Summary
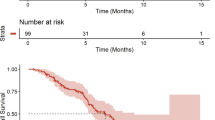
Background Dabrafenib is a BRAF inhibitor that has demonstrated clinical activity with a good tolerability profile in patients with BRAF V600E mutated metastatic melanoma. This study evaluated the safety and tolerability, pharmacokinetics and preliminary efficacy of dabrafenib in Japanese patients. Methods This phase I, open-label, dose escalation study was conducted in 12 Japanese patients with BRAF V600 mutation positive solid tumours. Primary endpoint was safety, assessed by monitoring and recording of all adverse events (AEs), serious AEs, drug-related AEs; secondary endpoints were pharmacokinetic profiles and efficacy measured by tumour response. This study is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, number NCT01582997. Results Of the 12 patients enrolled, 3 each received 75 mg and 100 mg dabrafenib while 6 received 150 mg dabrafenib twice daily orally. Melanoma and thyroid cancer were the primary tumours reported in 11 (92%) and 1 (8%) patients respectively. Most AEs were grade 1 or 2 and considered related to study treatment. Most common AEs reported in the 12 patients were alopecia in 7 (58%); pyrexia, arthralgia and leukopenia in 6 (50%) each, hyperkeratosis and nausea in 4 (33%) each. Partial response as best overall response was reported in 7 of 12 (58%) patients and in 6 (55%) with malignant melanoma. No dose-limiting toxicity (DLTs) were reported during the DLT evaluation periods. Conclusions Dabrafenib was well tolerated and rapidly absorbed administered as single- or multiple dose. Comparable safety and pharmacokinetic profiles were observed compared with non-Japanese patients. Dabrafenib has promising clinical activity in Japanese patients with BRAF mutated malignant melanoma.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davies H, Bignell GR, Cox C, Stephens P, Edkins S, Clegg S, Teague J, Woffendin H, Garnett MJ, Bottomley W, Davis N, Dicks E, Ewing R, Floyd Y, Gray K, Hall S, Hawes R, Hughes J, Kosmidou V, Menzies A, Mould C, Parker A, Stevens C, Watt S, Hooper S, Wilson R, Jayatilake H, Gusterson BA, Cooper C, Shipley J, Hargrave D, Pritchard-Jones K, Maitland N, Chenevix-Trench G, Riggins GJ, Bigner DD, Palmieri G, Cossu A, Flanagan A, Nicholson A, Ho JW, Leung SY, Yuen ST, Weber BL, Seigler HF, Darrow TL, Paterson H, Marais R, Marshall CJ, Wooster R, Stratton MR, Futreal PA (2002) Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature 417(6892):949–954. doi:10.1038/nature00766
Puxeddu E, Filetti S (2014) BRAF mutation assessment in papillary thyroid cancer: are we ready to use it in clinical practice? Endocrine 45(3):341–343. doi:10.1007/s12020-013-0139-0
Clancy C, Burke JP, Kalady MF, Coffey JC (2013) BRAF mutation is associated with distinct clinicopathological characteristics in colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Color Dis 15(12):e711–e718. doi:10.1111/codi.12427
Tiacci E, Trifonov V, Schiavoni G, Holmes A, Kern W, Martelli MP, Pucciarini A, Bigerna B, Pacini R, Wells VA, Sportoletti P, Pettirossi V, Mannucci R, Elliott O, Liso A, Ambrosetti A, Pulsoni A, Forconi F, Trentin L, Semenzato G, Inghirami G, Capponi M, Di Raimondo F, Patti C, Arcaini L, Musto P, Pileri S, Haferlach C, Schnittger S, Pizzolo G, Foa R, Farinelli L, Haferlach T, Pasqualucci L, Rabadan R, Falini B (2011) BRAF mutations in hairy-cell leukemia. N Engl J Med 364(24):2305–2315. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1014209
