Summary
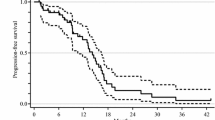
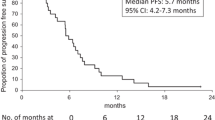
Background This phase I/II trial evaluated toxicity and antitumor activity of everolimus plus mFOLFOX6 + bevacizumab for first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC). Methods A phase I, modified 3 + 3 Fibonacci schema determined the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of everolimus, followed by phase II dose expansion. The phase II primary objective was progression-free survival at 6 months (PFS-6 m). Results The everolimus MTD was 10 mg daily with mFOLFOX6 + bevacizumab based on safety from phase I (n = 22). Twenty-five patients were treated in the phase II at 10 mg everolimus daily. Frequent grade 3–4 adverse events were neutropenia (64%), leukopenia (28%) and hypokalemia (26%). Grade 2 stomatitis was observed in 62% of patients. Two dose-limiting toxicities were observed with one attributed to everolimus 10 mg daily (grade 3 diarrhea, hypokalemia, and anorexia) and grade 3 coronary vasospasm attributed to fluorouracil. The objective response rate was 53% and was higher (86%) in those with PTEN deficiency. PFS-6 m was 96% (95% CI 89–99.9%) at the MTD (n = 35). The everolimus recommended phase II dose of this regimen is 7.5 mg daily due to frequent stomatitis and dose reductions. Conclusions Everolimus plus mFOLFOX-6 + bevacizumab is tolerable and demonstrated preliminary efficacy for first-line mCRC. Further studies are warranted in PTEN deficiency.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fresno Vara JA, Casado E, de Castro J, Cejas P, Belda-Iniesta C, Gonzalez-Baron M (2004) PI3K/Akt signalling pathway and cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 30(2):193–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2003.07.007
Mukohara T (2015) PI3K mutations in breast cancer: prognostic and therapeutic implications. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press) 7:111–123. https://doi.org/10.2147/BCTT.S60696
Garrido-Laguna I, Hong DS, Janku F, Nguyen LM, Falchook GS, Fu S, Wheler JJ, Luthra R, Naing A, Wang X, Kurzrock R (2012) KRASness and PIK3CAness in patients with advanced colorectal cancer: outcome after treatment with early-phase trials with targeted pathway inhibitors. PLoS One 7(5):e38033. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0038033
Cancer Genome Atlas Research N, Kandoth C, Schultz N, Cherniack AD, Akbani R, Liu Y, Shen H, Robertson AG, Pashtan I, Shen R, Benz CC, Yau C, Laird PW, Ding L, Zhang W, Mills GB, Kucherlapati R, Mardis ER, Levine DA (2013) Integrated genomic characterization of endometrial carcinoma. Nature 497(7447):67–73. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12113
Bardelli A, Siena S (2010) Molecular mechanisms of resistance to cetuximab and panitumumab in colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 28(7):1254–1261. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2009.24.6116
Kim A, Lee JE, Lee SS, Kim C, Lee SJ, Jang WS, Park S (2013) Coexistent mutations of KRAS and PIK3CA affect the efficacy of NVP-BEZ235, a dual PI3K/MTOR inhibitor, in regulating the PI3K/MTOR pathway in colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer 133(4):984–996. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.28073
Samuels Y, Wang Z, Bardelli A, Silliman N, Ptak J, Szabo S, Yan H, Gazdar A, Powell SM, Riggins GJ, Willson JK, Markowitz S, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, Velculescu VE (2004) High frequency of mutations of the PIK3CA gene in human cancers. Science 304(5670):554. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1096502
Barault L, Veyrie N, Jooste V, Lecorre D, Chapusot C, Ferraz JM, Lievre A, Cortet M, Bouvier AM, Rat P, Roignot P, Faivre J, Laurent-Puig P, Piard F (2008) Mutations in the RAS-MAPK, PI(3)K (phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase) signaling network correlate with poor survival in a population-based series of colon cancers. Int J Cancer 122(10):2255–2259. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.23388
Janku F, Wheler JJ, Westin SN, Moulder SL, Naing A, Tsimberidou AM, Fu S, Falchook GS, Hong DS, Garrido-Laguna I, Luthra R, Lee JJ, Lu KH, Kurzrock R (2012) PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibitors in patients with breast and gynecologic malignancies harboring PIK3CA mutations. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 30(8):777–782. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2011.36.1196
