Summary
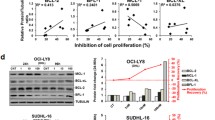
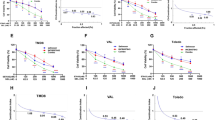
Despite the recent therapeutic progress, the prognoses of diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (DLBCLs) that concomitantly overexpress c-MYC and BCL2, i.e., double hit lymphoma (DHL) and double expressing lymphoma (DEL), remain poor. This study examined triple targeting of c-MYC, BCL2 and the B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling pathway for DHL and DEL. We first used AZD5153, a novel bivalent inhibitor for bromodomain-containing 4 (BRD4), in DHL- and DEL-derived cell lines, because BRD4 regulates disease type-oriented key molecules for oncogenesis. AZD5153 was more effective than conventional monovalent BRD4 inhibitors, JQ1 and I-BET151, in inhibiting cell proliferation of a DHL-derived cell line and two DEL-derived cell lines, with at least 10-fold lower half growth inhibitory concentrations. AZD5153 caused G1/S cell cycle blockade, while the apoptosis-inducing effect was relatively modest. At the molecular level, AZD5153 was potent in downregulating various molecules for oncogenesis, such as c-MYC, AKT2 and MAP3K; those involved in the BCR signaling pathway, such as CD19, BLNK and CD79B; and those associated with B-cell development, such as IKZF1, IKZF3, PAX5, POU2AF1 and EBF1. In contrast, AZD5153 did not decrease anti-apoptotic BCL2 proteins, and did not activate pro-apoptotic BH3-only proteins, except BAD. To augment cell death induction, we added a novel BH3-mimicking BCL2 inhibitor AZD4320 to AZD5153, and found that these two agents had a mostly synergistic antitumor effect by increasing cells undergoing apoptosis in all three cell lines. These results provide a rationale for dual targeting of BRD4 and BCL2 using AZD5153 and AZD4320 as a therapeutic strategy against DHL and DEL.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alizadeh AA, Eisen MB, Davis RE, Ma C, Lossos IS, Rosenwald A, Boldrick JC, Sabet H, Tran T, Yu X, Powell JI, Yang L, Marti GE, Moore T, Hudson J Jr, Lu L, Lewis DB, Tibshirani R, Sherlock G, Chan WC, Greiner TC, Weisenburger DD, Armitage JO, Warnke R, Levy R, Wilson W, Grever MR, Byrd JC, Botstein D, Brown PO, Staudt LM (2000) Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature 403:503–511
Savage KJ, Monti S, Kutok JL, Cattoretti G, Neuberg D, De Leval L, Kurtin P, Dal Cin P, Ladd C, Feuerhake F, Aguiar RC, Li S, Salles G, Berger F, Jing W, Pinkus GS, Habermann T, Dalla-Favera R, Harris NL, Aster JC, Golub TR, Shipp MA (2003) The molecular signature of mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma differs from that of other diffuse large B-cell lymphomas and shares features with classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 102:3871–3879
Friedberg JW (2017) How I treat double-hit lymphoma. Blood 30:590–596
Staiger AM, Ziepert M, Horn H, Scott DW, Barth TFE, Bernd HW, Feller AC, Klapper W, Szczepanowski M, Hummel M, Stein H, Lenze D, Hansmann ML, Hartmann S, Möller P, Cogliatti S, Lenz G, Trümper L, Löffler M, Schmitz N, Pfreundschuh M, Rosenwald A, Ott G, German High-Grade Lymphoma Study Group (2017) Clinical impact of the cell-of-origin classification and the MYC/BCL2 dual expresser status in diffuse large b-cell lymphoma treated within prospective clinical trials of the german high-grade non-hodgkin's lymphoma study group. J Clin Oncol 35:2515–2526
