Abstract
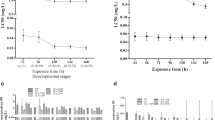
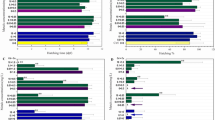
The aim of this research was to assess the combined effects of three heavy metals (copper, lead, cadmium) on the fertilization and offspring quality of the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus at EC50, NOEL, and EC1 concentrations. The observed data were compared with the predictions derived from approaches of Concentration Addition (CA) and Independent Action (IA) in order to evaluate the proper prediction of the observed mixture toxic effect. The P. lividus embryotoxicity of trace metals decreases as follows: Cu > Pb > Cd at all toxicity concentration tested. EC50 mixture revealed less toxic only than Cu; EC50 was 0.80 (±0.07) mg/l, the offspring malformations were mainly P1 type (skeletal alterations) up to 20% mixture concentration, and P2 type from 70% concentration. The NOEL and EC1 mixtures evidenced that all compounds contribute to the overall toxicity, even if present at low concentrations: the former EC50 was 0.532 (±0.058) mg/l and the latter was 1.081 (±0.240) mg/l. The developmental defects observed were mainly P1 type in both mixtures. Both CA and IA models did not accurately predict mixture toxicity for EC50 and NOEL mixtures. Instead, EC1 mixture effects seemed well represented by the IA model. The protective action of the CA model, although quite accurate when applied to simple biological systems like algae and bacteria, but failed to represent the worst-case in this study with more complex organisms. It would be useful to introduce in the models one or more factors that take into account the complexity of these biological systems.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altenburger R, Backhaus T, Boedeker W, Faust M, Scholze M, Grimme LH (2000) Predictability of the toxicity of multiple chemical mixtures to Vibrio fischeri: mixtures composed of similarly acting compounds. Environ Toxicol Chem 19:2341–2347
American Society for Testing and Materials, ASTM (2004) Standard guide for conducting static acute toxicity tests with echinoid embryos. ASTM Standard Guide E 1563–98. In: Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Section 11, vol 11.5
Amiard J-C, Amiard-Triquet C, Barka S, Pellerin J, Rainbow PS (2006) Metallothioneins in aquatic invertebrates: their role in metal detoxification and their use as biomarkers. Aquat Toxicol 76:160–202
Arizzi Novelli A, Argese E, Tagliapietra D, Bettiol C, Volpi Ghirardini A (2002) Toxicity of tributyltin and triphenyltin towards early life stages of Paracentrotus lividus (Echinodermata: Echinoidea). Environ Toxicol Chem 21:859–864
Arrhenius A, Gronvall F, Scholze M, Backhaus T, Blanck H (2004) Predictability of the mixture toxicity of 12 similarly acting congeneric inhibitors of photosystem II in marine periphyton and epipsammon communities. Aquat Toxicol 68:351–367
Arrhenius A, Backhaus T, Gronvall F, Junghans M, Scholze M, Blanck H (2006) Effects of three antifouling agents on algal communities and algal reproduction: mixture toxicity studies with TBT, irgarol, and sea-nine. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 50:335–345
Backhaus T, Altenburger R, Boedeker W, Faust M, Scholze M, Grimme H (2000a) Predictability of the toxicity of a multiple mixture of dissimilarly acting chemicals to Vibrio fischeri. Environ Toxicol Chem 19:2348–2356
Backhaus T, Scholze M, Grimme LH (2000b) The single substance and mixture toxicity of quinolones to the bioluminescent bacterium Vibrio fischeri. Aquat Toxicol 49:49–61
Backhaus T, Altenburger R, Arrhenius A, Blanck H, Faust M, Finizio A, Gramatica P, Grote M, Junghans M, Meyer W, Pavan M, Porsbring T, Scholze M, Todeschini R, Vighi M, Walter H, Grimme LH (2003) The BEAM project: prediction and assessment of mixture toxicities in the aquatic environment. Cont Shelf Res 23:1757–1769
Barata C, Baird DJ, Nogueira AJA, Agra AR, Soares MVM (2007) Life-history responses of Daphnia magna Straus to binary mixtures of toxic substances: pharmacological versus ecotoxicological modes of action. Aquat Toxicol 84:439–449
Bellas J (2008) Prediction and assessment of mixture toxicity of compounds in antifouling paints using the sea-urchin embryo-larval bioassay. Aquat Toxicol 88:308–315
