Summary
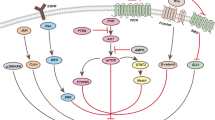
Many compounds structurally similar to chromones have been developed to enhance the sensitizing effect of cancer cells to chemotherapeutic agents. Most of these compounds have been shown to promote this sensitization by targeting the repair pathways. One such compound is LTUR6, which enhances the sensitization of doxorubicin to colon cancer cells HT29, by inhibiting the phosphorylation of the double stranded break (DSB) repair enzyme AKT. The downstream regulatory targets of AKT that enhance doxorubicin mediated cytotoxicity in the presence of LTUR6 remains elusive. In this study, we performed comparative analyses of 43 kinase phosphorylation sites using the human phospho-kinase array proteome profiler. Results revealed altered expression levels of multiple proteins that regulated apoptotic signalling pathways. Increased activation of mTOR, RSK1/2/3, p38α and PRAS40 after combination treatment with LTUR6 and doxorubicin over doxorubicin alone was observed. This study provides a deeper insight into the key proteins involved and presents a novel molecular pathway.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cantley LC (2002) The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science 296(5573):1655–1657. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.296.5573.1655
Fruman DA, Meyers RE, Cantley LC (1998) Phosphoinositide kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biochem.67.1.481
Vivanco I, Sawyers CL (2002) The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-AKT pathway in humancancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2:489–501. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc839
Katso R, Okkenhaug K, Ahmadi K, White S, Timms J, Waterfield MD (2001) Cellular function of phosphoinositide 3-kinases: implications for development, immunity, homeostasis, and cancer. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 17:615–675. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.cellbio.17.1.615
Akinleye A, Chen Y, Mukhi N, Song Y, Liu D (2013) Ibrutinib and novel BTK inhibitors in clinical development. J Hematol Oncol 6:59
Burris HA (2013) Overcoming acquired resistance to anticancer therapy: focus on the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 71:829–842
Workman P, Clarke PA, Raynaud FI, RLM VM (2010) Drugging the PI3 kinome: from chemical tools to drugs in the clinic. Cancer Res 70:2146–2157
Sarbassov DD, Guertin DA, Ali SM, Sabatini DM (2005) Phosphorylation and regulation of Akt/PKB by the rictor-mTOR complex. Science 307(5712):1098–1101. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1106148
Morrison R, Al-Rawi JMA (2016) Synthesis, structure elucidation, DNA-PK, PI3K, anti-platelet and anti-bacteria activity of linear 5, 6, and 10-substituted-2-morpholino-chromen-oxazine-dione and angular 3, 4, 6-substituted-8-morpholino-chromen-oxazine-2,10-dione. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 31:86–95. https://doi.org/10.1080/14756366.2016.1190710
Suraj R, Radhamani S, Meehan-Andrews T, Bradley C (2017) Role of a novel benzoxazine derivative in the chemosensitization of colon cancer. Apoptosis 22:988–1000. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-017-1380-4
Anjum R, Blenis J (2008) The RSK family of kinases: emerging roles in cellular signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:747–758
Frödin M, Gammeltoft S (1999) Role and regulation of 90 kDa ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK) in signal transduction. Mol Cell Endocrinol 151:65–77
Neise D, Sohn D, Stefanski A et al (2013) The p90 ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK) inhibitor BI-D1870 prevents gamma irradiation-induced apoptosis and mediates senescence via RSK- and p53-independent accumulation of p21WAF1/CIP1. Cell Death Dis 4:e859. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2013.386
Carriere A (2008) The RSK factors of activating the Ras/MAPK signaling cascade. Front Biosci Volume:4258. https://doi.org/10.2741/3003
Hay N, Sonenberg N (2004) Upstream and downstream of mTOR. Genes Dev 18:1926–1945
Yang H, Rudge DG, Koos JD, Vaidialingam B, Yang HJ, Pavletich NP (2013) MTOR kinase structure, mechanism and regulation. Nature 497:217–223. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12122
Park S, Chapuis N, Tamburini J, Bardet V, Cornillet-Lefebvre P, Willems L, Green A, Mayeux P, Lacombe C, Bouscary D (2010) Role of the PI3K/AKT and mTOR signaling pathways in acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 95:819–828. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2009.013797
Martelli AA, Evangelisti C, Chiarini F, McCubrey JA (2010) The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT/mTOR signaling network as a therapeutic target in acute myelogenous leukemia patients. Oncotarget 1:89–103. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.114
Thedieck K, Polak P, Kim ML, Molle KD, Cohen A, Jenö P, Arrieumerlou C, Hall MN (2007) PRAS40 and PRR5-like protein are new mTOR interactors that regulate apoptosis. PLoS One 2:e1217. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0001217
Laplante M, Sabatini DM (2012) mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell 149:274–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.017
Han EKH, Leverson JD, McGonigal T, Shah OJ, Woods KW, Hunter T, Giranda VL, Luo Y (2007) Akt inhibitor A-443654 induces rapid Akt Ser-473 phosphorylation independent of mTORC1 inhibition. Oncogene 26:5655–5661. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210343
Zuluaga S, Álvarez-Barrientos A, Gutiérrez-Uzquiza A et al (2007) Negative regulation of Akt activity by p38α MAP kinase in cardiomyocytes involves membrane localization of PP2A through interaction with caveolin-1. Cell Signal. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2006.05.032
Gratton JP, Morales-Ruiz M, Kureishi Y, Fulton D, Walsh K, Sessa WC (2001) Akt Down-regulation of p38 signaling provides a novel mechanism of vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated cytoprotection in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 276:30359–30365. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M009698200
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. Jasim Al-Rawi and Rick Morrison for supplying LTUR6 compound, which was synthesized in their laboratory. The authors would like to thank Dr. Mike Angove for his constant encouragement and support.
Funding
This work was funded by Australian Postgraduate Award and LaTrobe University Postgraduate Research Scholarship (PhD fellowship to Rejitha Suraj).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suraj, R., Al-Rawi, J. & Bradley, C. Inhibition of AKT signalling by benzoxazine derivative LTUR6 through the modulation of downstream kinases. Invest New Drugs 37, 779–783 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-019-00726-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-019-00726-2