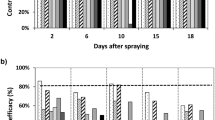
Abstract
Soybean pest control in Argentina is done just by chemical control using broad-spectrum pesticides. Alpaida veniliae (Araneae, Araneidae) is one of the most abundant spider species of the orb web weaver guild in soybean, and it is considered a very important polyphagous predator, attacking different insects’ families. The objective of this study was to determine if neurotoxic insecticides commonly used in soybean crops and a new active ingredient registered in Argentina (spinosad) adversely affected survival, prey consumption, mating behaviour, web building and reproductive capacity of A. veniliae females, under standard laboratory conditions. Spinosad was the most harmful insecticide due to high acute toxicity, even at lower concentrations than those registered for its field use and for its sublethal effects also. Cypermethrin caused several sublethal effects although its acute toxicity on spider was lower than other insecticides. It reduced prey consumption, affected web building, caused abnormalities in eggs sacs and decreased drastically the fecundity and fertility at sublethal concentrations. Endosulfan did not reduce prey consumption but it affected web building, caused abnormalities in eggs sacs and egg masses, and decreased the fecundity and fertility. Spinosad was also the compound with the most drastic effect on web building, it did not reduce prey consumption and fecundity, but fertility was reduced and abnormalities in egg sacs and egg masses were observed. The use of these insecticides in IPM programs according to their potential toxicity on spider communities is discussed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal N, Brar DS (2006) Effects of different neem preparations in comparison to synthetic insecticides on the whitefly parasitoid Encarsia sophia (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae) and the predator Chrysoperla carnea (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae) on cotton under laboratory conditions. J Pest Sci 79:201–207
Ahmed S, Maqsood A (2006) Toxicity of some insecticides on Bracon hebetor under laboratory conditions. Phytoparasitica 34:401–404
Bel’skaya E, Esyunin S (2003) Arachnids (Arachnidae) in a spring wheat agrocenosis in southern sverdlovsk oblast and the effect of treatment with decis, a pyrethroid insecticide, on their populations. Russ J Ecol 34(5):359–362
Benamú MA (2010) Composición y estructura de la comunidad de arañas en el sistema de cultivo de soja transgénica. PhD thesis, Facultad de Ciencias Naturales y Museo (UNLP), Argentina
Benamú M, Schneider M, Sánchez N (2010) Effects of the herbicide glyphosate on biological attributes of Alpaida veniliae (Araneae, Araneidae), in laboratory. Chemosphere 78:871–876
Benamú M, Sánchez N, González A (2011) Postembryonic development and population parameters of Alpaida veniliae (Araneae, Araneidae), reared in the laboratory. J Nat Hist 45(25–26):1607–1617
Bindraban PS, Franke AC, Ferraro DO, Ghersa CM, Lotz LAP, Nepomuceno A, Smulders MJM, van de Wei CCM (2009) GM-related sustainability: agro-ecological impacts, risks and opportunities of soy production in Argentina and Brazil. Plant Research International B.V, Wageningen
CASAFE (2011) Guía de productos fitosanitarios para la República Argentina, 16th edn. Buenos Aires, Argentina
Chi H (1997) Computer program for the Probit analysis. National Chung Hsing University, Taichung
Dağh F, Bahşi SU (2009) Topical and residual toxicity of six pesticides to Orius majusculus. Phytoparasitica 37:399–405
Desneux N, Wajnberg E, Fauvergue X, Privet S, Kaiser L (2004) Sublethal effects of a neurotoxic insecticide on the oviposition behaviour and the patch-time allocation in two aphid parasitoids, Diaeretiella rapae and Aphidius matricariae. Entomol Exp Appl 112:227–235
Desneux N, Denoyelle R, Kaiser L (2006) A multi-step bioassay to assess the effect of the deltamethrin on the parasitic wasp Aphidius ervi. Chemosphere 65:1697–1706