Belyaeva EA, Glazunov VV, Korotkov SM (2004) Cd2+ promoted mitochondrial permeability transition: a comparison with other heavy metals. Acta Biochim Pol 51:545–551
Bliss CI (1939) The toxicity of poisons applied jointly. Ann J Appl Biol 26:585–615
Braek GS, Jensen A, Mohus A (1976) Heavy-metal tolerance of marine-phytoplankton 3. Combined effects of Cu and Zn ions on cultures of 4 common species. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 25:37–50
Bressan M, Marin M, Brunetti R (1995) Influence of temperature and salinity on embryonic-development of Paracentrotus-lividus (lmk, 1816). Hydrobiologia 304:175–184
Broderius SJ, Kahl MD, Hoglund MD (1995) Use of joint toxic response to define the primary mode of toxic action for diverse industrial organic chemicals. Environ Toxicol Chem 9:1591–1605
Carr RS (1996) Sediment quality assessment studies of Tampa Bay, Florida. Environ Toxicol Chem 15:1218–1231
Cedergreen N, Christensen AM, Kamper A, Kudsk P, Mathiassen SK, Streibig JC, Sorensen H (2008) A review of independent action compared to concentration addition as reference models for mixtures of compounds with different molecular target sites. Environ Toxicol Chem 27:1621–1632
Cesar A, Marin A, Marin-Guirao L, Vita R (2004) Amphipod and sea urchin tests to assess the toxicity of Mediterranean sediments: the case of Portman Bay. Sci Mar 68:205–213
Chapple G, Byrne JP (1996) Direct determination of trace metals in seawater using ETV-ICP-MS. J Anal At Spectrom 11:549–553
Dassenakis MI, Kloukiniotou MA, Pavlidou AS (1996) The influence of long existing pollution on trace metal levels in a small tidal Mediterranean Bay. Mar Pollut Bull 32:275–282
Dinnel PA, Link JM, Stober QJ, Letorneau MW, Roberts WE (1989) Comparative sensitivity of sea urchin sperm bioassays to metals and pesticide toxicity tests. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 18:748–755
Drescher K, Boedeker W (1995) Assessment of the combined effects of substances: the relationship between concentration addition and independent action. Biometrics 51:716–730
Dunnett CW (1955) A multiple comparisons procedure for comparing several treatments with a control. J Amer Statistical Assoc 509:1096–1121
Dunnett CW (1964) New tables for multiple comparisons with a control. Biometrics 20:482–491
Faust M (1999) Combined effect of pollutants on aquatic organisms; verification of predictability using a mono-cellular green algae. University of Bremen, Bremen.
Faust M, Altenburger R, Backhaus T, Blanck H, Boedeker W, Gramatica P, Hamer V, Scholze M, Vighi M, Grimme LH (2001) Predicting the joint algal toxicity of multi-component s-triazine mixtures at low-effect concentrations of individual toxicants. Aquat Toxicol 56:13–32
Faust M, Altenburger R, Backhaus T, Blanck H, Boedeker W, Gramatica P, Hamer V, Scholze M, Vighi M, Grimme LH (2003) Joint algal toxicity of 16 dissimilarly acting chemicals is predictable by the concept of independent action. Aquat Toxicol 63:43–63
Fernandez N, Beiras R (2001) Combined toxicity of dissolved mercury with Cu, Pb, and Cd on embryogenesis and early larval growth of the Paracentrotus lividus sea-urchin. Ecotoxicology 5:263–271
Filosto S, Roccheri MC, Bonaventura R, Matranga V (2008) Environmentally relevant Cd concentrations affect development and induce apoptosis of Paracentrotus lividus larvae cultured in vitro. Cell Biol Toxicol 24:603–610
Foulkes EC (2000) Transport of toxic heavy metals across cell membranes. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 223:234–240
George SG (1990) Biochemical and cytological assessments of metal toxicity in marine animals. In: Furness RW, Rainbow PS (eds) Heavy metals in the marine environment. CRC Press, Boca Raton, p 256
Hernando MD, Ejerhoon M, Fernandez-Alba AR, Chisti Y (2003) Combined toxicity effects of MTBE and pesticides measured with Vibrio fisheri and Daphnia magna bioassays. Wat Res 37:4091–4098
Heyvang I (1994) Toxicité des micropollutants en milieu marin. Mise au point d’un test simplifi′e bas′e sur l’utilisation d’oeufs d’embryons et de pluteus de Paracentrotus lividus. Exemples d’applications. IFREMER
His E, Heyvang I, Geffard O, De Mountadouin X (1999) A comparison between oyster (Crassostrea gigas) and sea urchin (Paracentrotus lividus) larval bioassay for toxicological studies. Water Res 7:1706–1718
