Abstract
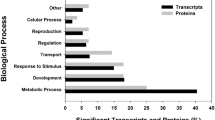
Eisenia fetida is a terrestrial organism, which can be used to diagnose sub-lethal concentrations of PFOA by using molecular biomarkers. In order to identify potential molecular biomarkers, we have exposed E. fetida to 10 mg/kg of PFOA in soil for 8 months. The mRNA isolation, sequencing, transcriptome assembly followed by differential gene expression studies have revealed that genes that are involved in apoptotic process, reproduction, calcium signalling, neuronal development and lipid metabolism are predominantly affected. Highly specific genes that are altered by PFOA can be further validated and used as biomarker to detect sub-lethal concentrations of PFOA in the soil.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott BD, Wolf CJ, Schmid JE, Das KP, Zehr RD, Helfant L, Nakayama S, Lindstrom AB, Strynar MJ, Lau C (2007) Perfluorooctanoic acid induced developmental toxicity in the mouse is dependent on expression of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-alpha. Toxicol Sci 98:571–581
Abbott BD, Wood CR, Watkins AM, Tatum-Gibbs K, Das KP, Lau C (2012) Effects of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) on expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPAR) and nuclear receptor-regulated genes in fetal and postnatal CD-1 mouse tissues. Reprod Toxicol 33:491–505
Arias EV, Mallavarapu M, Naidu R (2015a) Identification of the source of PFOS and PFOA contamination at a military air base site. Environ Monit Assess 187:4111
Arias EVA, Mallavarapu M, Naidu R (2015b) Treatment technologies for aqueous perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA): A critical review with an emphasis on field testing. Environ Technol Innov 4:168–181
Bouché MB (1972) Lombriciens de France: écologie et systématique
Brulle F, Morgan AJ, Cocquerelle C, Vandenbulcke F (2010) Transcriptomic underpinning of toxicant-mediated physiological function alterations in three terrestrial invertebrate taxa: a review. Environ Pollut 158:2793–2808
Cáceres T, Megharaj M, Naidu R (2011) Toxicity and transformation of insecticide fenamiphos to the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Ecotoxicology 20:20–28
Choi SK, Kim JH, Park JK, Lee KM, Kim E, Jeon WB (2013) Cytotoxicity and inhibition of intercellular interaction in N2a neurospheroids by perfluorooctanoic acid and perfluorooctanesulfonic acid. Food Chem Toxicol 60:520–529
Edwards CA (2004) Earthworm ecology. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Giesy JP, Kannan K (2002) Perfluorochemical surfactants in the environment. Environ Sci Technol 36:146a–152a
Gong P, Guan X, Inouye LS, Pirooznia M, Indest KJ, Athow RS, Deng Y, Perkins EJ (2007) Toxicogenomic analysis provides new insights into molecular mechanisms of the sublethal toxicity of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene in Eisenia fetida. Environ Sci Technol 41:8195–8202
Gong P, Guan X, Inouye LS, Deng Y, Pirooznia M, Perkins EJ (2008) Transcriptomic analysis of RDX and TNT interactive sublethal effects in the earthworm Eisenia fetida. BMC Genom 9(Suppl 1):S15
Gong P, Guan X, Pirooznia M, Liang C, Perkins EJ (2012) Gene expression analysis of CL-20-induced reversible neurotoxicity reveals GABA(A) receptors as potential targets in the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Environ Sci Technol 46:1223–1232
Grabherr MG, Haas BJ, Yassour M, Levin JZ, Thompson DA, Amit I, Adiconis X, Fan L, Raychowdhury R, Zeng Q, Chen Z, Mauceli E, Hacohen N, Gnirke A, Rhind N, di Palma F, Birren BW, Nusbaum C, Lindblad-Toh K, Friedman N, Regev A (2011) Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat Biotechnol 29:644–652
Guruge KS, Yeung LW, Yamanaka N, Miyazaki S, Lam PK, Giesy JP, Jones PD, Yamashita N (2006) Gene expression profiles in rat liver treated with perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA). Toxicol Sci 89:93–107
Haas BJ, Papanicolaou A, Yassour M, Grabherr M, Blood PD, Bowden J, Couger MB, Eccles D, Li B, Lieber M, Macmanes MD, Ott M, Orvis J, Pochet N, Strozzi F, Weeks N, Westerman R, William T, Dewey CN, Henschel R, Leduc RD, Friedman N, Regev A (2013) De novo transcript sequence reconstruction from RNA-seq using the Trinity platform for reference generation and analysis. Nat Protoc 8:1494–1512
