Abstract
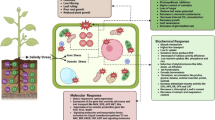
We investigated whether spermidine (Spd) application alleviates salinity-induced damage in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L), and explored defence mechanisms associated with stress-related ion balance, antioxidant metabolism, and gene expression. We examined the response of 30-day-old alfalfa maintained in hydroponic culture tests for 7 days and subjected to one of six treatments: half-strength Hoagland solution (control); 1% NaCl; 10 μM Spd + 1% NaCl; 20 μM Spd + 1% NaCl; 40 μM Spd + 1% NaCl; and 60 μM Spd + 1% NaCl. In salinity-stressed plants, chlorophyll b, chlorophyll a + b, and total protein showed significant decreases, while marked increases were detected in relative electrolyte leakage, H2O2 content, glutathione (GSH), superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), peroxidase (POD), glutathione reductase (GR) activity, the Na+/K+ ratio, and APX1, APX2, GR, and SOD gene expression levels. Chlorophyll a and total protein content markedly increased under exogenous application of 20 μM Spd, while H2O2 content, GSH, SOD, CAT, POD, GR activity, the Na+/K+ ratio, and APX2, GR, and SOD expression levels all decreased. These results indicated that exogenous application of 20 μM spermidine effectively alleviates salinity-induced damage in alfalfa. These findings could benefit alfalfa cultivation and promote the development and utilization of saline–alkali soil.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad P, Jaleel CA, Sharma S (2010) Antioxidant defence system, lipid peroxidation, proline-metabolizing enzymes, and biochemical activities in two Morus alba genotypes subjected to NaCl stress. Russ J Plant Physiol 57:509–517. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443710040084
Alhasnawi AN, Che Radziah CMZ, Kadhimi AA, Isahak A, Mohamad A, Yusoff WMW (2016) Enhancement of antioxidant enzyme activities in rice callus by ascorbic acid under salinity stress. Biol Plant 60:783–787. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-016-0603-9
Alvarez I, Tomaro ML, Benavides MP (2003) Changes in polyamines, proline and ethylene in sunflower calluses treated with NaCl. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 74:51–59. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023302012208
Anjum SA, Wang L, Farooq M, Khan I, Xue L (2011) Methyl jasmonate-induced alteration in lipid peroxidation, antioxidative defence system and yield in soybean under drought. J Agron Crop Sci 197:296–301. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-037X.2011.00468.x
Anower MR, Mott IW, Peel MD, Wu Y (2013) Characterization of physiological responses of two alfalfa half-sib families with improved salt tolerance. Plant Physiol Biochem 71:103–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2013.06.026
Assaha DVM, Ueda A, Saneoka H, Al-Yahyai R, Yaish MW (2017) The role of Na+ and K+ transporters in salt stress adaptation in glycophytes. Front Physiol 8:509. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2017.00509
Azooz MM, Youssef AM, Ahmad P (2011) Evaluation of salicylic acid (SA) application on growth, osmotic solutes and antioxidant enzyme activities on broad bean seedlings grown under diluted seawater. Int J Plant Physiol Biochem 3:253–264
Cui WT, Fang P, Zhu KK, Mao Y, Gao CY, Xie YJ, Wang J, Shen WB (2014) Hydrogen-rich water confers plant tolerance to mercury toxicity in alfalfa seedlings. Ecotox Environ Safe 105:103–111
de Carvalho K, de Campos MKF, Domingues DS, Pereira LFP, Vieira LGE (2013) The accumulation of endogenous proline induces changes in gene expression of several antioxidant enzymes in leaves of transgenic Swingle citrumelo. Mol Biol Rep 40:3269–3279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-2402-5
Du CX, Fan HF, Guo SR (2010) Applying spermidine for differential responses of antioxidant enzymes in cucumber subjected to short-term salinity. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 135:18–24
Duan JJ, Li J, Guo SR, Kang YY (2008) Exogenous spermidine affects polyamine metabolism in salinity-stressed Cucumis sativus roots and enhances short-term salinity tolerance. J Plant Physiol 165:1620–1635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2007.11.006
Faghire M, Bargaz A, Farissi M, Palma F, Mandri B, Lluch C, Tejera García NA, Herrera-Cervera JA, Oufdou K, Ghoulam C (2011) Effect of salinity on nodulation, nitrogen fixation and growth of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) inoculated with rhizobial strains isolated from the Haouz region of Morocco. Symbiosis 55:69–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-011-0144-0
Farissi M, Bouizgaren A, Faghire M, Bargaz A, Ghoulam C (2011) Agro- physiological responses of Moroccan alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) populations to salt stress during germination and early seedling stages. Seed Sci Technol 39:389–401. https://doi.org/10.15258/sst.2011.39.2.11
Farissi M, Ghoulam C, Bouizgaren A (2013) Changes in water deficit saturation and photosynthetic pigments of alfalfa populations under salinity and assessment of proline role in salt tolerance. Agric Sci Res J 3:29–35
Ferreira JFS, Cornacchione MV, Liu X, Suarez DL (2015) Nutrient composition, forage parameters, and antioxidant capacity of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) in response to saline irrigation water. Agriculture 5:577–597. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture5030577