Hayes MP, Wang H, Espinal-Witter R, Douglas W, Solomon GJ, Baker SJ, Ellenson LH (2006) PIK3CA and PTEN mutations in uterine endometrioid carcinoma and complex atypical hyperplasia. Clin Cancer Res 12(20 Pt 1):5932–5935. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-1375
Janku F, Hong DS, Fu S, Piha-Paul SA, Naing A, Falchook GS, Tsimberidou AM, Stepanek VM, Moulder SL, Lee JJ, Luthra R, Zinner RG, Broaddus RR, Wheler JJ, Kurzrock R (2014) Assessing PIK3CA and PTEN in early-phase trials with PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibitors. Cell Rep 6(2):377–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2013.12.035
Di Nicolantonio F, Arena S, Tabernero J, Grosso S, Molinari F, Macarulla T, Russo M, Cancelliere C, Zecchin D, Mazzucchelli L, Sasazuki T, Shirasawa S, Geuna M, Frattini M, Baselga J, Gallicchio M, Biffo S, Bardelli A (2010) Deregulation of the PI3K and KRAS signaling pathways in human cancer cells determines their response to everolimus. J Clin Invest 120(8):2858–2866. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI37539
Tabernero J, Rojo F, Calvo E, Burris H, Judson I, Hazell K, Martinelli E, Ramon y Cajal S, Jones S, Vidal L, Shand N, Macarulla T, Ramos FJ, Dimitrijevic S, Zoellner U, Tang P, Stumm M, Lane HA, Lebwohl D, Baselga J (2008) Dose- and schedule-dependent inhibition of the mammalian target of rapamycin pathway with everolimus: a phase I tumor pharmacodynamic study in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 26(10):1603–1610. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2007.14.5482
O'Donnell A, Faivre S, Burris HA 3rd, Rea D, Papadimitrakopoulou V, Shand N, Lane HA, Hazell K, Zoellner U, Kovarik JM, Brock C, Jones S, Raymond E, Judson I (2008) Phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of the oral mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor everolimus in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 26(10):1588–1595. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2007.14.0988
Gold PJ ID, Arthur J, et al. (2008) Phase II trial of RAD001 in patients with refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. J clinical Oncol 27 (15s):[abstract513]
Ng K, Tabernero J, Hwang J, Bajetta E, Sharma S, Del Prete SA, Arrowsmith ER, Ryan DP, Sedova M, Jin J, Malek K, Fuchs CS (2013) Phase II study of everolimus in patients with metastatic colorectal adenocarcinoma previously treated with bevacizumab-, fluoropyrimidine-, oxaliplatin-, and irinotecan-based regimens. Clinical cancer research: an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 19(14):3987–3995. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-0027
Harzstark AL, Small EJ, Weinberg VK, Sun J, Ryan CJ, Lin AM, Fong L, Brocks DR, Rosenberg JE (2011) A phase 1 study of everolimus and sorafenib for metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer 117(18):4194–4200. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.25931
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, Wanders J, Kaplan RS, Rubinstein L, Verweij J, Van Glabbeke M, van Oosterom AT, Christian MC, Gwyther SG (2000) New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States. National Cancer Institute of Canada Journal of the National Cancer Institute 92(3):205–216. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/92.3.205
Longo DL, Duffey PL, DeVita VT Jr, Wesley MN, Hubbard SM, Young RC (1991) The calculation of actual or received dose intensity: a comparison of published methods. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 9(11):2042–2051. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.1991.9.11.2042
Saltz LB, Clarke S, Diaz-Rubio E, Scheithauer W, Figer A, Wong R, Koski S, Lichinitser M, Yang TS, Rivera F, Couture F, Sirzen F, Cassidy J (2008) Bevacizumab in combination with oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy as first-line therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer: a randomized phase III study. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 26(12):2013–2019. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2007.14.9930
Garg K, Broaddus RR, Soslow RA, Urbauer DL, Levine DA, Djordjevic B (2012) Pathologic scoring of PTEN immunohistochemistry in endometrial carcinoma is highly reproducible. Int J Gynecol Pathol 31(1):48–56. https://doi.org/10.1097/PGP.0b013e3182230d00
