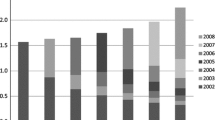
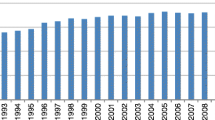
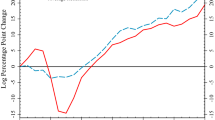
Abstract
This paper utilizes new Dutch transaction-level data on international trade to investigate the microeconomic patterns of Dutch exports. First, we show that self-selection based on ex-ante productivity drives firms’ export decisions, which we subsequently relate to various sources of fixed market-entry costs: governance and regulatory quality, the extent of corruption, and cultural proximity. Second, we provide evidence that firms learn to export by trial and error, so as to obtain experience in exporting and to gather knowledge about the potential of foreign markets. Such experimentation appears to be reflected in the volatility of a firm’s export product portfolio. More volatility is associated with a higher survival rate in the export market. Finally, we draw conclusions on the potential implications for trade policy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albornoz, F., Calvo Pardo, H., Corcos, G., & Ornelas, E. (2010). Sequential exporting. CEPR Discussion Paper.
Amador, J., & Opmorolla, L. D. (2008). Product and destination mix in export markets. paper presented at conference Productivity and Internationalisation, The Hague, September 2010.
Anderson J., Marcouiller D. (2002) Insecurity and the pattern of trade: An empirical investigation. Review of Economics and Statistics 84(2): 342–352
Atkeson, A., & Burstein, A. (2008). Pricing-to-market, trade costs, and international relative prices. UCLA paper, Los Angeles.
Baldwin, R., & Harrigan, J. (2007). Zeros, quality and space: Trade theory and trade evidence. NBER Working Paper 13214.
Bernard, A., & Jensen, J. (1995). Exporters, jobs, and wages in US manufacturing: 1976–1987. Brookings Papers on Economic Activity: Microeconomics, pp. 67–119.
Bernard A., Eaton J., Jensen J., Kortum S. (2003) Plants and productivity in international trade. American Economic Review 93: 1268–1290
Bernard A., Jensen J., Redding S., Schott P. (2007) Firms in international trade. Journal of Economic Perspectives 21(3): 105–130
Bernard A., Redding S., Schott P. (2010) Multiple-product firms and product switching. American Economic Review 100: 70–97
Bernard, A., Redding, S., & Schott, P. (2011). Multiple-product firms and trade liberalization. The Quarterly Journal of Economics, 126(3) (forthcoming).
Besedeš T., Prusa T. (2006) Product differentiations and duration of US import trade. Journal of International Economics 70: 339–358
Besedeš, T., & Prusa, T. (2011). The role of the extensive and intensive margins and export growth. Journal of Development Economics (forthcoming).
Bjornskov D., Dreher A., Fisher J. (2008) Cross-country determinants of life satisfaction: Exploring different determinants across groups in society. Social Choice and Welfare 30(1): 119–173
Blalock G., Gertler P. (2009) How firm capabilities affect who benefits from foreign technology. Journal of Development Economics 90: 192–199
Blum B., Goldfarb A. (2006) Doe the internet defy the law of gravity?. Journal of International Economics 70: 384–405
Chaney Th. (2008) Distorted gravity: The intensive and extensive margins of international trade. American Economic Review 98(4): 1707–1721
Crozet, M., Koenig, P., & Rebeyrol, V. (2008). Exporting to insecure markets: A firm-level analysis. CEPII Working Paper 2008-13.
Das S. M. R., Tybout J. (2007) Market entry costs, producer heterogeneity and export dynamics. Econometrica 75(3): 837–873
Eaton J., Kortum S., Kramarz F. (2004) Dissecting trade: Firms, industries and export destinations. AEA Papers and Proceedings 94(2): 150–154
Eaton, J., Kortum S., & Kramarz, F. (2008) An anatomy of international trade: Evidence from French firms. NBER Working Paper 14610.