Hu S, Xu-Monette ZY, Tzankov A, Green T, Wu L, Balasubramanyam A, Liu WM, Visco C, Li Y, Miranda RN, Montes-Moreno S, Dybkaer K, Chiu A, Orazi A, Zu Y, Bhagat G, Richards KL, Hsi ED, Choi WW, Zhao X, van Krieken JH, Huang Q, Huh J, Ai W, Ponzoni M, Ferreri AJ, Zhou F, Slack GW, Gascoyne RD, Tu M, Variakojis D, Chen W, Go RS, Piris MA, Møller MB, Medeiros LJ, Young KH (2013) MYC/BCL2 protein coexpression contributes to the inferior survival of activated B-cell subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and demonstrates high-risk gene expression signatures: a report from the international DLBCL rituximab-CHOP consortium program. Blood 121:4021–4031
Rosenthal A, Younes A (2017) High grade B-cell lymphoma with rearrangements of MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6: Double hit and triple hit lymphomas and double expressing lymphoma. Blood 31:37–42
Kawashima I, Inamoto Y, Maeshima AM, Nomoto J, Tajima K, Honda T, Shichijo T, Kawajiri A, Takemura T, Onishi A, Ito A, Tanaka T, Fuji S, Kurosawa S, Kim SW, Maruyama D, Tobinai K, Kobayashi Y, Fukuda T (2018) Double-Expressor Lymphoma Is Associated with Poor Outcomes after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 24:294–300
Herrera AF, Mei M, Low L, Kim HT, Griffin GK, Song JY, Merryman RW, Bedell V, Pak C, Sun H, Paris T, Stiller T, Brown JR, Budde LE, Chan WC, Chen R, Davids MS, Freedman AS, Fisher DC, Jacobsen ED, Jacobson CA, LaCasce AS, Murata-Collins J, Nademanee AP, Palmer JM, Pihan GA, Pillai R, Popplewell L, Siddiqi T, Sohani AR, Zain J, Rosen ST, Kwak LW, Weinstock DM, Forman SJ, Weisenburger DD, Kim Y, Rodig SJ, Krishnan A, Armand P (2017) Relapsed or Refractory Double-Expressor and Double-Hit Lymphomas Have Inferior Progression-Free Survival After Autologous Stem-Cell Transplantation. J Clin Oncol 35:24–31
Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Pileri SA, Harris NL, Stein H, Siebert R, Advani R, Ghielmini M, Salles GA, Zelenetz AD, Jaffe ES. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms
Stasik CJ, Nitta H, Zhang W, Mosher CH, Cook JR, Tubbs RR, Unger JM, Brooks TA, Persky DO, Wilkinson ST, Grogan TM, Rimsza LM (2010) Increased MYC gene copy number correlates with increased mRNA levels in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Haematologica 95:597–603
Sasaki N, Kuroda J, Nagoshi H, Yamamoto M, Kobayashi S, Tsutsumi Y, Kobayashi T, Shimura Y, Matsumoto Y, Taki T, Nishida K, Horiike S, Akao Y, Taniwaki M (2011) Bcl-2 is a better therapeutic target than c-Myc, but attacking both could be a more effective treatment strategy for B-cell lymphoma with concurrent Bcl-2 and c-Myc overexpression. Exp Hematol 39:817–828
Beck-Engeser GB, Lum AM, Huppi K, Caplen NJ, Wang BB, Wabl M (2008) Pvt1-encoded microRNAs in oncogenesis. Retrovirology 5:4
Jackstadt R, Hermeking H (2015) MicroRNAs as regulators and mediators of c-MYC function. Biochim Biophys Acta 849:544–553
Musilova K, Mraz M (2015) MicroRNAs in B-cell lymphomas: how a complex biology gets more complex. Leukemia 29:1004–1017
Iqbal J, Neppalli VT, Wright G, Dave BJ, Horsman DE, Rosenwald A, Lynch J, Hans CP, Weisenburger DD, Greiner TC, Gascoyne RD, Campo E, Ott G, Müller-Hermelink HK, Delabie J, Jaffe ES, Grogan TM, Connors JM, Vose JM, Armitage JO, Staudt LM, Chan WC (2006) BCL2 expression is a prognostic marker for the activated B-cell-like type of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 24:961–968