Brastianos PK, Taylor-Weiner A, Manley PE, Jones RT, Dias-Santagata D, Thorner AR, Lawrence MS, Rodriguez FJ, Bernardo LA, Schubert L, Sunkavalli A, Shillingford N, Calicchio ML, Lidov HG, Taha H, Martinez-Lage M, Santi M, Storm PB, Lee JY, Palmer JN, Adappa ND, Scott RM, Dunn IF, Laws ER Jr, Stewart C, Ligon KL, Hoang MP, Van Hummelen P, Hahn WC, Louis DN, Resnick AC, Kieran MW, Getz G, Santagata S (2014) Exome sequencing identifies BRAF mutations in papillary craniopharyngiomas. Nat Genet 46(2):161–165. doi:10.1038/ng.2868
Curtin JA, Fridlyand J, Kageshita T, Patel HN, Busam KJ, Kutzner H, Cho KH, Aiba S, Brocker EB, LeBoit PE, Pinkel D, Bastian BC (2005) Distinct sets of genetic alterations in melanoma. N Engl J Med 353(20):2135–2147. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa050092
Bhatia P, Friedlander P, Zakaria EA, Kandil E (2015) Impact of BRAF mutation status in the prognosis of cutaneous melanoma: an area of ongoing research. Ann Transl Med 3(2):24. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2305-5839.2014.12.05
Maurer G, Tarkowski B, Baccarini M (2011) Raf kinases in cancer-roles and therapeutic opportunities. Oncogene 30(32):3477–3488. doi:10.1038/onc.2011.160
Ascierto PA, Kirkwood JM, Grob JJ, Simeone E, Grimaldi AM, Maio M, Palmieri G, Testori A, Marincola FM, Mozzillo N (2012) The role of BRAF V600 mutation in melanoma. J Transl Med 10:85. doi:10.1186/1479-5876-10-85
Sakaizawa K, Ashida A, Uchiyama A, Ito T, Fujisawa Y, Ogata D, Matsushita S, Fujii K, Fukushima S, Shibayama Y, Hatta N, Takenouchi T, Uehara J, Okuyama R, Yamazaki N, Uhara H (2015) Clinical characteristics associated with BRAF, NRAS and KIT mutations in Japanese melanoma patients. J Dermatol Sci 80(1):33–37. doi:10.1016/j.jdermsci.2015.07.012
Fukushima T, Suzuki S, Mashiko M, Ohtake T, Endo Y, Takebayashi Y, Sekikawa K, Hagiwara K, Takenoshita S (2003) BRAF mutations in papillary carcinomas of the thyroid. Oncogene 22(41):6455–6457. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1206739
Ito Y, Yoshida H, Maruo R, Morita S, Takano T, Hirokawa M, Yabuta T, Fukushima M, Inoue H, Tomoda C, Kihara M, Uruno T, Higashiyama T, Takamura Y, Miya A, Kobayashi K, Matsuzuka F, Miyauchi A (2009) BRAF mutation in papillary thyroid carcinoma in a Japanese population: its lack of correlation with high-risk clinicopathological features and disease-free survival of patients. Endocr J 56(1):89–97
Namba H, Nakashima M, Hayashi T, Hayashida N, Maeda S, Rogounovitch TI, Ohtsuru A, Saenko VA, Kanematsu T, Yamashita S (2003) Clinical implication of hot spot BRAF mutation, V599E, in papillary thyroid cancers. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88(9):4393–4397. doi:10.1210/jc.2003-030305
Konishi K, Takimoto M, Kaneko K, Makino R, Hirayama Y, Nozawa H, Kurahashi T, Kumekawa Y, Yamamoto T, Ito H, Yoshikawa N, Kusano M, Nakayama K, Rembacken BJ, Ota H, Imawari M (2006) BRAF mutations and phosphorylation status of mitogen-activated protein kinases in the development of flat and depressed-type colorectal neoplasias. Br J Cancer 94(2):311–317. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6602911
Yokota T, Ura T, Shibata N, Takahari D, Shitara K, Nomura M, Kondo C, Mizota A, Utsunomiya S, Muro K, Yatabe Y (2011) BRAF mutation is a powerful prognostic factor in advanced and recurrent colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer 104(5):856–862. doi:10.1038/bjc.2011.19
