fluorosis for children in southwestern China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 185(2–3), 1340–1347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.10.052.
Luo, K., Lirong, X., Jian, T., Douhu, W., & Lianhua, X. (2004a). Selenium source in the selenosis area of the Daba region, south Qinling Mountain, China. Environmental Geology, 45, 426–432. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-003-0893-z.
Luo, K., Ren, D., Xu, L., Dai, S., Cao, D., Feng, F., et al. (2004b). Fluorine content and distribution pattern in Chinese coals. International Journal of Coal Geology, 57(2), 143–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2003.10.003.
Luo, K., Xu, L., Li, R., & Xiang, L. (2002). Fluorine emission from combustion of steam coal of north China plate and northwest China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 47(16), 1346–1350. https://doi.org/10.1360/02tb9298.
Ministry of Environment. (2011). Soil, ground water and sediment standards for use under part XV.1 of the Environmental Protection Act. Canada, Ontario: Ministry of the Environment, Canada. PIBS #7382e01.
National Research Council. (2006). Fluoride in drinking water: A scientific review of EPA, #039; standards. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press.
Ni, R., & Luo, K. (2015). Determination of total selenium and arsenic in coal by wet digestion hydride generation atomic fluorescence spectrometry (HG-AFS). Guang pu xue yu guang pu fen xi = Guang pu, 35(5), 1404–1408.
Ni, R., Luo, K., Tian, X., Yan, S., Zhong, J., & Liu, M. (2016). Distribution and geological sources of selenium in environmental materials in Taoyuan County, Hunan Province China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 38(3), 927–938.
Palmer, C. A., & Lyons, P. C. (1996). Selected elements in major minerals from bituminous coal as determined by INAA: Implications for removing environmentally sensitive elements from coal. International Journal of Coal Geology, 32(1), 151–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-5162(96)00035-3.
Ren, D., Zhao, F., Dai, S., Zhang, J., & Luo, K. (2006). Geochemistry of trace elements in coal (p. 556). Beijing.: Science Press. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Rong, J. Y., Chen, X., Fan, J. X., & Zhan, R. B. (2005). Restudy of two of SilurianGSSPs: the base of the Silurian and the base of the Wenlock Series. Professional Papers of Stratigraphy and Palaeontology, 28, 41–60.
Ren, Z. X., Shen, X. P., & Chen, F. L. (2014). Analysis on the geological features and ore-forming condition at southern margin of Ordos basin. World Nuclear Geosciences, 31(3), 514–518.
SEPAC. (1995). Environmental quality standard for soils (GB 15618–1995). Beijing: State Environmental Protection Admisntratction of China (SEPAC).
Shi, G. L., Lou, L. Q., Zhang, S., Xia, X. W., & Cai, Q. S. (2013). Arsenic, copper, and zinc contamination in soil and wheat during coal mining, with assessment of health risks for the inhabitants of Huaibei China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20(12), 8435–8445. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1842-3.
Sørensen, K., Van den Broucke, S., Fullam, J., Doyle, G., Pelikan, J., Slonska, Z., et al. (2012). Health literacy and public health: A systematic review and integration of definitions and models. BMC Public Health, 12(1), 80. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-12-80.
Sun, D. J. (2004). Strengthen in the study of the hot spots about the prevention of endemic fluorosis. Chinese Journal of Endemiology, 23, 97–99.
Tan, J. A., Zhu, W., Wang, W., Li, R., Hou, S., Wang, D., et al. (2002). Selenium in soil and endemic diseases in China. Science of the Total Environment, 284(1), 227–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(01)00889-0.
Tang, W. C., He, J. P., Shi, Z. W., Zhu, B., & Jiang, H. (2002). An Investigation on arsenic surrounding and arsenic poisoning in endemic fluorosis of the type of burning coal pollution in Ankang city. China Journal Control of Endemic Disease, 17(2), 110–113.
Tang, X. Y., & Huang, W. H. (2004). Trace element in China coals (pp. 1–193). Beijing: Commercial Publishing House Press. (in Chinese).
Tang, Y., Chang, C., Zhang, Y., & Li, W. (2009). Migration and distribution of fifteen toxic trace elements during the coal washing of the Kailuan Coalfield, Hebei Province China. Energy Exploration & Exploitation, 27(2), 143–152. https://doi.org/10.1260/0144-5987.27.2.143.
Tseng, C. H., Tseng, C. P., Chiou, H. Y., Hsueh, Y. M., Chong, C. K., & Chen, C. (2002). Epidemiologic evidence of diabetogenic effect of arsenic. Toxicology Letters, 133, 69–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4274(02)00085-1.
USEPA. (2011). Exposure factors handbook, edition EPA/600/R-09/052F, published by United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA), Washington, DC: National Center for Environmental Assessment, Office of Research and Development.
Walpole, S. C., Prieto-Merino, D., Edwards, P., Cleland, J., Stevens, G., & Roberts, I. (2012). The weight of nations: an estimation of adult human biomass. BMC Public Health, 12(1), 439. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-12-439.
Wang, J. (2010). Late Paleozoic macrofloral assemblages from Weibei coalfield, with reference to vegetational change through the late Paleozoic ice-age in the North China block. International Journal of Coal Geology, 83, 292–317.
Wang, J. Q., Liu, C. Y., Guo, Z., & Zhang, D. D. (2015). Sedimentary response of regional tectonic transformation Late Triassic Yanchang period at the central and southern Ordos Basin. Earth Frontiers, 22(3), 194–204.