Hu LP, Xiang LX, Li ST, Zou ZR, Hu XH (2016) Beneficial role of spermidine in chlorophyll metabolism and D1 protein content in tomato seedlings under salinity-alkalinity stress. Physiol Plant 156:468–477. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.12398
Hu LX, Li HY, Pang HC, Fu JM (2012) Responses of antioxidant gene, protein and enzymes to salinity stress in two genotypes of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne) differing in salt tolerance. J Plant Physiol 169:146–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2011.08.020
Kamiab F, Talaie A, Khezri M, Javanshah A (2014) Exogenous application of free polyamines enhance salt tolerance of pistachio (Pistacia vera L.) seedlings. Plant Growth Regul 72:257–268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-013-9857-9
Kaya C, Ashraf M, Sönmez O, Tuna AL, Aydemir S (2015) Exogenously applied nitric oxide confers tolerance to salinity-induced oxidative stress in two maize (Zea mays L.) cultivars differing in salinity tolerance. Turk J Agric For 39:909–919. https://doi.org/10.3906/tar-1411-26
Khan MH, Panda SK (2008) Alterations in root lipid peroxidation and antioxidative responses in two rice cultivars under NaCl-salinity stress. Acta Physiol Plant 30:81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-007-0093-7
Koca H, Bor M, Özdemir F, Türkan Ì (2007) The effect of salt stress on lipid peroxidation, antioxidative enzymes and proline content of sesame cultivars. Environ Exp Bot 60:344–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2006.12.005
Li GZ, Peng XQ, Wei LT, Kang GZ (2013) Salicylic acid increases the contents of glutathione and ascorbate and temporally regulates the related gene expression in salt-stressed wheat seedlings. Gene 529:321–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2013.07.093
Li RL, Shi FC, Fukuda KJ, Yang YL (2010) Effects of salt and alkali stresses on germination, growth, photosynthesis and ion accumulation in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Soil Sci Plant Nutr 56:725–733. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1747-0765.2010.00506.x
Li Z, Zhang Y, Zhang XQ, Peng Y, Merewitz E, Ma X, Huang LK, Yan YH (2016) The alterations of endogenous polyamines and phytohormones induced by exogenous application of spermidine regulate antioxidant metabolism, metallothionein and relevant genes conferring drought tolerance in white clover. Environ Exp Bot 124:22–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2015.12.004
Martins N, Osório ML, Gonçalves S, Osório J, Romano A (2013) Differences in Al tolerance between Plantago algarbiensis and P. almogravensis reflect their ability to respond to oxidative stress. Biometals 26:427–437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-013-9625-3
Mostofa MG, Yoshida N, Fujita M (2014) Spermidine pretreatment enhances heat tolerance in rice seedlings through modulating antioxidative and glyoxalase systems. Plant Growth Regul 73:31–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-013-9865-9
Ordoñez NM, Marondedze C, Thomas L, Pasqualini S, Shabala L, Shabala S, Gehring C (2014) Cyclic mononucleotides modulate potassium and calcium flux responses to H2O2 in Arabidopsis roots. FEBS Lett 588:1008–1115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2014.01.062
Puyang XH, An MY, Han LB, Zhang XZ (2015) Protective effect of spermidine on salt stress induced oxidative damage in two Kentucky bluegrass (Poa pratensis L.) cultivars. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 117:96–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.03.023
Qiu ZB, Guo JL, Zhu AJ, Zhang L, Zhang MM (2014) Exogenous jasmonic acid can enhance tolerance of wheat seedlings to salt stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 104:202–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.03.014
Radhakrishnan R, Lee IJ (2014) Effect of low dose of spermidine on physiological changes in salt-stressed cucumber plants. Russ J Plant Physiol 61:90–96. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443714010129
Rasool S, Ahmad A, Siddiqi TO, Ahmad P (2013) Changes in growth, lipid peroxidation and some key antioxidant enzymes in chickpea genotypes under salt stress. Acta Physiol Plant 35:1039–1050. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-012-1142-4
Raza SH, Athar HR, Ashraf M, Hameed A (2007) Glycinebetaine-induced modulation of antioxidant enzymes activities and ion accumulation in two wheat cultivars differing in salt tolerance. Environ Exp Bot 60:368–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2006.12.009
Roychoudhury A, Basu S, Sengupta DN (2011) Amelioration of salinity stress by exogenously applied spermidine or spermine in three varieties of indica rice differing in their level of salt tolerance. J Plant Physiol 168:317–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2010.07.009
Sairam RK, Srivastava GC (2002) Changes in antioxidant activity in sub-cellular fractions of tolerant and susceptible wheat genotypes in response to long term salt stress. Plant Sci 162:897–904. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9452(02)00037-7
Saleethong P, Sanitchon J, Kong-ngern K, Theerakulpisut P (2011) Pretreatment with spermidine reverses inhibitory effects of salt stress in two rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars differing in salinity tolerance. Asian J Plant Sci 10:245–254. https://doi.org/10.3923/ajps.2011.245.254
Sang T, Shan X, Li B, Shu S, Sun J, Guo SR (2016) Comparative proteomic analysis reveals the positive effect of exogenous spermidine on photosynthesis and salinity tolerance in cucumber seedlings. Plant Cell Rep 35:1769–1782. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-016-1995-x