Hagenaars A, Vergauwen L, Benoot D, Laukens K, Knapen D (2013) Mechanistic toxicity study of perfluorooctanoic acid in zebrafish suggests mitochondrial dysfunction to play a key role in PFOA toxicity. Chemosphere 91:844–856
Hansen KJ, Johnson HO, Eldridge JS, Butenhoff JL, Dick LA (2002) Quantitative characterization of trace levels of PFOS and PFOA in the Tennessee River. Environ Sci Technol 36:1681–1685
Harada K, Saito N, Inoue K, Yoshinaga T, Watanabe T, Sasaki S, Kamiyama S, Koizumi A (2004) The influence of time, sex and geographic factors on levels of perfluorooctane sulfonate and perfluorooctanoate in human serum over the last 25 years. J Occup Health 46:141–147
Hirano T, Tamae K (2011) Earthworms and soil pollutants. Sensors 11:11157–11167
Hoff PT, van de Vijver K, van Dongen W, Esmans EL, Blust R, de Coen WM (2003) Perfluorooctane sulfonic acid in bib (Trisopterus luscus) and plaice (Pleuronectes platessa) from the Western Scheldt and the Belgian North Sea: distribution and biochemical effects. Environ Toxicol Chem 22:608–614
Hu XZ, Hu DC (2009) Effects of perfluorooctanoate and perfluorooctane sulfonate exposure on hepatoma Hep G2 cells. Arch Toxicol 83:851–861
Huang Q, Zhang J, Martin FL, Peng S, Tian M, Mu X, Shen H (2013) Perfluorooctanoic acid induces apoptosis through the p53-dependent mitochondrial pathway in human hepatic cells: a proteomic study. Toxicol Lett 223:211–220
Jeon J, Kannan K, Lim HK, Moon HB, Ra JS, Kim SD (2010) Bioaccumulation of perfluorochemicals in Pacific oyster under different salinity gradients. Environ Sci Technol 44:2695–2701
Jiang Q, Lust RM, Dewitt JC (2013) Perfluorooctanoic acid induced-developmental cardiotoxicity: are peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha) and bone morphorgenic protein 2 (BMP2) pathways involved? J Toxicol Environ Health A 76:635–650
Johansson N, Fredriksson A, Eriksson P (2008) Neonatal exposure to perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) causes neurobehavioral defects in adult mice. Neurotoxicology 29:160–169
Kleszczyński K, Składanowski AC (2011) Mechanism of cytotoxic action of perfluorinated acids. III. Disturbance in Ca2+ homeostasis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 251:163–168
Kristensen SL, Ramlau-Hansen CH, Ernst E, Olsen SF, Bonde JP, Vested A, Halldorsson TI, Becher G, Haug LS, Toft G (2013) Long-term effects of prenatal exposure to perfluoroalkyl substances on female reproduction. Hum Reprod 28:3337–3348
Kubwabo C, Vais N, Benoit FM (2004) A pilot study on the determination of perfluorooctanesulfonate and other perfluorinated compounds in blood of Canadians. J Environ Monit 6:540–545
Langmead B, Trapnell C, Pop M, Salzberg SL (2009) Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol 10:R25
Liu X, Jin Y, Liu W, Wang F, Hao S (2011) Possible mechanism of perfluorooctane sulfonate and perfluorooctanoate on the release of calcium ion from calcium stores in primary cultures of rat hippocampal neurons. Toxicol In Vitro 25:1294–1301
Mariussen E (2012) Neurotoxic effects of perfluoroalkylated compounds: mechanisms of action and environmental relevance. Arch Toxicol 86:1349–1367
Mayilswami S, Krishnan K, Megharaj M, Naidu R (2014) Chronic PFOS exposure alters the expression of neuronal development-related human homologues in Eisenia fetida. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 110c:288–297
McMurdo CJ, Ellis DA, Webster E, Butler J, Christensen RD, Reid LK (2008) Aerosol enrichment of the surfactant PFO and mediation of the water–air transport of gaseous PFOA. Environ Sci Technol 42:3969–3974
Menzel R, Swain S, Hoess S, Claus E, Menzel S, Steinberg C, Reifferscheid G, Sturzenbaum S (2009) Gene expression profiling to characterize sediment toxicity—a pilot study using Caenorhabditis elegans whole genome microarrays. BMC Genom 10:160
Oakes KD, Sibley PK, Solomon KR, Mabury SA, van der Kraak GJ (2004) Impact of perfluorooctanoic acid on fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas) fatty acyl-CoA oxidase activity, circulating steroids, and reproduction in outdoor microcosms. Environ Toxicol Chem 23:1912–1919