Wang, R., Xu, Z., Santosh, M., Liang, F., & Fu, X. (2017). Petrogenesis and tectonic implications of the Early Paleozoic intermediate and mafic intrusions in the South Qinling Belt, Central China: Constraints from geochemistry, zircon U–Pb geochronology and Hf isotopes. Tectonophysics, 712–713(Supplement C), 270–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2017.05.021.
Wang, S. (1996). Coal accumulation and coal resource evaluation of Ordos Basin (p. 437). Beijing: China Coal Industry Publishing House. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang, S., Luo, K., Wang, X., & Sun, Y. (2016). Estimate of sulfur, arsenic, mercury, fluorine emissions due to spontaneous combustion of coal gangue: An important part of Chinese emission inventories. Environmental Pollution, 209, 107–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2015.11.026.
Wang, Z., & Gao, Y. (2001). Biogeochemical cycling of selenium in Chinese environments. Applied Geochemistry, 16(11), 1345–1351. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-2927(01)00046-4.
WEC. (2013). World energy resources (p. 468).
Wu, D., Deng, H., Zheng, B., Wang, W., Tang, X., & Xiao, H. (2008). Iodine in Chinese coals and its geochemistry during coalification. Applied Geochemistry, 23(8), 2082–2090. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2008.04.022.
Xiang, Q., Liang, Y., Zhou, M., & Zang, H. (2003). Blood lead of children in Wamiao–Xinhuai intelligence study. Fluoride, 36(3), 198–199.
Xiong, Y. M., Mo, X. Y., Zou, X. Z., Song, R. X., Sun, W. Y., Lu, W., et al. (2010). Association study between polymorphisms in selenoprotein genes and susceptibility to Kashin–Beck disease. Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 18(6), 817–824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2010.02.004.
Xue, G., Liu, H., & Lia, W. (2012). Deformed coal types and pore characteristics in Hancheng coalmines in Eastern Weibei coalfields. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 22, 681–686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2012.08.015.
Yang, L., Peterson, P. J., Williams, W. P., Wang, W., Li, R., & Tan, J. A. (2003). Developing environmental health indicators as policy tools for endemic fluorosis management in the People’s Republic of China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 25(3), 281–295. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024543819240.
Yao, Y., Liu, D., Tang, D., Tang, S., Che, Y., & Huang, W. (2009). Preliminary evaluation of the coalbed methane production potential and its geological controls in the Weibei Coalfield, Southeastern Ordos Basin China. International Journal of Coal Geology, 78(1), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2008.09.011.
You, C. F., & Xu, X. C. (2010). Coal combustion and its pollution control in China. Energy, 35(11), 4467–4472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2009.04.019.
Yu, J., Qian, H., Li, Y., Wang, Y., Zhang, X., & Liang, X. (2007). Arsenic trioxide (As2O3) reduces the invasive and metastatic properties of cervical cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Gynecology Oncology, 106, 400–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygyno.2007.04.016.
Zhang, A. H., Yang, G. H., Li, J., & Wang, R. (2000). The situation of DNA synthesis, DNA damage and DNA repair in arsenism patients blood cells caused by coal-burning. Carcinogen Teratogen Mutagen, 12(2), 76–79. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ABJB200002003.htm.
Zhang, A. Y., Wu, D. M., Guo, L., & Wang, Y. L. (1987). The geochemistry of marine black shale formation and its metallogenic significance (pp. 1–39). Beijing: Science Publication House.
Zhang, Y. J., & Da, Y. B. (2015). The decomposition of energy-related carbon emission and its decoupling with economic growth in China. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 41(Supplement C), 1255–1266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.09.021.
Zhao, F., Ren, D., Zheng, B., Hu, T., & Liu, T. (1998). Modes of occurrence of arsenic in high arsenic coal by extended X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy. Chinese Science Bulletin, 43, 1660–1663. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02883414.
Zhao, J. X., Chen, H. D., & Shi, Z. Q. (2001). The way and implications of rebuilding paleogeomorphology; taking the research of paleogeomorphology of the Ordos Basin before Jurassic deposition as example. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology, 28(3), 260–266.
Zhenmin, G., Taiyi, L., & Shengrong, L. (1997). The origin of metal-enriched layer in the black rock series. Geology and Geochemistry, 1, 18–23.
Zhou, C., Liu, G., Cheng, S., Fang, T., & Lam, P. K. S. (2014). The environmental geochemistry of trace elements and naturally radionuclides in a coal gangue brick-making plant. Scientific Reports, 4, 6221. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep06221. https://www.nature.com/articles/srep06221#supplementary-information.
Zhu, J. M., Zheng, B. S., Liu, S. R., Li, S. H., Su, H. C., & Mao, D. J. (2000). Some new forms of native selenium and their genetic investigation. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 20(4), 337–341.
Acknowledgements
The National Basic Research Program of China (Grant No. 2014CB238906, AA17202026), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41172310 and 41472322) and CAS-TWAS Ph.D. fellowship, supported this study. The author also acknowledges the local guileless residents of Weibei, Shaanxi, for them allow us to go to their homes and farming fields to collect samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hussain, R., Luo, K. Geochemical valuation and intake of F, As, and Se in coal wastes contaminated areas and their potential impacts on local inhabitants, Shaanxi China. Environ Geochem Health 40, 2667–2683 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0131-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0131-y