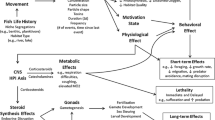
Abstract
The northeastern USA receives some of the highest levels of atmospheric mercury deposition of any region in North America. Moreover, fish from many lakes in this region carry Hg burdens that present health risks to both human and wildlife consumers. The overarching goal of this study was to identify the attributes of lakes in this region that are most likely associated with high Hg burdens in fish. To accomplish this, we compared data collected in four separate multi-lake studies. Correlations among Hg in fish (4 studies) or in zooplankton and fish (2 studies) and numerous chemical, physical, land use, and ecological variables were compared across more than 150 lakes. The analysis produced three general findings. First, the most important predictors of Hg burdens in fish were similar among datasets. As found in past studies, key chemical covariates (e.g., pH, acid neutralizing capacity, and SO4) were negatively correlated with Hg bioaccumulation in the biota. However, negative correlations with several parameters that have not been previously identified (e.g., human land use variables and zooplankton density) were also found to be equally important predictors. Second, certain predictors were unique to individual datasets and differences in lake population characteristics, sampling protocols, and fish species in each study likely explained some of the contrasting results that we found in the analyses. Third, lakes with high rates of Hg bioaccumulation and trophic transfer have low pH and low productivity with relatively undisturbed watersheds suggesting that atmospheric deposition of Hg is the dominant or sole source of input. This study highlights several fundamental complexities when comparing datasets over different environmental conditions but also underscores the utility of such comparisons for revealing key drivers of Hg trophic transfer among different types of lakes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.P. Allen T.R. Whittier D.P. Larsen P.R. Kaufmann R.J. O’Connor R.M. Hughes R.S. Stemberger S.S. Dixit R.O. Brinkhurst A.T. Herlihy S.G. Paulsen (1999) ArticleTitleConcordance of taxonomic composition patterns across multiple lake assemblages: effects of scale, body size, and land use Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 56 2029–40
R.C. Back C.J. Watras (1995) ArticleTitleMercury in zooplankton of Northern Wisconsin lakes – taxonomic and site-specific trends Water Air Soil Pollut. 80 931–38 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXnsVCgsrY%3D
G. Cabana A. Tremblay J. Kalff J.B. Rasmussen (1994) ArticleTitlePelagic food-chain structure in Ontario Lakes – a determinant of mercuy levels in lake trout (Salvelinus-namaycush) Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 51 IssueID2 381–89 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXks1Gjsrs%3D Occurrence Handle10.1139/f94-039
C.Y. Chen C.L. Folt (2000) ArticleTitleBioaccumulation and diminution of arsenic and lead in a freshwater food web Environ. Sci. Technol. 34 IssueID18 3878–84 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXlslWks7g%3D
C.Y. Chen R.S. Stemberger B. Klaue J.D. Blum P.C. Pickhardt C.L. Folt (2000) ArticleTitleAccumulation of heavy metals in food web components across a gradient of lakes Limnol. Oceanogr. 45 IssueID7 1525–36 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXosFymt7w%3D
Chen, C.Y. and Folt, (2005) C.L. High plankton densities reduce mercury biomagnification. Environ Sci. Technol. 39, 115–121
S.C. Choi T. Chase R. Bartha (1994) ArticleTitleMetabolic pathways leading to mercury methylation in Desulfovibrio–desulfuricans Ls Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 60 4072–77 Occurrence Handle16349435 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXmslKntLg%3D
DiFranco, J., Bacon, L., Mower, B. and Courtemanch, D. (1995). Fish tissue contamination in Maine Lakes. State of Maine Department of Environmental Protection
DiPasquale, M.M., Agee, J.L., Kieu, L.H. and Harms, H.A. (2004). Microbial mercury cycling in the San Francisco Bay sediments: from regions to the rhizosphere. E.O.S. Proc. 2004 A.G.U. Annual Symposium, Montreal, Canada. American Geophysical Union, Washington DC (AGU)
C.T. Driscoll C. Blette C. Yan C.L. Schofield R. Munson J. Holsapple (1995) ArticleTitleThe role of dissolved organic-carbon in the chemistry and bioavailability of mercury in remote Adirondack lakes Water Air Soil Pollut. 80 499–508 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXnsVChtL8%3D
C.T. Driscoll J. Holsapple C.L. Schofield R. Munson (1998) ArticleTitleThe chemistry and transport of mercury in a small wetland in the Adirondack region of New York, USA Biogeochemistry 40 137–46 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXitlakur8%3D
