Abstract
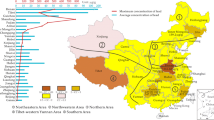
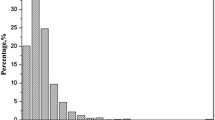
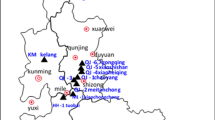
The content and distribution of the lead in coal, gangue and the sulfur ball and the pyritic gangue </A>of the Permo-Carboniferous in the North China Plate have been systematically studied (nearly 300 samples) in this paper. The Permo-Carboniferous coals in the North China Plate account for nearly 44.45 of total Chinese coal resources, and most of the steam coals in China come from the Permo-Carboniferous coals in the North China Plate. The result shows that lead content in the coal varied from 1.45 to 63.60 mg kg−1, averaging 23.95 mg kg−1; the lead content of the sulfur ball and the pyritic gangue in the coal seam ranges from 70.26–1060 mg kg−1, with an average of 271.28 mg kg−1; the lead content of the gangue is from 29.5 to 77.81 mg kg−1, averaging at 40.77 mg kg−1. The lead in the coal seam is mainly concentrated in the pyrite, such as sulfur ball, pyritic gangue or pyrite, and is the least concentrated in the organic of coal. The content of the lead has a direct ratio with the ash and the pyretic sulfur. Coal washing can reduce the content of the pyretic sulfur and the lead.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
WM Chen ZS Zhang (1993) Coal Chemistry Coal Industry Press Beijing
YQ Cheng (1998) ArticleTitleOn spreading the application of clean coal technology in China China Coal 24 IssueID4 14–19
HW Dai R Li LZ Li KY Xie (1997) ArticleTitleOn the adjustment of varieties, quality and mix of steam coal products in China China Coal 23 IssueID9 12–15
XQ Dai DY Ruan (2002) ArticleTitleInhibitory effect of Pb2+ on slow-inactivating K+ current in acutely isolated rat dorsal root ganglion neuronus Chinese J Pharmacol Toxicol 16 IssueID3 176–181
ZZ Elwira K Jan (2003) ArticleTitleDynamics of trace elements release in a coal pyrolysis process Fuel 82 1281–1290 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0016-2361(03)00031-0
WT Fan HS Pan (1995) ArticleTitleTo develop clean coal technology in China China Coal 1 16–22
JG Farmer LJ Eades MC Graham (1999) ArticleTitleThe lead content and isotopic composition of British coals and their implications for past and present releases of lead to the UK environment Environ Geochem Health 21 IssueID3 257–272 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1006688515919
RB Finkelman (1994) ArticleTitleModes of occurrence of potentially hazardous elements in coal, levels of confidence Fuel Process Technol 39 21–34 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0378-3820(94)90169-4
RX Guo JL Yang DY Liu ZY Liu (2002) ArticleTitleTransformation behavior of trace elements during coal pyrolysis Fuel Process Technol 77—78 137–143 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0378-3820(02)00041-3
YT Guo HM Hou J Li JL Chang (1994) ArticleTitleDissipation pattern of arsenic, fluorine, mercury, lead and cadmium in the process of coal incineration China Coalfield Geol 6 IssueID4 54–56
DL Johnson JK Bretsch (2002) ArticleTitleSoil lead and children’s blood lead levels in Syracuse, NY, USA Environ Geochem Health 24 IssueID4 375–385 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1020500504167
DH Liu TQ Zhang (2000) ArticleTitleThe lead levels in blood of preschool children and the lead content of environments in Taiyuanin Chinese J School Health 21 IssueID6 450–451
KL Luo DH Wang JA Tan LZ Wang FJ Feng RB Li (2002) Lead emission amount from coal combustion and its environment effect in Xi’an City, Environ Sci 23 IssueID1 123–125
K Meng XL Zhang JY Qin DX Wang (1995) ArticleTitleAnalysis of factors effecting lead pollution in urban environment of China Acta Sci Circum 15 IssueID2 135–141
CG Natalie LS Freeman J Marta M Lisa B E.P. Maurice (2001) ArticleTitleContribution of children’s activities to lead contamination of food J Exposure Anal Environ Epidemiol 11 IssueID5 407–413 Occurrence Handle10.1038/sj.jea.7500183
JL Pirkle DJ Brody EW Gunter RA Kramer DC Paschal KM Flegal TD Matte (1994) ArticleTitleThe decline in blood lead levels in the United States JAMA 272 284–291 Occurrence Handle10.1001/jama.272.4.284
DY Ren DW Xu JY Zhang FH Zhao G Li L Xie (1999) ArticleTitleDistribution of associated elements in coals from Shenbei Coalfield J China University Mining Technol 28 IssueID1 1–6
DY Ren FH Zhao YQ Wang SJ Yang (1999) ArticleTitleDistribution of minor and trace elements in Chinese coals Int J Coal Geol 40 109–118 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0166-5162(98)00063-9
DJ Swaine (1990) Trace Elements in Coal Bullerworths London 278
DJ Swaine (2000) ArticleTitleWhy trace elements are important Fuel Process Technol 65—66 21–33 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0378-3820(99)00073-9
YG Tang HY Zhang SF Dai XH Yang DY Chen (1999) ArticleTitleGeochemical characteristics of lead in coal Coal Geol Explora 29 7–10
V Valkovic (1983) Trace Elements in Coal CRC Press Boca Raton, FL, USA 161
RT Wu (1996) ArticleTitleThe developing trend of coal production in China China Coal 22 IssueID12 11–14
DW Ye (2001) ArticleTitleSome suggestions for the development of steam coal preparation and processing Coal Prepara Technol 5 1–6
Y Zeng (2001) ArticleTitleSpecial coal types in Western China and their exploitation and utilization J China Coal Soc 26 IssueID4 337–340
J Zhang CL Han YQ Xu (2003) ArticleTitleThe release of the hazardous elements from coal in the initial stage of combustion process Fuel Process Technol 1661 1–13
XG Zhuang SK Yang RS Zeng WD Xu (1999) ArticleTitleCharacteristics of trace elements in coals from several main coal districts in China Geol Sci Technol Inform 8 IssueID3 63–66
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kunli, L., Jidong, L. & Lianwu, C. Lead distribution in Permo-Carboniferous coal from the North China Plate, China. Environ Geochem Health 27, 31–37 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-004-5669-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-004-5669-1