Shahda S YM, Picus J, et al. (2011) Phase I study of everolimus (RAD001) with irinotecan and cetuximab in second-line metastatic colorectal cancer: Hoosier oncology group GI05-102- final report. J clinical Oncol 29s:[abstract 3587]
Townsend AR PL, Hardingham J, et al. (2011) A phase Ib/II study of second-line therapy with panitumumab, irinotecan, and everolimus in metastatic colorectal cancer with KRAS wild type. J clinical Oncol 29s:[abstract TPS162]
Bernardi R, Guernah I, Jin D, Grisendi S, Alimonti A, Teruya-Feldstein J, Cordon-Cardo C, Simon MC, Rafii S, Pandolfi PP (2006) PML inhibits HIF-1alpha translation and neoangiogenesis through repression of mTOR. Nature 442(7104):779–785. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05029
Guertin DA, Sabatini DM (2007) Defining the role of mTOR in cancer. Cancer Cell 12(1):9–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2007.05.008
Hudson CC, Liu M, Chiang GG, Otterness DM, Loomis DC, Kaper F, Giaccia AJ, Abraham RT (2002) Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha expression and function by the mammalian target of rapamycin. Mol Cell Biol 22(20):7004–7014. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.22.20.7004-7014.2002
Bullock KE, Hurwitz HI, Uronis HE, Morse MA, Blobe GC, Hsu SD, Zafar SY, Nixon AB, Howard LA, Bendell JC (2009) Bevacizumab (B) plus everolimus (E) in refractory metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC). J Clin Oncol 27(15_suppl):4080–4080. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2009.27.15_suppl.4080
Altomare I, Bendell JC, Bullock KE, Uronis HE, Morse MA, Hsu SD, Zafar SY, Blobe GC, Pang H, Honeycutt W, Sutton L, Hurwitz HI (2011) A phase II trial of bevacizumab plus everolimus for patients with refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. Oncologist 16(8):1131–1137. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2011-0078
Wolpin BM, Ng K, Zhu AX, Abrams T, Enzinger PC, McCleary NJ, Schrag D, Kwak EL, Allen JN, Bhargava P, Chan JA, Goessling W, Blaszkowsky LS, Supko JG, Elliot M, Sato K, Regan E, Meyerhardt JA, Fuchs CS (2013) Multicenter phase II study of tivozanib (AV-951) and everolimus (RAD001) for patients with refractory, metastatic colorectal cancer. Oncologist 18(4):377–378. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2012-0378
Rugo HS, Hortobagyi GN, Yao J, Pavel M, Ravaud A, Franz D, Ringeisen F, Gallo J, Rouyrre N, Anak O, Motzer R (2016) Meta-analysis of stomatitis in clinical studies of everolimus: incidence and relationship with efficacy. Ann Oncol 27(3):519–525. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdv595
Rugo H SL, Beck J, et al (2016) Prevention of everolimus/exemestane stomatitis in postmenopausal women with hormone receptor–positive metastatic breast cancer using a dexamethasone-based mouthwash: results of the SWISH trial. Abstract MASCC-0638. MASCC/ISOO International Symposium on Supportive Care in Cancer Presented June 23, 2016 24 (1):1–249. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-016-3209-z
Rugo HS, Beck JT, Glaspy JA, Peguero JA, Pluard TJ, Dhillon N, Hwang LC, Nangia CS, Mayer IA, Meiller TF, Chambers MS, Warsi G, Sweetman RW, Sabo JR, Seneviratne L (2016) Prevention of everolimus/exemestane (EVE/EXE) stomatitis in postmenopausal (PM) women with hormone receptor-positive (HR+) metastatic breast cancer (MBC) using a dexamethasone-based mouthwash (MW): results of the SWISH trial. Journal of Clinical Oncology 34(26_suppl):189–189. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2016.34.26_suppl.189
Funding
This study was funded by Novartis Pharmaceuticals and the Huntsman Cancer Institute. clinical trial NCT01047293.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Sunil Sharma received research support from Novartis Pharmaceuticals and has served on Novartis Pharmaceuticals advisory boards. All other authors have no financial interests to disclose surrounding this manuscript.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weldon Gilcrease, G., Stenehjem, D.D., Wade, M.L. et al. Phase I/II study of everolimus combined with mFOLFOX-6 and bevacizumab for first–line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. Invest New Drugs 37, 482–489 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-018-0645-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-018-0645-2