Summary
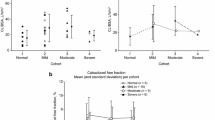
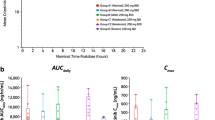
Purpose Trabectedin is metabolized by the liver and has been associated with transient, noncumulative transaminase elevation. Two recent studies further characterize hepatic tolerability with trabectedin therapy: a phase 1 pharmacokinetic study (Study #1004; NCT01273493) in patients with advanced malignancies and hepatic impairment (HI), and a phase 3 study (Study #3007; NCT01343277) of trabectedin vs. dacarbazine in patients with advanced sarcomas and normal hepatic function. Methods In Study #1004, patients received a single 3-h intravenous (IV) infusion of trabectedin: control group, trabectedin 1.3 mg/m2; HI group (baseline total bilirubin >1.5 and ≤3× upper limit of normal [ULN]; AST and ALT ≤2.5× ULN), trabectedin 0.58 or 0.9 mg/m2. In Study #3007, the trabectedin group received 1.5 mg/m2 by 24-h IV infusion every 3 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Results In Study #1004, dose-normalized trabectedin exposure was higher in HI patients (n = 6) versus controls (n = 9) (geometric mean ratios [90% CI] AUClast: 1.97 [1.20; 3.22]). In Study #3007, following trabectedin administration, 90% of patients had elevated ALT (32% grade 3–4) and 84% had elevated AST (17% grade 3–4). Transaminase elevations were transient and noncumulative. Progression-free survival was similar in patients with grade 3–4 hepatotoxicity (n = 109) versus grade 0–2 hepatotoxicity (n = 231) (median [95% CI]: 4.63 [4.01, 5.85] months versus 3.55 [2.73, 4.63] months; P = 0.545, HR = 0.91 [0.68–1.23]). Conclusion Trabectedin treatment of patients with HI results in higher plasma exposures. Hepatotoxicity in patients with normal liver function can be effectively addressed through dose reductions and delays.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
(2017) Yondelis® (trabectedin) [product insert]. Janssen Products, LP, Horsham
Demetri GD, von Mehren M, Jones RL, Hensley ML, Schuetze SM, Staddon A et al (2016) Efficacy and safety of trabectedin or dacarbazine for metastatic liposarcoma or leiomyosarcoma after failure of conventional chemotherapy: results of a phase iii randomized multicenter clinical trial. J Clin Oncol 34:786–793
Monk BJ, Herzog TJ, Kaye SB, Krasner CN, Vermorken JB, Muggia FM et al (2010) Trabectedin plus pegylated liposomal doxorubicin in recurrent ovarian cancer. J Clin Oncol 28:3107–3114
(2012) Yondelis® (trabectedin) [summary of product characteristics]. Pharma Mar, S.A., Madrid
Allavena P, Signorelli M, Chieppa M, Erba E, Bianchi G, Marchesi F et al (2005) Anti-inflammatory properties of the novel antitumor agent yondelis (trabectedin): inhibition of macrophage differentiation and cytokine production. Cancer Res 65:2964–2971
D'Incalci M, Erba E, Damia G, Galliera E, Carrassa L, Marchini S et al (2002) Unique features of the mode of action of et-743. Oncologist 7:210–216
Germano G, Frapolli R, Belgiovine C, Anselmo A, Pesce S, Liguori M et al (2013) Role of macrophage targeting in the antitumor activity of trabectedin. Cancer Cell 23:249–262
Germano G, Frapolli R, Simone M, Tavecchio M, Erba E, Pesce S et al (2010) Antitumor and anti-inflammatory effects of trabectedin on human myxoid liposarcoma cells. Cancer Res 70:2235–2244
Demetri GD, Chawla SP, von Mehren M, Ritch P, Baker LH, Blay JY et al (2009) Efficacy and safety of trabectedin in patients with advanced or metastatic liposarcoma or leiomyosarcoma after failure of prior anthracyclines and ifosfamide: results of a randomized phase ii study of two different schedules. J Clin Oncol 27:4188–4196
Reid JM, Kuffel MJ, Ruben SL, Morales JJ, Rinehart KL, Squillace DP et al (2002) Rat and human liver cytochrome p-450 isoform metabolism of ecteinascidin 743 does not predict gender-dependent toxicity in humans. Clin Cancer Res 8:2952–2962
Brandon EF, Meijerman I, Klijn JS, den Arend D, Sparidans RW, Lazaro LL et al (2005) In-vitro cytotoxicity of et-743 (trabectedin, yondelis), a marine anti-cancer drug, in the hep g2 cell line: influence of cytochrome p450 and phase ii inhibition, and cytochrome p450 induction. Anti-Cancer Drugs 16:935–943
Donald S, Verschoyle RD, Edwards R, Judah DJ, Davies R, Riley J et al (2002) Hepatobiliary damage and changes in hepatic gene expression caused by the antitumor drug ecteinascidin-743 (et-743) in the female rat. Cancer Res 62:4256–4262
Machiels JP, Staddon A, Herremans C, Keung C, Bernard A, Phelps C et al (2014) Impact of cytochrome p450 3a4 inducer and inhibitor on the pharmacokinetics of trabectedin in patients with advanced malignancies: open-label, multicenter studies. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 74:729–737