Silini A, Cherif-Silini H, Yahialui B (2016) Growing varieties durum wheat (Triticum durum) in response to the effect of osmolytes and inoculation by Azotobacter chroococcum under salt stress. Afr J Microbiol Res 10:387–399. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJMR2015.7723
Sreenivasulu N, Grimm B, Wobus U, Weschke W (2000) Differential response of antioxidant compounds to salinity stress in salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive seedlings of foxtail millet (Setaria italica). Physiol Plant 109:435–442. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1399-3054.2000.100410.x
Tuteja N, Sahoo RK, Garg B, Tuteja R (2013) OsSUV3 dual helicase functions in salinity stress tolerance by maintaining photosynthesis and antioxidant machinery in rice (Oryza sativa L. cv. IR64). Plant J 76:115–127. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12277
Verma S, Mishra SH (2005) Putrescine alleviation of growth in salt stressed Brassica juncea by inducing antioxidative defense system. J Plant Physiol 162:669–677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2004.08.008
Wang N, Qi HK, Qiao WQ, Shi JB, Xu QH, Zhou H, Yan GT, Huang Q (2017) Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) genotypes with contrasting K+/Na+ ion homeostasis: implications for salinity tolerance. Acta Physiol Plant 39:77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-017-2381-1
Wang N, Qiao WQ, Liu XH, Shi JB, Xu QH, Zhou H, Yan GT, Huang Q (2017) Relative contribution of Na+/K+ homeostasis, photochemical efficiency and antioxidant defence system to differential salt tolerance in cotton (Gossypium hirutum L.) cultivars. Plant Physiol Biochem 119:121–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2017.08.024
Wang WW, Bai XY, Dong YJ, Chen WF, Song YL, Tian XY (2016) Effects of application of exogenous NO on the physiological characteristics of perennial ryegrass grown in Cd-contaminated soil. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 16:731–744. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-95162016005000053
Wang YQ, Li L, Cui WT, Xu S, Shen WB, Wang R (2012) Hydrogen sulfide enhances alfalfa (Medicago sativa) tolerance against salinity during seed germination by nitric oxide pathway. Plant Soil 351:107–119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-011-0936-2
Xu X, Shi G, Ding C, Xu Y, Zhao J, Yang H, Pan Q (2011) Regulation of exogenous spermidine on the reactive oxygen species level and polyamine metabolism in Alternanthera philoxeroides (Mart.) Griseb under copper stress. Plant Growth Regul 63:251–258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-010-9522-5
Yasmeen A, Basra SMA, Farooq M, Rehman H, Hussain N, Athar HR (2013) Exogenous application of moringa leaf extract modulates the antioxidant enzyme system to improve wheat performance under saline conditions. Plant Growth Regul 69:225–233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-012-9764-5
Yamamoto A, Shim I, Fujihara S (2012) Chilling-stress responses by rice seedlings grown with different ammonium concentrations and its relationship to leaf spermidine content. J Plant Biol 55:191–197. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-011-0072-9
Yiu JC, Liu CW, Fang DYT, Lai YS (2009) Waterlogging tolerance of Welsh onion (Allium fistulosum L.) enhanced by exogenous spermidine and spermine. Plant Physiol Biochem 47:710–716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2009.03.007
Zhang Y, Zhang H, Zou ZR, Liu Y, Hu XH (2015) Deciphering the protective role of spermidine against saline–alkaline stress at physiological and proteomic levels in tomato. Phytochemistry 110:13–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2014.12.021
Zhu H, Ding GH, Fang K, Zhao FG, Qin P (2006) New perspective on the mechanism of alleviating salt stress by spermidine in barley seedlings. Plant Growth Regul 49:147–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-006-9004-y
Zhu JK (2003) Regulation of ion homeostasis under salt stress. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:441–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1369-5266(03)00085-2
Zhu KK, Zhang J, Cui WT, Jin QJ, Samma MK, Shen WB (2014) Role of heme oxygenase-1 in spermidine-induced alleviation of salt toxicity during alfalfa seed germination. Plant Soil 375:275–287. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1964-x
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the Independent Innovation and Achievement Transformation Project of Shandong Province, the Key Research and Development Program (Industry Key Technology) of Shandong Province, and the Key Research and Development Program of Shandong Province for their support for our study.
Funding
This work was financially supported by grants from the Independent Innovation and Achievement Transformation Project of Shandong Province (2014ZZCX07402), the Key Research and Development Program (Industry Key Technology) of Shandong Province (2016CYJS05A02), and the Key Research and Development of Shandong Province (2017CXGC0306).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lou, Y., Guan, R., Sun, M. et al. Spermidine application alleviates salinity damage to antioxidant enzyme activity and gene expression in alfalfa. Ecotoxicology 27, 1323–1330 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-018-1984-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-018-1984-7