Desneux N, Decourtye A, Delpuech J (2007) The sublethal effects of pesticides on beneficial arthropods. Annu Rev Entomol 52:81–106
Dinter A, Phoehling H (1995) Side-effects of insecticides on two Erigonid spider species. Entomol Exp Appl 74(2):151–163
EJF (2002) End of the road for endosulfan: a call for action against a dangerous pesticide. Environmental Justice Foundation, London
Filgus M, Castañé C, Gabarra R (1999) Residual toxicity of some insecticides on the predatory bugs Dicyphus tamaninii and Macrolophus caliginosus. Biocontrol 44:89–98
Foelix R (1996) Biology of spiders, Second edn. Oxford University Press, New York, p 330
Frampton G, Van den Brink P (2007) Collembola and macroarthropod community responses to carbamate, organophosphate and synthetic pyrethroid insecticides: direct and indirect effects. Environ Pollut 147:14–25
Galvan TL, Koch RL, Hutchison WD (2005) Toxicity of commonly used insecticides in sweet corn and soybean to multicolored Asian lady beetle (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). J Econ Entomol 98:780–789
Haseeb M, Liu TX, Jones WA (2004) Effects of selected insecticides on Cotesia plutellae endoparasitoid of Plutella xylostella. Biocontrol 49:33–46
Haynes FK (1988) Subltethal effects of neurotoxic insecticides on insect behaviour. Annu Rev Entomol 33:149–168
Hesselberg T, Vollrath F (2004) The effects of neurotoxins on web-geometry and web-building behaviour in Araneus diadematus Cl. Physiol Behav 82:519–529
Jalali MA, Van Leeuwen T, Tirry L, De Clerq P (2009) Toxicity of selected insecticides to the two-spot ladybird Adalia bipunctata. Phytoparasitica 37:323–326
Jergentz S, Mugni H, Bonetto C, Schulz R (2005) Assessment of insecticide contamination in runoff and stream water of small agricultural streams in the main soybeans area of Argentina. Chemosphere 61:817–826
Jones W, Ciomperlik MA, Wolfenbarger DA (1998) Lethal and sublethal effects of insecticides on two parasitoids attacking Bemisia argentifolii (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae). Biol Control 11:70–76
Kim DS, Brooks DJ, Riedl H (2006) Lethal and sublethal effects of abamectin, spinosad, methoxyfenozide and acetamiprid on the predaceous plant bug Deraeocoris brevis. Biocontrol 51:465–484
Kogan M, Jepson P (2007) Perspectives in ecological theory and integrated pest management. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p 400
Longley M, Jepson P (1996) The influence of insecticide residues on primary parasitoid and hyperparasitoid foraging behaviour in the laboratory. Entomol Exp Appl 81:259–269
MAGyP (2012), Ministerio de Agricultura, Ganadería y Pesca. Presidencia de la Nación Argentina, www.minagri.gob.ar. Accessed 24 Feb 2012
Mahdian K, Van Leeuwen T, Tirry L, De Clerq P (2007) Susceptibility of the predatoryt stinkbug Picromerus bidens to selected insecticides. Biocontrol 52:765–774
Minervino E (1996) Estudio biológico y ecobiológico de arañas depredadoras de plagas de la soja. PhD Thesis, Facultad de Ciencias Naturales y Museo (UNLP), Argentina
Nation JL (2002a) Reproduction. In: Nation JL (ed) Insect physiology and biochemistry. CRC publisher, New York, pp 425–454
Nation JL (2002b) Hormones and Development. In: Nation JL (ed) Insect physiology and biochemistry. CRC publisher, New York, pp 119–156
Pekár S (1998) Effect os selective insecticidas on the beneficial spider community of a pear orchard in the Czech Republic. In: P.A. Selden (ed) Proceedings of the 17th European Colloquium of Arachnology, Edinburgh 1997, pp. 338–342
Rimoldi F, Schneider MI, Ronco AE (2008) Susceptibility of Chrysoperla externa eggs (Neuroptera: Chrisopidae) to conventional and biorational insecticides. Environ Entomol 37:1252–1257
Rimoldi F, Schneider MI, Ronco AE (2012) Short and Long-term effects of endosulfan, cypermethrin, spinosad, and methoxyfenozide on adults of Chrysoperla externa (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae). J Econ Entomol 105:1982–1987
Samu F, Vollrath F (1992) Spider orb web as bioassay for pesticide side effects. Entomol Exp Appl 62:117–124