Dierlamm J, Murga Penas EM, Bentink S, Wessendorf S, Berger H, Hummel M, Klapper W, Lenze D, Rosenwald A, Haralambieva E, Ott G, Cogliatti SB, Möller P, Schwaenen C, Stein H, Löffler M, Spang R, Trümper L, Siebert R, Deutsche Krebshilfe Network Project "Molecular Mechanisms in Malignant Lymphomas" (2008) Gain of chromosome region 18q21 including the MALT1 gene is associated with the activated B-cell-like gene expression subtype and increased BCL2 gene dosage and protein expression in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Haematologica 93:688–696
Cai Q, Medeiros LJ, Xu X, Young KH (2015) MYC-driven aggressive B-cell lymphomas: biology, entity, differential diagnosis and clinical management. Oncotarget 6:38591–38616
Kuroda J, Taniwaki M (2009) Involvement of BH3-only proteins in hematologic malignancies. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 71:89–101
Schenk RL, Strasser A, Dewson G (2017) BCL-2: Long and winding path from discovery to therapeutic target. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 482:459–469
Smith DP, Bath ML, Metcalf D, Harris AW, Cory S (2006) MYC levels govern hematopoietic tumor type and latency in transgenic mice. Blood 108:653–661
Johnson-Farley N, Veliz J, Bhagavathi S, Bertino JR (2015) ABT-199, a BH3 mimetic that specifically targets Bcl-2, enhances the antitumor activity of chemotherapy, bortezomib and JQ1 in "double hit" lymphoma cells. Leuk Lymphoma 56:2146–2152
Cinar M, Rosenfelt F, Rokhsar S, Lopategui J, Pillai R, Cervania M, Pao A, Cinar B, Alkan S (2015) Concurrent inhibition of MYC and BCL2 is a potentially effective treatment strategy for double hit and triple hit B-cell lymphomas. Leuk Res 39:730–738
Rickert RC (2013) New insights into pre-BCR and BCR signalling with relevance to B cell malignancies. Nat Rev Immunol 13:578–591
Nicodeme E, Jeffrey KL, Schaefer U, Beinke S, Dewell S, Chung CW, Chandwani R, Marazzi I, Wilson P, Coste H, White J, Kirilovsky J, Rice CM, Lora JM, Prinjha RK, Lee K, Tarakhovsky A (2010) Suppression of inflammation by a synthetic histone mimic. Nature 468:1119–1123
Filippakopoulos P, Qi J, Picaud S, Shen Y, Smith WB, Fedorov O, Morse EM, Keates T, Hickman TT, Felletar I, Philpott M, Munro S, McKeown MR, Wang Y, Christie AL, West N, Cameron MJ, Schwartz B, Heightman TD, La Thangue N, French CA, Wiest O, Kung AL, Knapp S, Bradner JE (2010) Selective inhibition of BET bromodomains. Nature 468:1067–1073
Chaidos A, Caputo V, Gouvedenou K, Liu B, Marigo I, Chaudhry MS, Rotolo A, Tough DF, Smithers NN, Bassil AK, Chapman TD, Harker NR, Barbash O, Tummino P, Al-Mahdi N, Haynes AC, Cutler L, Le B, Rahemtulla A, Roberts I, Kleijnen M, Witherington JJ, Parr NJ, Prinjha RK, Karadimitris A (2014) Potent antimyeloma activity of the novel bromodomain inhibitors I-BET151 and I-BET762. Blood 123:697–705
Ott CJ, Kopp N, Bird L, Paranal RM, Qi J, Bowman T, Rodig SJ, Kung AL, Bradner JE, Weinstock DM (2012) BET bromodomain inhibition targets both c-Myc and IL7R in high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 120:2843–2852
Chapuy B, McKeown MR, Lin CY, Monti S, Roemer MG, Qi J, Rahl PB, Sun HH, Yeda KT, Doench JG, Reichert E, Kung AL, Rodig SJ, Young RA, Shipp MA, Bradner JE (2013) Discovery and characterization of super-enhancer-associated dependencies in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Cancer Cell 24:777–790
Trabucco SE, Gerstein RM, Evens AM, Bradner JE, Shultz LD, Greiner DL, Zhang H (2015) Inhibition of bromodomain proteins for the treatment of human diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res 21:113–122
Puissant A, Frumm SM, Alexe G, Bassil CF, Qi J, Chanthery YH, Nekritz EA, Zeid R, Gustafson WC, Greninger P, Garnett MJ, McDermott U, Benes CH, Kung AL, Weiss WA, Bradner JE, Stegmaier K (2013) Targeting MYCN in neuroblastoma by BET bromodomain inhibition. Cancer Discov 3:308–323