Pardo B, Salazar R, Ciruelos E, Cortes-Funes H, Garcia M, Majem M et al (2012) Phase i and pharmacokinetic study of trabectedin 3-hour infusion every three weeks in patients with advanced cancer and alteration of hepatic function. Med Oncol 29:2240–2250
Child CG, Turcotte JG (1964) Surgery and portal hypertension. In: Child CG (ed) The liver and portal hypertension. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 50–64
Pugh RN, Murray-Lyon IM, Dawson JL, Pietroni MC, Williams R (1973) Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg 60:646–649
Reuben A (2004) Hy's law. Hepatology 39:574–578
(2009) Guidance for industry. Drug-induced liver injury: premarketing clinical evaluation. Food and Drug Administration, US Department of Health and Human Services, Rockville
Robles-Diaz M, Lucena MI, Kaplowitz N, Stephens C, Medina-Caliz I, Gonzalez-Jimenez A, et al (2014) Use of hy's law and a new composite algorithm to predict acute liver failure in patients with drug-induced liver injury. Gastroenterology 147:109-118.e105
Senior JR (2013) Why the threshold criteria should not be modified for detection of possibly serious drug-induced hepatotoxicity in special groups of trial subjects. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf 22:579–582
(2010) Guidance for industry: pharmacokinetics in patients with impaired renal function - study design, data analysis, and impact on dosing and labeling. Food and Drug Administration, US Department of Health and Human Services, Rockville
Gomez J, Lopez Lazaro L, Guzman C, Gonzalez A, Misset GL, Twelves C, et al (2000) Identification of biochemical parameters that predict severe toxicity in patients treated with et-423. Journal of clinical oncology 19:187:abstract 727
Le Cesne A, Yovine A, Blay JY, Delaloge S, Maki RG, Misset JL et al (2012) A retrospective pooled analysis of trabectedin safety in 1,132 patients with solid tumors treated in phase ii clinical trials. Investig New Drugs 30:1193–1202
Martin-Liberal J, Judson I (2013) Safety evaluation of trabectedin in treatment of soft-tissue sarcomas. Expert Opin Drug Saf 12:905–911
Vincenzi B, Stumbo L, Maltese G, Cerbone L, Spalato Ceruso M, Badalamenti G et al (2015) Lack of correlation between liver tests abnormalities and trabectedin efficacy in the treatment of soft tissue sarcoma: a retrospective study. Sci Rep 5:12077
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the patients for their participation in this study and acknowledge the collaboration and commitment of all investigators and clinical site staff for their participation in this study. The authors also thank Peter Zannikos, PhD, of Janssen Research & Development LLC (Raritan, NJ, USA) for supporting the development of the PK study design and Chi Fung Keung for involvement in the pharmacokinetic data analysis. This study was funded by Janssen Research & Development, LLC (Raritan, NJ, USA). Medical writing support for this manuscript was provided by Yvonne E. Yarker, PhD, ISMPP CMPP™ of InSeption (Lansdale, PA, USA), supported by Janssen Research & Development, LLC (Raritan, NJ, USA).
Funding
This study was funded by Janssen Research & Development, LLC, Raritan, NJ, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The following authors declare that they have no conflict of interest: Emiliano Calvo, Analia Azaro, Luc Dirix, Manon Huizing, Patricia LoRusso, Francis Mark Senecal, and Lorrin Yee.
Jordi Rodon: Member of Advisory Boards of Orion, Peptomyc, Novartis, Lilly, and Servier.
George D. Demetri: Research support from Bayer, Novartis, Pfizer, and Janssen Oncology; Consulting fees from Novartis, EMD-Serono, Sanofi Oncology, Janssen Oncology, PharmaMar, Daiichi-Sankyo, Adaptimmune, and Eisai; Patent licensed to Novartis from Dana-Farber Cancer Institute with royalty paid to Dana-Farber Cancer Institute; Blueprint Medicines Member, Board of Directors, Member, Scientific Advisory Board, consulting fees, and equity (minor stake, public).
Margaret von Mehren: Member of Janssen Advisory Board, and Scientific Steering Committee for the study in this report.
The following authors are Janssen/Johnson & Johnson employees: Italo Poggesi (and shareholder), Jan de Jong (and stock owner), Spyros Triantos (and shareholder), Youn C. Park, Roland E. Knoblauch (and stock owner), and Trilok V. Parekh (and shareholder).
Research involving human participants and/or animals
Ethical approval: All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 318 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Calvo, E., Azaro, A., Rodon, J. et al. Hepatic safety analysis of trabectedin: results of a pharmacokinetic study with trabectedin in patients with hepatic impairment and experience from a phase 3 clinical trial. Invest New Drugs 36, 476–486 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-017-0546-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-017-0546-9