Abstract
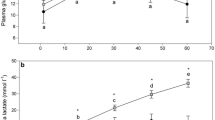
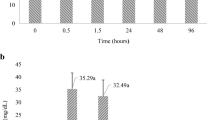
Acute exposure to contaminants frequently induces stress, but prolonged exposures, such as those experienced by individuals in wild populations, can impair the capacity to mount a stress response. Using the round goby (Neogobius melanostomus), a small benthic fish and potential sentinel species for habitat contamination in the Great Lakes, we explored the impacts of living in highly polluted areas. Round goby were collected from highly contaminated and less contaminated areas of Hamilton Harbour (a well-known site of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) and heavy metal contamination). The cortisol stress responses of fish from sites of high and low contamination were compared using an EIA assay on blood collected (n = 112) either prior to or 0, 10, 30, 60, 240 min and 24 h following the application of a 4-min confined air exposure stressor. Plasma cortisol levels were elevated at 10 and 30 min post-stressor (100.3 and 87.5 ng/mL), and returned to levels similar to baseline (22.3 ng/mL) 1 h after the stressor. In contrast to predictions, round goby from areas of high and low contamination had similar cortisol levels at all timepoints. We also monitored stress responses immediately after a chasing stressor (n = 19). During the chasing stressor, contaminated-site round goby exhausted faster than individuals from a less contaminated site, although they had similar levels of plasma cortisol (23.5 versus 20.9 ng/mL) and lactate (2.53 versus 1.98 mmol/L). Our results indicate that not all fishes may demonstrate impaired stress responses, even in highly contaminated habitats; however, such animals may still have increased vulnerability to predation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aluru N, Vijayan MM (2006) Aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation impairs cortisol release to stress in rainbow trout by disrupting the rate-limiting steps in steroidogenesis. Endocrinology 147:1895–1903
Andersson T, Forlin L, Hardig J, Larsson A (1988) Physiological disturbances in fish living in coastal water polluted with bleached kraft pulp mill effluents. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 45:1525–1536
Barbieri E (2007) The use of active metabolism and swimming activity to evaluate the toxicity of dodecil benzene sodium sulfonate (LAS-C12) on the Mugil platanus (mullet) according to the temperature and salinity. Water Environ Res Estados Unidos 79:707–719
Barton BA (2002) Stress in fishes: a diversity of responses with particular reference to changes in circulating corticosteroids. Integr Comp Biol 42:517–525
Barton BA, Schreck CB, Barton LD (1987) Effects of chronic cortisol administration and daily acute stress on growth, physiological conditions, and stress responses in juvenile rainbow trout. Dis Aquat Org 2:173–185
Basu N, Kennedy CJ, Hodson PV, Iwama GK (2002) Altered stress responses in rainbow trout following a dietary administration of cortisol and beta-napthoflavone. Fish Physiol Biochem 25:131–140
Benguira S, Leblond VS, Weber J-P, Hontela A (2002) Loss of capacity to elevate plasma cortisol in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) treated with a single injection of o, p’-dichlorodiphenyldichloroethane. Environ Toxicol Chem 21:1753–1756
Bleau H, Daniel C, Chevalier G, van Tra H, Hontela A (1996) Effects of acute exposure to mercury chloride and methylmercury on plasma cortisol, T3, T4, glucose and liver glycogen in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus). Aquat Toxicol 34:221–235
Bowley L, Alam F, Marentette JR, Balshine S, Wilson JY (2010) Characterization of vitellogenin gene expression in round goby Neogobius melanostomus using a quantitative PCR assay. Environ Toxicol Chem 29:2751–2760
Brodeur JC, Sherwood G, Rasmussen JB, Hontela A (1997) Impaired cortisol secretion in yellow perch (Perca flavescens) from lakes contaminated by heavy metals: in vivo and in vitro assessment. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 54:2752–2758
Bury NR, Jie L, Flik G, Lock RAC, Wendelaar Bonga SE (1998) Cortisol protects against copper induced necrosis and promotes apoptosis in fish gill chloride cells in vitro. Aquat Toxicol 40:193–202
Carragher JF, Sumpter JP (1990) The effect of cortisol on the secretion of sex steroids from cultured ovarian follicles of rainbow trout. Gen Comp Endocrinol 77:403–407
