Summary
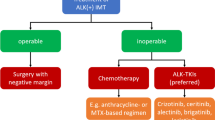
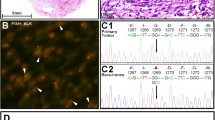
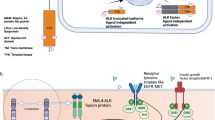
An inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (IMT) is a rare mesenchymal neoplasm that typically develops in the lungs and seldom in the head and neck region. It is often related to the anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) fusion gene. Crizotinib, a first-generation ALK inhibitor, has been shown to have a notable response in patients with ALK-positive IMT. Here, we report the first case of a 46-year-old man with IMT harboring a novel SQSTM1–ALK fusion gene who demonstrated marked response to alectinib. The patient presented a right neck mass (5-cm diameter) that progressively enlarged and expanded to the upper mediastinum. ALK-rearranged IMT was diagnosed after complete tumor resection. Spindle cells displayed diffuse cytoplasmic staining for ALK on immunohistochemistry. A fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis revealed the translocation of a part of the ALK gene locus at chromosome 2p23. FoundationOne CDx™ assay identified an SQSTM1-ALK gene fusion. After a year, right cervical, subclavian, and mediastinal lymph node metastases, considered unresectable, developed. Notably, the patient exhibited a marked response to alectinib treatment and has sustained for 17 months following systemic therapy initiation without significant adverse events. This report highlights the possibility of alectinib being a reasonable option for advanced IMT with the SQSTM1-ALK fusion.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fletcher CD, Mertens F, Bridge JA (2013) Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumour. WHO Press, Geneva, pp 91–93
Coffin CM, Watterson J, Priest JR, Dehner LP (1995) Extrapulmonary inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (inflammatory pseudotumor). A clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 84 cases. Am J Surg Pathol 19:859–872
Kim JH, Cho JH, Park MS, Chung JH, Lee JG, Kim YS, Kim SK, Kim SK, Shin DH, Choi BW, Choe KO, Chang J (2002) Pulmonary inflammatory pseudotumor--a report of 28 cases. Korean J Intern Med 17:252–258
Bando T, Fujimura M, Noda Y, Hirose J, Ohta G, Matsuda T (1994) Pulmonary plasma cell granuloma improves with corticosteroid therapy. Chest 105:1574–1575
Kovach SJ, Fischer AC, Katzman PJ, Salloum RM, Ettinghausen SE, Madeb R, Koniaris LG (2006) Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors. J Surg Oncol 94:385–391
Coffin CM, Patel A, Perkins S, Elenitoba-Johnson KS, Perlman E, Griffin CA (2001) Alk1 and p80 expression and chromosomal rearrangements involving 2p23 in inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor. Mod Pathol 14:569–576
Mano H (2012) ALKoma: a cancer subtype with a shared target. Cancer Discov 2:495–502
Lovly CM, Gupta A, Lipson D, Otto G, Brennan T, Chung CT, Borinstein SC, Ross JS, Stephens PJ, Miller VA, Coffin CM (2014) Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors harbor multiple potentially actionable kinase fusions. Cancer Discov 4:889–895
Lawrence B, Perez-Atayde A, Hibbard MK, Rubin BP, Dal Cin P, Pinkus JL, Pinkus GS, Xiao S, Yi ES, Fletcher CD, Fletcher JA (2000) TPM3-ALK and TPM4-ALK oncogenes in inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors. Am J Pathol 157:377–384
Butrynski JE, D'Adamo DR, Hornick JL, Dal Cin P, Antonescu CR, Jhanwar SC, Ladanyi M, Capelletti M, Rodig SJ, Ramaiya N, Kwak EL, Clark JW, Wilner KD, Christensen JG, Janne PA, Maki RG, Demetri GD, Shapiro GI (2010) Crizotinib in ALK-rearranged inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor. N Engl J Med 363:1727–1733
Mosse YP, Lim MS, Voss SD, Wilner K, Ruffner K, Laliberte J, Rolland D, Balis FM, Maris JM, Weigel BJ, Ingle AM, Ahern C, Adamson PC, Blaney SM (2013) Safety and activity of crizotinib for paediatric patients with refractory solid tumours or anaplastic large-cell lymphoma: a children's oncology group phase 1 consortium study. Lancet Oncol 14:472–480
Sakamoto H, Tsukaguchi T, Hiroshima S, Kodama T, Kobayashi T, Fukami TA, Oikawa N, Tsukuda T, Ishii N, Aoki Y (2011) CH5424802, a selective ALK inhibitor capable of blocking the resistant gatekeeper mutant. Cancer Cell 19:679–690