Samu F, Matthew G, Lake D, Vollrath F (1992) Spider webs are efficient collectors of agronomical spray. Pest Sci 36:47–51
Scheiner S, Gurevitch J (2001) Design and analysis of ecological experiments. Oxford University Press. Oxford, New York, p 415
Schneider M, Smagghe G, Gobbi A, Viñuela E (2003) Toxicity and pharmacokinetics of insect growth regulators and other novel insecticides on pupae of Hyposoter didymator (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae), a parasitoid of early larval instars of lepidopteran pests. J Econ Entomol 96:1054–1065
Schneider M, Smagghe G, Pineda S, Viñuela E (2004) Action of insect growth regulator insecticides and spinosad on life history parameters and absorption in third-instar larvae of the endoparasitoid Hyposoter didymator. Biol Control 31:189–198
Schneider M, Smagghe G, Pineda S, Viñuela E (2008) The ecological impact of four IGR insecticides in adults of Hyposoter didymator (Hym., Ichneumonidae): pharmacokinetics approach. Ecotoxicology 17:181–188
Schneider M, Sanchez N, Pineda S, Chi H, Ronco A (2009) Impact of glyphosate on the development, fertility and demography of Chrysoperla externa (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae): ecological approach. Chemosphere 76:1451–1455
SENASA (2013) Endosulfan: nuevas medidas para la importación, elaboración y uso en Argentina. http://www.senasa.gov.ar. Accessed 20 Feb 2013
Shaw E, Waddicor M, Langan M (2006) Impact of cypermethrin on feeding behaviour and mortality of the spider Pardosa amentata in arenas with artificial “vegetation”. Pest Manag Sci 62:64–68
Stark J, Banks J (2003) Population-level effects of pesticides and other toxicants on arthropods. Annu Rev Entomol 48:505–519
Stark J, Vargas R, Banks J (2007) Incorporating ecologically relevant measures of pesticide effect for estimating the compatibility of pesticides and biocontrol agents. J Econ Entomol 100(4):1027–1032
Stenersen J (2004) Chemical Pesticides: Mode of action and toxicology. CRS press, Boca Raton, p 296
Tabanor ME, Hyslop E (2005) Effect of sublethal concentrations of endosulfan on growth and fecundity of two species of snails. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 74:1173–1178
Ventura Garcia P, Pereira N, Oliveira LM (2009) Side-effects of organic and synthetic pesticides on cold-stored diapausing prepuae of Trichogramma cordubensis. Biocontrol 54:451–458
Wang F, Jiang X, Bian YR, Yao FX, Gao HJ, Yu GF, Munch JC, Schroll R (2007) Organochlorine pesticides in soils under different land usage in the Taihu lake region, China. J Environ Sci 19:584–590
Watson GB (2001) Actions of insecticidal spinosyns on γ-aminobutyric acid responses from small-diameter cockroach neurons. Pestic Biochem Physiol 71:20–28
Wiles J, Jepson P (1994) Sublethal effects of deltamethrin residues on the within-crop behaviour and distribution of Coccinella septempunctata. Entomol Exp Appl 72:33–45
Williams T, Valle J, Viñuela E (2003) Is the naturally-derived insecticide Spinosad® compatible with insect natural enemies? Biocontrol Sci Technol 13:459–475
Zar H (1996) Biostatistical analysis. Prentice-Hall Inc., New Jersey 718 pp
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by a PICT 0115150 BID 1728 OCAR project from the Argentine National Agency for the Promotion of Science and Technology (ANPCyT). The authors thank to Gleba SA and DowAgrosciences SA for the donation of Glexthrin®, Endosulfan 25® and Tracer® samples, respectively. We thank also to R. Sosa and A. Cabrera for their valuable assistance in the field and laboratory work. We are also indebted to two anonymous reviewers for constructive criticism.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benamú, M.A., Schneider, M.I., González, A. et al. Short and long-term effects of three neurotoxic insecticides on biological and behavioural attributes of the orb-web spider Alpaida veniliae (Araneae, Araneidae): implications for IPM programs. Ecotoxicology 22, 1155–1164 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-013-1102-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-013-1102-9