Pirooznia M, Gong P, Guan X, Inouye LS, Yang K, Perkins EJ, Deng Y (2007) Cloning, analysis and functional annotation of expressed sequence tags from the Earthworm Eisenia fetida. BMC Bioinform 8(Suppl 7):S7
Reinecke AJ, Reinecke SA (2004a) Earthworms as test organisms in ecotoxicological assessment of toxicant impacts on ecosystems. In: Edwards CA (ed) Earthworm Ecology. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp. 299–327
Reinecke SA, Reinecke AJ (2004b) The comet assay as biomarker of heavy metal genotoxicity in earthworms. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 46:208–215
Ren H, Vallanat B, Nelson DM, Yeung LWY, Guruge KS, Lam PKS, Lehman-Mckeeman LD, Corton JC (2009) Evidence for the involvement of xenobiotic-responsive nuclear receptors in transcriptional effects upon perfluoroalkyl acid exposure in diverse species. Reprod Toxicol 27:266–277
Ricketts HJ, Morgan AJ, Spurgeon DJ, Kille P (2004) Measurement of annetocin gene expression: a new reproductive biomarker in earthworm ecotoxicology. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 57:4–10
Robinson MD, McCarthy DJ, Smyth GK (2010) edgeR: a Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 26:139–140
Rosen MB, Thibodeaux JR, Wood CR, Zehr RD, Schmid JE, Lau C (2007) Gene expression profiling in the lung and liver of PFOA-exposed mouse fetuses. Toxicology 239:15–33
Rosen MB, Lee JS, Ren H, Vallanat B, Liu J, Waalkes MP, Abbott BD, Lau C, Corton JC (2008) Toxicogenomic dissection of the perfluorooctanoic acid transcript profile in mouse liver: evidence for the involvement of nuclear receptors PPAR alpha and CAR. Toxicol Sci 103:46–56
Rosen MB, Schmid JE, Das KP, Wood CR, Zehr RD, Lau C (2009) Gene expression profiling in the liver and lung of perfluorooctane sulfonate-exposed mouse fetuses: COMPARISON to changes induced by exposure to perfluorooctanoic acid. Reprod Toxicol 27:278–288
Sanchez-Hernandez J (2006) Earthworm biomarkers in ecological risk assessment. Reviews of environmental contamination and toxicology. Springer, New York
Shin HM, Vieira VM, Ryan PB, Steenland K, Bartell SM (2011) Retrospective exposure estimation and predicted versus observed serum perfluorooctanoic acid concentrations for participants in the C8 Health Project. Environ Health Perspect 119:1760–1765
Steenbergen NT, Iaccino F, de Winkel M, Reijnders L, Peijnenburg WJ (2005) Development of a biotic ligand model and a regression model predicting acute copper toxicity to the earthworm Aporrectodea caliginosa. Environ Sci Technol 39:5694–5702
Wei Y, Dai J, Liu M, Wang J, Xu M, Zha J, Wang Z (2007) Estrogen-like properties of perfluorooctanoic acid as revealed by expressing hepatic estrogen-responsive genes in rare minnows (Gobiocypris rarus). Environ Toxicol Chem 26:2440–2447
Wei Y, Liu Y, Wang J, Tao Y, Dai J (2008) Toxicogenomic analysis of the hepatic effects of perfluorooctanoic acid on rare minnows (Gobiocypris rarus). Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 226:285–297
Ye L, Zhao B, Yuan K, Chu Y, Li C, Zhao C, Lian QQ, Ge RS (2012) Gene expression profiling in fetal rat lung during gestational perfluorooctane sulfonate exposure. Toxicol Lett 209:270–276
Zhao Y, Tan YS, Haslam SZ, Yang C (2010) Perfluorooctanoic acid effects on steroid hormone and growth factor levels mediate stimulation of peripubertal mammary gland development in C57Bl/6 mice. Toxicol Sci 115(1):214–224
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the Ramaciotti Centre for Genomics, The University of New South Wales, Sydney for mRNA sequencing and eResearch SA for computing facility. Mrs. Srinithi Mayilswami is a recipient of IPRS and CRCCARE top-up scholarships.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mayilswami, S., Krishnan, K., Megharaj, M. et al. Gene expression profile changes in Eisenia fetida chronically exposed to PFOA. Ecotoxicology 25, 759–769 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-016-1634-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-016-1634-x