Hunt JW, Anderson BS, Turpen SL, Englund MA, Piekarski W (1997) Precision and sensitivity of a seven-day growth and survival toxicity test using the west coast marine mysid crustacean Holmesimysis costata. Environ Toxicol Chem 1:824–834
Jonker MJ, Svendsen C, Bedaux JJM et al (2005) Significance testing of synergistic/antagonistic, dose level-dependent, or dose ratio-dependent effects in mixture dose-response analysis. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:2701–2713
Junghans M, Backhaus T, Faust M (2006) Application and validation of approaches for the predictive hazard assessment of realistic pesticide mixtures. Aquat Toxicol 76:93–110
Kamo M, Nagai T (2008) An application of the biotic ligand model to predict the toxic effects of metal mixtures. Environ Toxicol Chem 27:1479–1487
King CK, Riddle MJ (2001) Effects of metal contaminants on the development of the common Antarctic sea urchin Sterechinus neumayeri and comparisons of sensitivity with tropical and temperate echinoids. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 215:143–154
Kobayashi N, Okamura H (2002) Effects of new antifouling compounds on the development of sea urchin. Mar Pollut Bull 44:748–751
Kobayashi N, Okamura H (2005) Effects of heavy metals on sea urchin embryo development. Part 2 Interactive toxic effects of heavy metals in synthetic mine effluents. Chemosphere 61:1198–1203
Kraak MHS, Wink YA, Stuijfzand SC, Buckert-de Jonga MC, de Groota CJ, Admiraal W (1994) Chronic ecotoxicity of Zn and Pb to the zebra mussel Dreissena polymorpha. Aquat Toxicol 30:77–89
Llamas A, Ullrich CI, Sanz A (2000) Cd2+ effects on transmembrane electrical potential difference, respiration, and membrane permeability of rice (Oryza sativa) roots. Plant Soil 219:21–28
Loewe S (1927) Die Mischarznei. Versuch einer allgemeinen Pharmakologie der Arzneikombinationen. Klin Wochenschr 6:1077–1085
Loewe S, Muischnek H (1926) Effect of combinations: mathematical basis of problem. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol 114:313–326
Lorenzo JI, Nieto O, Beiras R (2002) Effect of humic acids on speciation and toxicity of copper to Paracentrotus lividus larvae in seawater. Aquat Toxicol 58:27–41
Manfra L, Accornero A (2002) Monitoraggio delle concentrazioni di metalli pesanti nelle acque costiere della Campania. Annali dell’Università degli studi di Napoli Parthenope, LXVI, pp 53–63
Manfra L, Accornero A (2005) Trace metal concentrations in coastal marine waters of the central Mediterranean. Mar Pollut Bull 50:686–692
Manzo S (2004) Sea urchin embryotoxicity test: proposal for a simplified bioassay. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 57:123–128
Manzo S, Buono S, Cremisini C (2006) Toxic effects of irgarol and diuron on sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus early development, fertilization, and offspring quality. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 51:61–68
Manzo S, Buono S, Cremisini C (2008) Predictability of copper, irgarol, and diuron combined effects on sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 54:57–68
Marin MG, Moschino V, Cima F, Celli C (2000) Embryotoxicity of butyltin compounds to the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus. Mar Environ Res 50:231–235
Moore DRJ, Caux PY (1997) Estimating low toxic effects. Environ Toxicol Chem 16:794–801
Nacci D, Serbst J, Gleason TR, Cayula S, Thursby G, Munns WR Jr, Johnston RK (2000) Biological responses of sea urchin Arbacia punctulata to lead contamination for an estuarine ecological risk assessment. J Aquat Ecosyst Stress Recovery 7:187–199
Norwood WP, Borgmann U, Dixon DG (2003) Effects of metal mixtures on aquatic biota: a review of observations and methods. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 9:795–811
Novelli AA, Losso C, Ghetti PF, Volpi Ghirardini A (2003) Toxicity of heavy metals using sperm cell and embryo toxicity bioassays with Paracentrotus lividus (Echinodermata: Echinoidea): comparisons with exposure concentrations in the lagoon of Venice, Italy. Environ Toxicol Chem 22:1295–1301
Otitoloju AA (2002) Evaluation of the joint-action toxicity of binary mixtures of heavy metals against the mangrove periwinkle Tympanotonus fuscatus var radula (L.). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 53:404–415