Cross EE, Rawding RS (2009) Acute thermal tolerance in the round goby, Apollonia melanostoma (Neogobius melanostomus). J Therm Biol 34:85–92
DeBoeck G, DeWachter B, Vlaeminck A, Blust R (2003) Effect of cortisol treatment and/or sublethal copper exposure on copper uptake and heat shock protein levels in common carp, Cyprinus carpio. Environ Toxicol Chem 22:1122–1126
Eales JG, Brown SB (2005) Thyroid hormones. In: Mommsen TP, Moon TW (eds) Environmental toxicology. Biochemistry and molecular biology of fishes, vol. 6. Elsevier, New York, pp 397–412
Forlin L, Andersson T, Balk L, Larsson A (1995) Biochemical and physiological effects in fish exposed to bleached kraft mill effluents. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 30:164–170
Friedmann AS, Watzin MC, Brinck-Johnsen T, Leite JC (1996) Low levels of dietary methylmercury inhibit growth and gonadal development in juvenile walleye (Stizostedion vitreum). Aquat Toxicol 35:265–278
Gagnon A, Jumarie C, Hontela A (2006) Effects of Cu on plasma cortisol and cortisol secretion by adrenocortical cells of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquat Toxicol 78:59–65
Gendron AD, Bishop CA, Fortin R, Hontela A (1997) In vivo testing of the functional integrity of the corticosterone-producing axis in mudpuppy (Amphibia) exposed to chlorinated hydrocarbons in the wild. Environ Toxicol Chem 16:1694–1706
Girard C, Brodeur JC, Hontela A (1998) Responsiveness of the interrenal tissue of yellow perch (Perca flavescens) from contaminated sites to an ACTH challenge test in vivo. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 55:438–450
Gravel A, Campbell PGC, Hontela A (2005) Disruption of the hypothalamo-pituitary-interrenal axis in 1+ yellow perch (Perca flavescens) chronically exposed to metals in the environment. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 62:982–990
Gregory TR, Wood CM (1999) The effects of chronic plasma cortisol elevation on the feeding behaviour, growth, competitive ability, and swimming performance of juvenile rainbow trout. Physiol Biochem Zool 72:286–295
Hamilton Harbour Remedial Action Plan (RAP) (1992) Hamilton Harbour Stage 1 Report: environmental conditions and problem definition. Burlington, Ontario
Hamilton Harbour Remedial Action Plan (RAP) (2003) Remedial action plan for Hamilton Harbour: Stage 2 Update 2002. Burlington, Ontario, Canada
Hontela A (1997) Endocrine and physiological responses of fish to xenobiotics: role of glucocortisoid hormones. Rev Toxicol 1:1–46
Hontela A (1998) Interrenal dysfunction in fish from contaminated sites: in vivo and in vitro assessment. Environ Toxicol Chem 17:44–48
Hontela A (2005) Adrenal toxicology: environmental pollutants and the HPI axis. In: Mommsen TP, Moon TW (eds) Environmental toxicology. Biochemistry and molecular biology of fishes, vol. 6. Elsevier, New York, pp 331–364
Hontela A, Rasmussen JB, Audet C, Chevalier G (1992) Impaired cortisol stress response in fish from environments polluted by PAHs, PCBs and mercury. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 22:278–283
Hontela A, Dumont P, Duclos D, Fortin R (1995) Endocrine and metabolic dysfunction in yellow perch, Perca flavescens, exposed to organic contaminants and heavy metals in the St. Lawrence River. Environ Toxicol Chem 14:725–731
Hontela A, Daniel C, Ricard AC (1996) Effects of acute and subacute exposures to cadmium on the interrenal and thyroid function in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquat Toxicol 35:171–182
Hontela A, Daniel C, Rasmussen JB (1997) Structural and functional impairment of the hypothalamo-pituitary-interrenal axis in fish exposed to bleached kraft mill effluent in the St Maurice River, Québec. Ecotoxicology 6:1–12
Hopkins WA, Snodgrass JW, Staub BP, Jackson BP, Congdon JD (2003) Altered swimming performance of a benthic fish (Erimyzon sucetta) exposed to contaminated sediments. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 44:383–389
Hutchinson TH, Ankly GT, Segner H, Tyler CR (2006) Screening and testing for endocrine disruption in fish—biomarkers as “signposts”, not “traffic lights”, in risk assessment. Environ Health Perspect 114(s1):106–114
Ilan Z, Yaron Z (1983) Interference of o, p’-DDD with interrenal function and cortisol metabolism in Saratherodon aureus (Steindachner). J Fish Biol 22:657–669
International Joint Commission (IJC) (1999) Hamilton Harbour Area of Concern Status Assessment. Windsor, Ontario