Nakayama N, Nakayama K, Yeasmin S, Ishibashi M, Katagiri A, Iida K, Fukumoto M, Miyazaki K (2008) KRAS or BRAF mutation status is a useful predictor of sensitivity to MEK inhibition in ovarian cancer. Br J Cancer 99(12):2020–2028. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6604783
Eisen T, Ahmad T, Flaherty KT, Gore M, Kaye S, Marais R, Gibbens I, Hackett S, James M, Schuchter LM, Nathanson KL, Xia C, Simantov R, Schwartz B, Poulin-Costello M, O'Dwyer PJ, Ratain MJ (2006) Sorafenib in advanced melanoma: a phase II randomised discontinuation trial analysis. Br J Cancer 95(5):581–586. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6603291
Ott PA, Hamilton A, Min C, Safarzadeh-Amiri S, Goldberg L, Yoon J, Yee H, Buckley M, Christos PJ, Wright JJ, Polsky D, Osman I, Liebes L, Pavlick AC (2010) A phase II trial of sorafenib in metastatic melanoma with tissue correlates. PLoS One 5(12):e15588. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0015588
Su Y, Vilgelm AE, Kelley MC, Hawkins OE, Liu Y, Boyd KL, Kantrow S, Splittgerber RC, Short SP, Sobolik T, Zaja-Milatovic S, Dahlman KB, Amiri KI, Jiang A, Lu P, Shyr Y, Stuart DD, Levy S, Sosman JA, Richmond A (2012) RAF265 inhibits the growth of advanced human melanoma tumors. Clin Cancer Res 18(8):2184–2198. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-11-1122
Chapman PB, Hauschild A, Robert C, Haanen JB, Ascierto P, Larkin J, Dummer R, Garbe C, Testori A, Maio M, Hogg D, Lorigan P, Lebbe C, Jouary T, Schadendorf D, Ribas A, O'Day SJ, Sosman JA, Kirkwood JM, Eggermont AM, Dreno B, Nolop K, Li J, Nelson B, Hou J, Lee RJ, Flaherty KT, McArthur GA (2011) Improved survival with vemurafenib in melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation. N Engl J Med 364(26):2507–2516. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1103782
Sosman JA, Kim KB, Schuchter L, Gonzalez R, Pavlick AC, Weber JS, McArthur GA, Hutson TE, Moschos SJ, Flaherty KT, Hersey P, Kefford R, Lawrence D, Puzanov I, Lewis KD, Amaravadi RK, Chmielowski B, Lawrence HJ, Shyr Y, Ye F, Li J, Nolop KB, Lee RJ, Joe AK, Ribas A (2012) Survival in BRAF V600-mutant advanced melanoma treated with vemurafenib. N Engl J Med 366(8):707–714. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1112302
Falchook GS, Long GV, Kurzrock R, Kim KB, Arkenau TH, Brown MP, Hamid O, Infante JR, Millward M, Pavlick AC, O'Day SJ, Blackman SC, Curtis CM, Lebowitz P, Ma B, Ouellet D, Kefford RF (2012) Dabrafenib in patients with melanoma, untreated brain metastases, and other solid tumours: a phase 1 dose-escalation trial. Lancet 379(9829):1893–1901. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(12)60398-5
Hauschild A, Grob JJ, Demidov LV, Jouary T, Gutzmer R, Millward M, Rutkowski P, Blank CU, Miller WH Jr, Kaempgen E, Martin-Algarra S, Karaszewska B, Mauch C, Chiarion-Sileni V, Martin AM, Swann S, Haney P, Mirakhur B, Guckert ME, Goodman V, Chapman PB (2012) Dabrafenib in BRAF-mutated metastatic melanoma: a multicentre, open-label, phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet 380(9839):358–365. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(12)60868-x
Long GV, Trefzer U, Davies MA, Kefford RF, Ascierto PA, Chapman PB, Puzanov I, Hauschild A, Robert C, Algazi A, Mortier L, Tawbi H, Wilhelm T, Zimmer L, Switzky J, Swann S, Martin AM, Guckert M, Goodman V, Streit M, Kirkwood JM, Schadendorf D (2012) Dabrafenib in patients with Val600Glu or Val600Lys BRAF-mutant melanoma metastatic to the brain (BREAK-MB): a multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 13(11):1087–1095. doi:10.1016/s1470-2045(12)70431-x