Yuan C, Ma MJ, Parker JV, Mekhail TM (2017) Metastatic anaplastic lymphoma kinase-1 (ALK-1)-rearranged inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma to the brain with leptomeningeal involvement: favorable response to serial ALK inhibitors: a case report. Am J Case Rep 18:799–804
Saiki M, Ohyanagi F, Ariyasu R, Koyama J, Sonoda T, Nishikawa S, Kitazono S, Yanagitani N, Horiike A, Ninomiya H, Ishikawa Y, Nishio M (2017) Dramatic response to alectinib in inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor with anaplastic lymphoma kinase fusion gene. Jpn J Clin Oncol 47:1189–1192
Ong HS, Ji T, Zhang CP, Li J, Wang LZ, Li RR, Sun J, Ma CY (2012) Head and neck inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (IMT): evaluation of clinicopathologic and prognostic features. Oral Oncol 48:141–148
Yamamoto H, Kohashi K, Oda Y, Tamiya S, Takahashi Y, Kinoshita Y, Ishizawa S, Kubota M, Tsuneyoshi M (2006) Absence of human herpesvirus-8 and Epstein-Barr virus in inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor with anaplastic large cell lymphoma kinase fusion gene. Pathol Int 56:584–590
Gómez-Román JJ, Sánchez-Velasco P, Ocejo-Vinyals G, Hernández-Nieto E, Leyva-Cobián F, Val-Bernal JF (2001) Human herpesvirus-8 genes are expressed in pulmonary inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (inflammatory pseudotumor). Am J Surg Pathol 25:624–629
Dickson BC, Swanson D, Charames GS, Fletcher CD, Hornick JL (2018) Epithelioid fibrous histiocytoma: molecular characterization of ALK fusion partners in 23 cases. Mod Pathol 31:753–762
d'Amore ES, Visco C, Menin A, Famengo B, Bonvini P, Lazzari E (2018) STAT3 pathway is activated in ALK-positive large B-cell lymphoma carrying SQSTM1-ALK rearrangement and provides a possible therapeutic target. Am J Surg Pathol 37:780–786
Takeuchi K, Soda M, Togashi Y, Ota Y, Sekiguchi Y, Hatano S, Asaka R, Noguchi M, Mano H (2011) Identification of a novel fusion, SQSTM1-ALK, in ALK-positive large B-cell lymphoma. Haematologica 96:464–467
Solomon BJ, Mok T, Kim DW, Wu YL, Nakagawa K, Mekhail T, Felip E, Cappuzzo F, Paolini J, Usari T, Iyer S, Reisman A, Wilner KD, Tursi J, Blackhall F (2014) Investigators P: first-line crizotinib versus chemotherapy in ALK-positive lung cancer. N Engl J Med 371:2167–2177
Yang JC, Ou SI, De Petris L, Gadgeel S, Gandhi L, Kim DW, Barlesi F, Govindan R, Dingemans AC, Crino L, Lena H, Popat S, Ahn JS, Dansin E, Golding S, Bordogna W, Balas B, Morcos PN, Zeaiter A, Shaw AT (2017) Pooled systemic efficacy and safety data from the pivotal phase II studies (NP28673 and NP28761) of alectinib in ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 12:1552–1560
Hida T, Nokihara H, Kondo M, Kim YH, Azuma K, Seto T, Takiguchi Y, Nishio M, Yoshioka H, Imamura F, Hotta K, Watanabe S, Goto K, Satouchi M, Kozuki T, Shukuya T, Nakagawa K, Mitsudomi T, Yamamoto N, Asakawa T, Asabe R, Tanaka T, Tamura T (2017) Alectinib versus crizotinib in patients with ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (J-ALEX): an open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet 390:29–39
Peters S, Camidge DR, Shaw AT, Gadgeel S, Ahn JS, Kim DW, Ou SI, Perol M, Dziadziuszko R, Rosell R, Zeaiter A, Mitry E, Golding S, Balas B, Noe J, Morcos PN, Mok T, Investigators AT (2017) Alectinib versus crizotinib in untreated ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 377:829–838
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Enago (www.enago.jp) for the English language review.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Ethical approval
This study does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from the patient for the publication of this case report.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Honda, K., Kadowaki, S., Kato, K. et al. Durable response to the ALK inhibitor alectinib in inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the head and neck with a novel SQSTM1–ALK fusion: a case report. Invest New Drugs 37, 791–795 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-019-00742-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-019-00742-2