T.E. Essington J.N. Houser (2003) ArticleTitleThe effect of whole-lake nutrient enrichment on mercury concentration in age-1 yellow perch Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 132 57–68 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXhtVSht7w%3D
D.C. Evers K.M. Taylor A. Major R.J. Taylor R.H. Poppenga A.M. Scheuhammer (2003) ArticleTitleCommon loon eggs as indicators of methylmercury availability in North America Ecotoxicology 12 69–81 Occurrence Handle12739858 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXhsVGjtrw%3D
C.L. Folt K.H. Nislow M.E. Power (1998) ArticleTitleImplications of temporal and spatial scale for Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) research Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 55 IssueIDSuppl. 1 9–21
C.C. Gilmour G.S. Riedel M.C. Ederington J.T. Bell J.M. Benoit G.A. Gill M.C. Stordal (1998) ArticleTitleMethylmercury concentrations and production rates across a trophic gradient in the northern Everglades Biogeochemistry 40 327–45 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXitlaku7g%3D
L. Hakanson A. Nilsson T. Andersson (1988) ArticleTitleMercury in fish in Swedish lakes Environ. Pollut. 49 145–62 Occurrence Handle15092669 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD2c7psVymsQ%3D%3D
B.D. Hall R.A. Bodaly R.J.P. Fudge J.W.M. Rudd D.M. Rosenberg (1997) ArticleTitleFood as a dominant pathway of methylmercury uptake by fish Water Air Soil Pollut. 100 13–24 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXotFSqt7g%3D
C.R. Hammerschmidt W.F. Fitzgerald (2004) ArticleTitleGeochemical controls on the production and distribution of Methylmercury in near-shore marine sediments Environ. Sci. Technol. 38 1487–95 Occurrence Handle15046351 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXkvVWqsw%3D%3D
A. Heyes T.R. Moore J.W.M. Rudd (1998) ArticleTitleMercury and methylmercury in decomposing vegetation of a pristine and impounded wetland J. Environ. Qual. 27 591–99 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXjtlWitLk%3D Occurrence Handle10.2134/jeq1998.273591x
H. Hintelmann R. Harris A. Heyes J.P. Hurley C.A. Kelly D.P. Krabbenhoft S. Lindberg J.W.M. Rudd K.J. Scott V.L. St. Louis (2002) ArticleTitleReactivity and mobility of new and old mercury deposition in a Boreal forest ecosystem during the first year of the METAALICUS study Environ. Sci. Technol. 36 5034–40 Occurrence Handle12523417 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XosVWhtb0%3D
M. Kainz M. Lucotte C.C. Parrish (2002) ArticleTitleMethyl mercury in zooplankton – the role of size, habitat, and food quality Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 59 1606–15 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XpsV2ms7s%3D
Kamman, N.C., Burgess, N.M., Driscoll, C.T., Simonin, H.A., Goodale, W., Linehan, J., Estabrook, R., Hutcheson, M., Major, A., Scheuhammer, A.M. and Scruton, D.A. (2005). Mercury in freshwater fish of northeast North America – a geographic perspective based on fish tissue monitoring databases. Ecotoxicology, 14, 163–180
N.C. Kamman P.M. Lorey C.T. Driscoll R. Estabrook A. Major B. Pientka E. Glassford (2004) ArticleTitleAssessment of mercury in waters, sediments, and biota of New Hampshire and Vermont lakes, USA, sampled using a geographically randomized design Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 23 194–207
Kamman, N.C., Driscoll, C.T., Estabrook, R., Evers, D.C. and Miller, E. (2003). Biogeochemistry of Mercury in Vermont and New Hampshire Lakes – An Assessment of Mercury in Waters, Sediments and Biota of Vermont and New Hampshire Lakes. Waterbury, VT: Comprehensive Final Project Report to USEPA. VT Department of Environmental Conservation
Kramar, J., Goodale, W. and Kaur. (2005). Use of GIS as a decision support tool for predicting areas that represent mercury risk to humans and biota Ecotoxicology, this volume
D.P. Larsen D.L. Stevens A.R. Selle S.G. Paulsen (1991) ArticleTitleEnvironmental monitoring and assessment program, EMAP-surface waters: a northeast lakes pilot Lake Reserv. Manage. 7 1–11 Occurrence Handle10.1080/07438149109354249
H. Liao C.L. Pierce J.G. Larscheid (2002) ArticleTitleDiet dynamics of the adult piscivorous fish community in Spirit Lake, Iowa, USA 1995–1997 Ecol. Freshw. Fish 11 IssueID3 178–89
S.N. Luoma A. Van Geen B.-G. Lee J.E. Cloern (1998) ArticleTitleMetal uptake by phytoplankton during a bloom in South San Francisco Bay: Implications for metal cycling in estuaries Limnol. Oceanogr. 43 1007–16 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXms1Slsb8%3D Occurrence Handle10.4319/lo.1998.43.5.1007
R.P. Mason J.R. Reinfelder F.M.M. Morel (1995) ArticleTitleBioaccumulation of mercury and methylmercury Water Air Soil Pollut. 80 915–21 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXnsVCgsrs%3D
R.G. Miller SuffixJr. (1981) Simultaneous Statistical Inference McGraw Hill NY
Miller, E.K., VanArsdale, A. Keeler, J. and Kamman, N. (2005). Estimation and mapping of wet and dry mercury deposition across northeastern north America 14, 53–70