King AJ, Arnone MR, Bleam MR, Moss KG, Yang J, Fedorowicz KE, Smitheman KN, Erhardt JA, Hughes-Earle A, Kane-Carson LS, Sinnamon RH, Qi H, Rheault TR, Uehling DE, Laquerre SG (2013) Dabrafenib; preclinical characterization, increased efficacy when combined with trametinib, while BRAF/MEK tool combination reduced skin lesions. PLoS One 8(7):e67583. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0067583
Flaherty KT, Infante JR, Daud A, Gonzalez R, Kefford RF, Sosman J, Hamid O, Schuchter L, Cebon J, Ibrahim N, Kudchadkar R, Burris HA 3rd, Falchook G, Algazi A, Lewis K, Long GV, Puzanov I, Lebowitz P, Singh A, Little S, Sun P, Allred A, Ouellet D, Kim KB, Patel K, Weber J (2012) Combined BRAF and MEK inhibition in melanoma with BRAF V600 mutations. N Engl J Med 367(18):1694–1703. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1210093
Welsh SJ, Corrie PG (2015) Management of BRAF and MEK inhibitor toxicities in patients with metastatic melanoma. Ther Adv Med Oncol 7(2):122–136. doi:10.1177/1758834014566428
Long GV, Stroyakovskiy D, Gogas H, Levchenko E, de Braud F, Larkin J, Garbe C, Jouary T, Hauschild A, Grob JJ, Chiarion Sileni V, Lebbe C, Mandala M, Millward M, Arance A, Bondarenko I, Haanen JB, Hansson J, Utikal J, Ferraresi V, Kovalenko N, Mohr P, Probachai V, Schadendorf D, Nathan P, Robert C, Ribas A, DeMarini DJ, Irani JG, Casey M, Ouellet D, Martin AM, Le N, Patel K, Flaherty K (2014) Combined BRAF and MEK inhibition versus BRAF inhibition alone in melanoma. N Engl J Med 371(20):1877–1888. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1406037
Chu EY, Wanat KA, Miller CJ, Amaravadi RK, Fecher LA, Brose MS, McGettigan S, Giles LR, Schuchter LM, Seykora JT, Rosenbach M (2012) Diverse cutaneous side effects associated with BRAF inhibitor therapy: a clinicopathologic study. J Am Acad Dermatol 67(6):1265–1272. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2012.04.008
Ascierto PA, Minor D, Ribas A, Lebbe C, O'Hagan A, Arya N, Guckert M, Schadendorf D, Kefford RF, Grob JJ, Hamid O, Amaravadi R, Simeone E, Wilhelm T, Kim KB, Long GV, Martin AM, Mazumdar J, Goodman VL, Trefzer U (2013) Phase II trial (BREAK-2) of the BRAF inhibitor dabrafenib (GSK2118436) in patients with metastatic melanoma. J Clin Oncol 31(26):3205–3211. doi:10.1200/jco.2013.49.8691
Scholtens A, Geukes Foppen MH, Blank CU, van Thienen JV, van Tinteren H, Haanen JB (2015) Vemurafenib for BRAF V600 mutated advanced melanoma: results of treatment beyond progression. Eur J Cancer 51(5):642–652. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2015.01.009
Menzies AM, Long GV, Murali R (2012) Dabrafenib and its potential for the treatment of metastatic melanoma. Drug Des Devel Ther 6:391–405. doi:10.2147/dddt.s38998
Bollag G, Hirth P, Tsai J, Zhang J, Ibrahim PN, Cho H, Spevak W, Zhang C, Zhang Y, Habets G, Burton EA, Wong B, Tsang G, West BL, Powell B, Shellooe R, Marimuthu A, Nguyen H, Zhang KY, Artis DR, Schlessinger J, Su F, Higgins B, Iyer R, D'Andrea K, Koehler A, Stumm M, Lin PS, Lee RJ, Grippo J, Puzanov I, Kim KB, Ribas A, McArthur GA, Sosman JA, Chapman PB, Flaherty KT, Xu X, Nathanson KL, Nolop K (2010) Clinical efficacy of a RAF inhibitor needs broad target blockade in BRAF-mutant melanoma. Nature 467(7315):596–599. doi:10.1038/nature09454