Jardine JJ, Van Der Kraak GJ, Munkittrick KR (1996) Capture and confinement stress in white sucker exposed to bleached kraft pulp mill effluent. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 33:287–298
Jude DJ, Janssen J, Crawford G (1995) Ecology, distribution and impact of the newly introduced round and tubenose gobies on the biota of the St. Clair and Detroit Rivers. In: Munawar M, Edsall T, Leach J (eds) The Lake Huron ecosystem: Ecology, fisheries and management. SPB Academic Publishing, Amsterdam, pp 447–460
Kime DE (1998) Endocrine disruption in fish. Kluwer, Norwell
Kirubagaran R, Joy KP (1991) Changes in the adrenocortical-pituitary activity in the catfish, Clarias batrachus (L.), after mercury treatment. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 22:36–44
Laflamme J-S, Couillard Y, Campbell PGC, Hontela A (2000) Interrenal metallothionein and cortisol secretion in relation to Cd, Cu and Zn exposure in yellow perch, Perca flavescens, from Abitibi lakes. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 57:1692–1700
Lappivaara J (2001) Effects of acute handling stress on whitefish Coregonus lavaretus after prolonged exposure to biologically treated and untreated bleached kraft mill effluent. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 41:55–64
Leblond VS, Bisson M, Hontela A (2001) Inhibition of cortisol secretion in dispersed head kidney cells of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) by endosulfan, an organochlorine pesticide. Gen Comp Endocrinol 121:48–56
Levesque HM, Dorval J, Hontela A, Van Der Kraak GJ, Campbell PGC (2003) Hormonal, morphological and physiological responses of yellow perch (Perca flavescens) to chronic environmental metal exposures. J Toxicol Environ Health A 66:657–676
Levitan WM, Taylor MH (1979) Physiology of salinity-dependent naphthalene toxicity in Fundulus heteroclitus. J Fish Res Board Can 36:615–620
Lockhart WL, Uthe JF, Kenney AR, Mehrle PM (1972) Methylmercury in northern pike (Esox lucius): distribution, elimination and some biochemical characteristics of contaminated fish. J Fish Res Board Can 29:1519–1523
Marentette JR, Gooderham KL, McMaster ME, Ng T, Parrott JL, Wilson JY, Wood CM, Balshine S (2010) Signatures of contamination in invasive round gobies (Neogobius melanostomus): a double strike for ecosystem health. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73:1755–1764
Marentette JR, Wang G, Tong S, Sopinka NM, Taves MD, Koops MA, Balshine S (2012) Laboratory and field evidence of sex-biased movement in the invasive round goby. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 21:1003–1012
McKenzie DJ, Garofalo E, Winter MJ, Ceradini S, Verweji F, Day N, Hayes R, van der Oost R, Butler PJ, Chipman JK, Taylor EW (2007) Complex physiological traits as biomarkers of the sub-lethal toxicological effects of pollutant exposure in fishes. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B 362:2043–2059
McMaster ME, Munkittrick KR, Luxon PL, van der Kraak GJ (1994) Impact of low-level sampling stress on interpretation of physiological responses of white sucker exposed to effluent from a bleached kraft pulp mill. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 27:251–264
Niimi AJ, Palazzo V (1986) Biological half-lives of eight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). Water Res 20:503–507
Norris DO (1999) Impaired adrenocortical response to stress by brown trout, Salmo trutta, living in metal-contaminated waters of the Eagle River, Colorado. Gen Comp Endocrinol 113:1–8
Norris DO, Donahue S, Dores RM, Lee JK, Maldonado TA, Ruth T, Woodling JD (1999) Impaired adrenocortical response to stress by brown trout, Salmo trutta, living in metalcontaminated waters of the Eagle River, Colorado. Gen Comp Endocrinol 113:1–8
Norris DO (2000) Endocrine disruptors of the stress axis in natural populations: how can we tell? Am Zool 40:393–401
Odermatt A, Gumy C, Atanasov AG, Dzyakanchuk AA (2006) Disruption of glucocorticoid action by environmental chemicals: potential mechanisms and relevance. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 102:222–231
Pickering AD (1989) Environmental stress and the survival of brown trout, Salmo trutta. Freshw Biol 21:47–55
Pickering AD, Pottinger TG (1989) Stress responses and disease resistance in salmonid fish: effects of chronic elevation of plasma cortisol. Fish Physiol Biochem 7:253–258
Pinchuk VI, Vasil’eva EK, Vasil’ev VP, Miller PJ (2003) Neogobius melanstomus (Pallas, 1814). In: Miller PJ (ed) The freshwater fishes of Europe. AULA-Verlag, pp 293–345