Pagano G, Esposito A, Giordano GG (1982) Fertilization and larval development in sea urchin following exposure of gametes and embryos to cadmium. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 11:47–55
Pagano G, Cipollaro M, Corsale G, Esposito A, Ragucci E, Giordano GG, Trieff NM (1986) The sea urchin: bioassay for the assessment of damage from environmental contaminants. In: Cairns J (ed) Community toxicity testing. American Society for Testing and Materials ASTM STP920, Philadelphia, pp 66–92
Pagano G, Iaccarino M, Guida M, Manzo S, Oral R, Romanelli R, Rossi M (1996a) Cadmium toxicity in spiked sediment to sea urchin embryos and sperm. Mar Environ Res 42:54–55
Pagano G, His E, Beiras R, De Biase A, Korkina LG, Iaccarino M, Oral R, Qiuniou F, Warnau M, Trieff NM (1996b) Cytogenetic, developmental, and biochemical effects of aluminium, iron, and their mixture in sea urchins and mussels. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 31:466–474
Pavicic MJ, van Winkelhoff AJ, Douque NH, Steures RW, de Graaff J (1994) Microbiological and clinical effects of metronidazole and amoxicillin in Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans-associated periodontitis. A 2-year evaluation. J Clin Periodontol 21:107–112
Phillips BM, Nicely PA, Hunt JW, Anderson BS, Tjeerdema RS, Palmer SE, Palmer FH, Puckett HM (2003) Toxicity of cadmium–copper–nickel–zinc mixtures to larval purple sea urchins. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 70:592–599
Radenac G, Fichet D, Miramand P (2001) Bioaccumulation and toxicity of four dissolved metals in Paracentrotus lividus sea urchin embryo. Mar Environ Res 51:151–166
Rosland E, Lund W (1998) Direct determination of trace metals in seawater by ICP-MS. J Anal At Spectrom 13:1239–1244
Scholze M, Boedeker W, Faust M, Backhaus T, Altenburger R, Grimme H (2001) A general best-fit method for concentration response curves and the estimation of low effect concentrations. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:448–457
Shriadah MA, Okbah MA, El-Deek MS (2004) Trace metals in the water columns of the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aqaba, Egypt. Water Air Soil Pollut 153:115–124
UNEP (1996) Guidelines for Integrated Planning Management of Coastal and Marine Areas in the Wider Caribbean Region. UNEP Caribbean Environment Programme, Kingston, Jamaica, 141 pp
US EPA (1993) A linear interpolation method for sublethal toxicity: the inhibition concentration (ICp) approach. National Effluent Toxicity Assessment Center Technical Report 03-93, Environmental Research Laboratory, Duluth, Minnesota
US EPA (1995) 600R95136 Short-term methods for estimating the chronic toxicity of effluents and receiving waters to West coast marine and estuarine organisms, Cincinnati, Ohio
Van Der Hoeven N, Noppert F, Annegaaike L (1997) How to measure no effect. Part I: towards a new measure of chronic toxicity in ecotoxicology. Introduction and workshop results. Environmetrics 8:241–248
Viarengo A (1985) Biochemical effects of trace-metals. Mar Pollut Bull 16:153–158
Volpi Ghirardini A, Arizzi Novelli A (2001) A sperm cell toxicity test procedure for the Mediterranean species Paracentrotus lividus (Echinodermata: Echinoidea). Environ Technol 22:439–445
Wang JY, Zhang MP, Xu JGWY (1995) Reciprocal effect of Cu, Cd, Zn on a kind of marine alga. Water Res 29:209–214
Warnau M, Pagano G (1994) Developmental toxicity of PbCl2 in the echinoid Paracentrotus lividus (Echinodermata). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 53:434–441
Warnau M, Iaccarino M, De Biase A, Temara A, Jangoux M, Dubois P, Pagano G (1996) Spermiotoxicity and embryotoxicity of heavy metals in the echinoid Paracentrotus lividus. Environ Toxicol Chem 15:1931–1936
Wood CM (2001) Toxic responses of the gill. In: Schlenk D, Benson WH (eds) Target organ toxicity in marine and freshwater teleosts, vol 1. Taylor and Francis, USA, pp 1–89
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manzo, S., Buono, S. & Cremisini, C. Cadmium, lead and their mixtures with copper: Paracentrotus lividus embryotoxicity assessment, prediction, and offspring quality evaluation. Ecotoxicology 19, 1209–1223 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-010-0506-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-010-0506-z