Evenson R., Westphal L. (1995) Technological change and technology strategy. In: Srinivasan T., Behrman J. (eds) Handbook of Development Economics 3rd edn. North-Holland, Amsterdam
Greenaway D., Kneller R. (2007) Firm heterogeneity, exporting and foreign direct investment. The Economic Journal 117: F134–F161
Heckman J. J. (1979) Sample selection bias as a specification error. Econometrica 47(1): 153–161
Helpman E., Melitz M., Yeaple S. (2004) Export versus FDI with heterogeneous firms. American Economic Review 94(1): 300–316
ISGEP: (2008) Understanding cross-country differences in exporter premia: Comparable evidence for 14 countries, International Study Group on Exports and Productivity. Review of World Economics 144(4): 596–635
Kaufman, D., Kraay, A., & Mastruzzi, M. (2009). Governance matters VIII: Aggregate and individual governance indicators 1996–2008. World Bank Policy Research Working Paper 4978, Washington.
Knetter M. (1993) International comparisons of price-to-market behavior. American Economic Review 83(3): 473–486
KOF institute. (2009). KOF Globalisation index. http://www.globalization.kof.ethz.ch/static/pdf/method_2009.pdf.
Kox H., Rojas-Romagosa H. (2010) Exports and productivity selection effects for Dutch firms. De Economist 158(3): 295–322
Krugman P. (1987) Pricing to market when the exchange rate Changes. In: Arndt S., Richardson J. (eds) Real financial linkages among open economies. MIT Press, London
Lapham B. (1995) A dynamic general equilibrium analysis of deviations from the laws of one price. Journal of Economic Dynamics and Control 19(8): 1355–1389
Lawless M. (2009) Firm export dynamics and the geography of trade. Journal of International Economics 77(2): 245–254
Lawless M. (2010) Deconstructing gravity: Trade costs and extensive and intensive margins. Canadian Journal of Economics 43(4): 1149–1172
Mayer Th., Ottaviano G. (2007) The happy few: The internationalisation of European firms. Bruegel Blueprint III, Bruegel
Melitz M. (2003) The impact of trade on aggregate industry productivity and intra-industry reallocations. Econometrica 71(6): 1695–1725
Mürakozy, B., & Bekès, G. (2009). Temporary trade. IEHAS Discussion Papers 0909, Institute of Economics, Hungarian Academy of Sciences.
North D. D. (1981) Structure and Change in Economic history. Norton & Co, New York
Rauch J., Watson J. (2003) Starting small in an unfamiliar environment. International Journal of Industrial Organization 21: 1021–1042
Roberts M., Tybout J. (1997) An empirical model of sunk costs and the decision to export. American Economic Review 87(4): 545–564
Smeets, R., Creusen, H. Lejour, A., & Kox, H. (2010). Export margins and export barriers: Covering market entry costs of exporters in the Netherlands. CPB Document 208.
Statistics Netherlands (CBS). (2009). Internationalisation monitor 2009.
Van Biesebroeck J. (2005) Exporting raises productivity in sub-Saharan manufacturing firms. Journal of International Economics 67(2): 373–391
Van der Wiel, H., Creusen, H., van Leeuwen, G., & van de Pijl, E. (2008). Cross your border and look around. CPB Document 170.
Verhoogen E. (2008) Trade, quality upgrading, and wage inequality in the Mexican manufacturing sector. Quarterly Journal of Economics 123(2): 489–530
Wagner J. (2007) Exports and productivity: A survey of the evidence from firm level data. The World Economy 30(10): 60–82
World Bank: (1993) The East Asian miracle. Oxford University Press, New York
World Bank: (1997) World Development Report 1997. Oxford University Press, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Creusen, H., Kox, H., Lejour, A. et al. Exploring the Margins of Dutch Exports: A Firm-Level Analysis. De Economist 159, 413–434 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10645-011-9172-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10645-011-9172-7