Kefford R, Arkenau H, Brown MP, et al (2010) Phase I/II study of GSK2118436, a selective inhibitor of oncogenic mutant BRAF kinase, in patients with metastatic melanoma and other solid tumors. J Clin Oncol 28 (S611):abstract 8503
Yoichi Moroi (2013) Patient Surveillance After Cancer Treatment,vol 1. doi:10.1007/978-1-60327-969-7_52
Acknowledgements
The study was funded by GlaxoSmithKline. Dabrafenib is an asset of Novartis AG as of March 2, 2015. We thank all the investigators and patients who participated in the study, their families as well as staff at the study centers. We also thank Dr. Krishna Swetha Gummuluri, Novartis Healthcare Pvt. Ltd., India, for medical writing support.
Funding
GlaxoSmithkline
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All of the authors had full access to data in the study, discussed the results, critically reviewed the draft manuscript, and approved the final manuscript for submission
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Y Fujiwara reports grants from AstraZeneca, Chugai, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eisai, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck Serono, MSD and Novartis; and honoraria and personal fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb and ONO. N Yamazaki reports personal fees from ONO, Takeda, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Chugai, Boehringer Ingelheim and research funding from ONO, Bristol-Myers Squibb and Novartis Pharma K.K. Y Kiyohara reports personal fees from ONO, Chugai, Bristol-Myers Squibb and grants from Chugai and MSD. N Yamamoto reports grants from Chugai,Taiho, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Quintiles, Astellas, BMS, Novartis, Daiichi-Sankyo, Pfizer,Boehringer Ingelheim, Kyowa-Hakko Kirin, Bayer, ONO and Takeda and other support from Chugai, Astrazeneca, Eli Lilly and BMS. H Nokihara reports grants from Merck Serono, Pfizer, Novartis, Daiichi Sankyo, GlaxoSmithKline and Quintiles and personal fees from Taiho Pharmaceuticals, Eisai, Chugai, Eli Lilly, AstraZeneca, Boehringer-Ingelheim,ONO, Sanofi and Bristol-Myers Squibb. K Namikawa reports personal fees from ONO, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp and Dohme, Toray Industries, Chugai and Novartis Pharmaceuticals. T Tamura reports personal fees from Chugai, Taiho, Eisai, Yakult, Eli Lilly, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, ONO and Kyowa Kirin. A Mukaiyama and F Zhang are employees of Novartis Pharma K.K., Japan. S Yoshikawa, and A Tsutsumida have nothing to disclose.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in the study were conducted in accordance with the International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) Guidelines for Good Clinical Practice (GCP) and the Declaration of Helsinki. All protocols and amendments were approved by the independent ethics committee or institutional review board for each study center. All patients provided written informed consent before participating in any study procedures.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujiwara, Y., Yamazaki, N., Kiyohara, Y. et al. Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetic profile of dabrafenib in Japanese patients with BRAF V600 mutation-positive solid tumors: a phase 1 study. Invest New Drugs 36, 259–268 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-017-0502-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-017-0502-8