Pottinger TG, Carrick TR, Hughes SE, Balm PHM (1996) Testosterone, 11-ketotestosterone, and estradiol-17B modify baseline and stress-induced interrenal and corticotropic activity in trout. Gen Comp Endocrinol 104:284–295
Pradelles P, Grassi J, Maclouf J (1990) Enzyme immunoassays of eicosanoids using acetylcholinesterase. Methods Enzymol 187:24–34
Pratap HB, Wendelaar Bonga SE (1990) Effects of water-borne cadmium on plasma cortisol and glucose in the cichlid fish Oreochromis mossambicus. Comp Biochem Physiol 95C:313–317
Quabius ES, Balm PHM, Wendelaar Bonga SE (1997) Interrenal stress responsiveness of tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) is impaired by dietary exposure to PCB 126. Gen Comp Endocrinol 108:472–482
Ray WJ, Corkum LD (2001) Habitat and site affinity of the round goby. J Great Lakes Res 27:329–334
Saunders AC, Feldman HA, Correia CE, Weinstein DA (2005) Clinical evaluation of a portable lactate meter in type I glycogen storage disease. J Inherit Metab Dis 28:695–701
Scott GR, Sloman KA (2004) The effects of environmental pollutants on complex fish behaviour: integrating behavioural and physiological indicators of toxicity. Aquat Toxicol 68:369–392
Sigismondi LA, Weber LJ (1988) Changes in avoidance response time of juvenile Chinook salmon exposed to multiple acute handling stresses. Trans Am Fish Soc 117:196–201
Thomas RE, Rice SD (1987) Effect of water-soluble fraction of Cook Inlet crude oil on swimming performance and plasma cortisol in juvenile Coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch). Comp Biochem Physiol 87C:177–180
Thomas P, Woodlin BR, Neff JM (1980) Biochemical responses of striped mullet Mugil cephalus to oil exposure I. Acute responses—interrenal activations and secondary stress responses. Mar Biol 59:141–149
Tyler CR, Jobling S, Sumpter JP (1998) Endocrine disruption in wildlife: a critical review of the evidence. Crit Rev Toxicol 28:319–361
Vélez-Espino LA, Koops MA, Balshine S (2010) Invasion dynamics of round goby (Neogobius melanostomus) in Hamilton Harbour, Lake Ontario. Biol Invasions 12:3861–3875
Vijayan MM, Prunet P, Boon AN (2005) Xenobiotic impact on corticosteroid signalling. In: Mommsen TP, Moon TW (eds) Environmental toxicology. Biochemistry and molecular biology of fishes, vol. 6. Elsevier, New York, pp 365–396
Weis JS (2002) Tolerance to environmental contaminants in the mummichog, Fundulus heteroclitus. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 8:933–953
Wendelaar Bonga SE (1997) The stress response in fish. Physiol Rev 77:591–625
Wicks BJ, Joensen R, Tang Q, Randall DJ (2002) Swimming and ammonia toxicity in salmonids: the effects of sublethal ammonia exposure on the swimming performance of coho salmon and the acute toxicity of ammonia in swimming and resting rainbow trout. Aquat Toxicol 59:55–69
Wilson JM, Vijayan MM, Kennedy CJ, Iwama GK, Moon TW (1998) B-naphthoflavone abolishes interrenal sensitivity to ACTH stimulation in rainbow trout. J Endocrinol 157:63–70
Young JAM, Marentette JR, Gross C, McDonald JI, Verma A, Marsh-Rollo SE, Macdonald PDM, Earn DJ, Balshine S (2010) Demography and substrate affinity of the round goby (Neogobius melanostomus) in Hamilton Harbour. J Great Lakes Res 36:115–122
Zeman AJ (2009) Contaminated sediments in Hamilton Harbour. Environment Canada Water Science and Technology Directorate (WSTD) Contribution No. 09-263
Acknowledgements
The authors thank G Wang, N Sopinka, S Venskaitis, A Chang and S Marsh-Rollo for field assistance; K Gilmour for her guidance in experimental design; N Sopinka, A Reddon, M Wong and K Cogliati for their valuable comments on the analyses and manuscript; M Koops, at the Department of Fisheries and Oceans (DFO), McMaster University, Canadian Foundation for Innovation and Ontario Ministry of Innovation and NSERC Discovery Grant program for financial support for the study. ST was supported by a DFO grant, JRM was supported by an NSERC CGS-D scholarship and SB was supported through the Canada Research Chair Program and the NSERC Discovery Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marentette, J.R., Tong, S. & Balshine, S. The cortisol stress response in male round goby (Neogobius melanostomus): effects of living in polluted environments?. Environ Biol Fish 96, 723–733 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-012-0064-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-012-0064-8