NESCAUM. (2003). Mercury Emissions from Coal-Fired Plants. Report 031104
L. Persson P. Bystrom E. Wahlstrom A. Nijlunsing S. Rosema (2000) ArticleTitleResource limitation during early ontogeny: constraints induced by growth capacity in larval and juvenile fish Oecologia 122 459–69
P.C. Pickhardt C.L. Folt C.Y. Chen B. Klaue J.D. Blum (2002) ArticleTitleAlgal blooms reduce the uptake of toxic methylmercury in freshwater food webs Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99 4419–23 Occurrence Handle11904388 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XivFShtLo%3D
Pickhardt, P.C., Folt, C.L., Chen, C.Y., Klaue, B. and Blum, J.D. (2004). Impacts of zooplankton composition and algal␣enrichment on the accumulation of mercury in an experimental freshwater food web. Sci. Tot. Environ (in press)
M.W. Prout E.L. Mills J.L. Forney (1990) ArticleTitleDiet, growth, and potential competitive interactions between Age-O White Perch and Yellow Perch in Oneida lake, New York Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 119 966–75
J. Rose M.S. Hutcheson C.R. West O. Pancorbo K. Hulme A. Cooperman G. DeCesare R. Isaac A. Screpetis (1999) ArticleTitleFish mercury distribution in massachusetts, USA lakes Environ.l Toxic. Chem. 18 1370–79 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXktVeqtbc%3D
SAS Institute Inc, 1995 JMP Statistics and Graphics Guide. Version 3.1 of JMP, Cary (N.C.).
D.M. Schael L.G. Rudstam J.R. Post (1991) ArticleTitleGape limitation and prey selection in larval Yellow Perch (Perca Flavescens), Fresh-water Drum (Aplodinotus Grunniens), and Black Crappie (Pomoxis Nigromaculatus) Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 48 1919–25 Occurrence Handle10.1139/f91-228
Simonin, H.A., Gloss, S.P., Driscoll, C.T., Schofield, C.L., Kretser, W.A., Karcher, R.W. and Symula, J. (1994). C.J. Watras and J.W. Huckabee (ed). Mercury Pollution Integration and Synthesis, pp. 457–69. Boca Raton, FL: Lewis Publishers.
R.S. Stemberger C.Y. Chen (1998) ArticleTitleFish tissue metals and zooplankton assemblages of northeastern US lakes Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 55 339–52 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXjsF2qs7w%3D
V.L. St. Louis J.W.M. Rudd C.A. Kelly K.G. Beaty N.S. Bloom R.J. Flett (1994) ArticleTitleImportance of wetlands as sources of methyl mercury to boreal forest ecosystems Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 51 1065–76 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXntVOltLY%3D
K. Suns G. Hitchin (1990) ArticleTitleInterrelationships between mercury levels in Yearling Yellow Perch, fish condition and water-quality Water Air and Soil Pollut. 50 255–65 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3cXltVejtrs%3D
C.J. Watras N.S. Bloom (1992) ArticleTitleMercury and methylmercury in individual zooplankton – Implications for bioaccumulation Limnol. Oceanogr. 37 1313–18
C.J. Watras K.A. Morrison J.S. Host N.S. Bloom (1995) ArticleTitleConcentration of mercury species in relationship to other site-specific factors in the surface waters of northern Wisconsin lakes Limnol. Oceanogr. 40 556–65 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXotFGms70%3D Occurrence Handle10.4319/lo.1995.40.3.0556
C.J. Watras R.C. Back S. Halvorsen R.J.M. Hudson K.A. Morrison S.P. Wente (1998) ArticleTitleBioaccumulation of mercury in pelagic freshwater food webs Sci. Tot. Environ. 219 183–208 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXlslWltrk%3D
T.R. Whittier S.G. Paulsen D.P. Larsen S.A. Peterson A.T. Herlihy P.R. Kaufmann (2002) ArticleTitleIndicators of ecological stress and their extent in the population of Northeastern Lakes: a regional-scale assessment BioScience 52 235–47
C.K. Wong (1993) ArticleTitleEffects of Chromium, Copper, Nickel, and Zinc on longevity and reproduction of the Cladoceran Moina Macrocopa Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 50 633–39 Occurrence Handle8490268 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXhvVGgsbo%3D
L. Wu D.A. Culver (1992) ArticleTitleOntogenic diet shift in Lake Erie age-O Yellow Perch (Perca flavescens) – a size-related response to zooplankton density Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 49 1932–37
R.B. Yeardley J.M. Lazorchak S.G. Paulsen (1998) ArticleTitleElemental fish tissue contamination in northeastern US lakes: evaluation of an approach to regional assessment Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 17 1875–84 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXlslGrtbs%3D
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, C.Y., Stemberger, R.S., Kamman, N.C. et al. Patterns of Hg Bioaccumulation and Transfer in Aquatic Food Webs Across Multi-lake Studies in the Northeast US. Ecotoxicology 14, 135–147 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-004-6265-y
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-004-6265-y