Lovén J, Hoke HA, Lin CY, Lau A, Orlando DA, Vakoc CR, Bradner JE, Lee TI, Young RA (2013) Selective inhibition of tumor oncogenes by disruption of super-enhancers. Cell 153:320–334
Boi M, Gaudio E, Bonetti P, Kwee I, Bernasconi E, Tarantelli C, Rinaldi A, Testoni M, Cascione L, Ponzoni M, Mensah AA, Stathis A, Stussi G, Riveiro ME, Herait P, Inghirami G, Cvitkovic E, Zucca E, Bertoni F (2015) The BET Bromodomain inhibitor OTX015 affects Pathogenetic pathways in preclinical B-cell tumor models and synergizes with targeted drugs. Clin Cancer Res 21:1628–1638
Decker TM, Kluge M, Krebs S, Shah N, Blum H, Friedel CC, Eick D (2017) Transcriptome analysis of dominant-negative Brd4 mutants identifies Brd4-specific target genes of small molecule inhibitor JQ1. Sci Rep 7:1684
Ishida CT, Bianchetti E, Shu C, Halatsch ME, Westhoff MA, Karpel-Massler G, Siegelin MD (2017) BH3-mimetics and BET-inhibitors elicit enhanced lethality in malignant glioma. Oncotarget 8:29558–29573
Amorim S, Stathis A, Gleeson M, Iyengar S, Magarotto V, Leleu X, Morschhauser F, Karlin L, Broussais F, Rezai K, Herait P, Kahatt C, Lokiec F, Salles G, Facon T, Palumbo A, Cunningham D, Zucca E, Thieblemont C (2016) Bromodomain inhibitor OTX015 in patients with lymphoma or multiple myeloma: a dose-escalation, open-label, pharmacokinetic, phase 1 study. Lancet Haematol 3:196–204
Zhao Y, Yang CY, Wang S (2013) The making of I-BET762, a BET bromodomain inhibitor now in clinical development. J Med Chem 56:7498–7500
Rhyasen GW, Hattersley MM, Yao Y, Dulak A, Wang W, Petteruti P, Dale IL, Boiko S, Cheung T, Zhang J, Wen S, Castriotta L, Lawson D, Collins M, Bao L, Ahdesmaki MJ, Walker G, O'Connor G, Yeh TC, Rabow AA, Dry JR, Reimer C, Lyne P, Mills GB, Fawell SE, Waring MJ, Zinda M, Clark E, Chen H (2016) AZD5153: a novel bivalent BET Bromodomain inhibitor highly active against hematologic malignancies. Mol Cancer Ther 15:2563–2574
Bradbury RH, Callis R, Carr GR, Chen H, Clark E, Feron L, Glossop S, Graham MA, Hattersley M, Jones C, Lamont SG, Ouvry G, Patel A, Patel J, Rabow AA, Roberts CA, Stokes S, Stratton N, Walker GE, Ward L, Whalley D, Whittaker D, Wrigley G, Waring MJ (2016) Optimization of a series of bivalent triazolopyridazine based bromodomain and extraterminal inhibitors: the discovery of (3R)-4-[2-[4-[1-(3-Methoxy-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazin-6-yl)-4-piperidyl]phenoxy]ethyl]-1,3-dimethyl-piperazin-2-one (AZD5153). J Med Chem 59:7801–7817
Li X, Zhang XA, Xie W, Li X, Huang S (2015) MYC-mediated synthetic lethality for treatment of hematological malignancies. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 15:53–70
Kuroda J, Puthalakath H, Cragg MS, Kelly PN, Bouillet P, Huang DC, Kimura S, Ottmann OG, Druker BJ, Villunger A, Roberts AW, Strasser A (2006) Bim and Bad mediate imatinib-induced killing of Bcr/Abl+ leukemic cells, and resistance due to their loss is overcome by a BH3 mimetic. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:14907–14912
Del Gaizo Moore V, Letai A (2013) BH3 profiling--measuring integrated function of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway to predict cell fate decisions. Cancer Lett 332:202–205
Wyce A, Ganji G, Smitheman KN, Chung CW, Korenchuk S, Bai Y, Barbash O, Le B, Craggs PD, McCabe MT, Kennedy-Wilson KM, Sanchez LV, Gosmini RL, Parr N, McHugh CF, Dhanak D, Prinjha RK, Auger KR, Tummino PJ (2013) BET inhibition silences expression of MYCN and BCL2 and induces cytotoxicity in neuroblastoma tumor models. PLoS One 8:72967
Fiskus W, Sharma S, Qi J, Valenta JA, Schaub LJ, Shah B, Peth K, Portier BP, Rodriguez M, Devaraj SG, Zhan M, Sheng J, Iyer SP, Bradner JE, Bhalla KN (2014) Highly active combination of BRD4 antagonist and histone deacetylase inhibitor against human acute myelogenous leukemia cells. Mol Cancer Ther 13:1142–1154
Sun B, Shah B, Fiskus W, Qi J, Rajapakshe K, Coarfa C, Li L, Devaraj SG, Sharma S, Zhang L, Wang ML, Saenz DT, Krieger S, Bradner JE, Bhalla KN (2015) Synergistic activity of BET protein antagonist-based combinations in mantle cell lymphoma cells sensitive or resistant to ibrutinib. Blood 126:1565–1574
Carretta M, Brouwers-Vos AZ, Bosman M, Horton SJ, Martens JHA, Vellenga E, Schuringa JJ (2017) BRD3/4 inhibition and FLT3-ligand deprivation target pathways that are essential for the survival of human MLL-AF9+ leukemic cells. PLoS One 12:e0189102
Wu X, Liu D, Gao X, Xie F, Tao D, Xiao X, Wang L, Jiang G, Zeng F (2017) Inhibition of BRD4 suppresses cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in renal cell carcinoma. Cell Physiol Biochem 41:1947–1956
Siu KT, Ramachandran J, Yee AJ, Eda H, Santo L, Panaroni C, Mertz JA, Sims Iii RJ, Cooper MR, Raje N (2017) Preclinical activity of CPI-0610, a novel small-molecule bromodomain and extra-terminal protein inhibitor in the therapy of multiple myeloma. Leukemia 31:1760–1769
Yogarajah M, Stone RM (2018) A concise review of BCL-2 inhibition in acute myeloid leukemia. Expert Rev Hematol 11:145–154
Kuo HP, Ezell SA, Schweighofer KJ, Cheung LWK, Hsieh S, Apatira M, Sirisawad M, Eckert K, Hsu SJ, Chen CT, Beaupre DM, Versele M, Chang BY (2017) Combination of Ibrutinib and ABT-199 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and follicular lymphoma. Mol Cancer Ther 16:1246–1256
Fong CY, Gilan O, Lam EY, Rubin AF, Ftouni S, Tyler D, Stanley K, Sinha D, Yeh P, Morison J, Giotopoulos G, Lugo D, Jeffrey P, Lee SC, Carpenter C, Gregory R, Ramsay RG, Lane SW, Abdel-Wahab O, Kouzarides T, Johnstone RW, Dawson SJ, Huntly BJ, Prinjha RK, Papenfuss AT, Dawson MA (2015) BET inhibitor resistance emerges from leukaemia stem cells. Nature 525:538–542
Rathert P, Roth M, Neumann T, Muerdter F, Roe JS, Muhar M, Deswal S, Cerny-Reiterer S, Peter B, Jude J, Hoffmann T, Boryń ŁM, Axelsson E, Schweifer N, Tontsch-Grunt U, Dow LE, Gianni D, Pearson M, Valent P, Stark A, Kraut N, Vakoc CR, Zuber J (2015) Transcriptional plasticity promotes primary and acquired resistance to BET inhibition. Nature 525:543–547
Funding
This work was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from The Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (MEXT KAKENHI 16 K09856) (MT); by the National Cancer Center Research and Development Fund (29-A-3); by a grant (Practical Research for Innovative Cancer Control) from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED) (17ck0106348h0001); and by the Takeda Science Foundation and Astra Zeneca (JK).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest in association with this study.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Table S1
(DOCX 73 kb)
Supplementary Table S2
(DOCX 90 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takimoto-Shimomura, T., Tsukamoto, T., Maegawa, S. et al. Dual targeting of bromodomain-containing 4 by AZD5153 and BCL2 by AZD4320 against B-cell lymphomas concomitantly overexpressing c-MYC and BCL2. Invest New Drugs 37, 210–222 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-018-0623-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-018-0623-8