Abstract
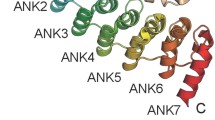
Gankyrin is an oncoprotein that plays a central role in the development of cancer. Although researchers have increasingly focused on the relationships of gankyrin with carcinogenesis, metastasis and prognosis of different cancers, the molecular mechanisms are still unclear. In recent years, several interacting partners of gankyrin and cell signaling pathways regulated by gankyrin have been elucidated. In addition, accumulating evidence has indicated the contribution of microRNAs to regulating gankyrin expression in tumor cells. In this review, we summarize the major known roles of gankyrin in cancer cells and highlight the potential clinical relevance of targeting gankyrin.

ᅟ




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang C, Yuan X, Zhang Y (2016) The co-expression of GPER and Gankyrin in ovarian endometriosis and its correlation with the rASRM stages. Arch Gynecol Obstet 293:133–141. doi:10.1007/s00404-015-3807-x
Zhao X, Liu F, Zhang Y et al (2016) Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of Gankyrin overexpression in cancers: evidence from a meta-analysis. Onco Targets Ther 9:1961–1968. doi:10.2147/OTT.S101687
Nakamura Y, Umehara T, Tanaka A et al (2007) Purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of the non-ATPase subunit Nas6 in complex with the ATPase subunit Rpt3 of the 26S proteasome from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun 63:190–192. doi:10.1107/S1744309107004848
Gao L, Xie H, Dong L et al (2014) Gankyrin is essential for hypoxia enhanced metastatic potential in breast cancer cells. Mol Med Rep 9:1032–1036. doi:10.3892/mmr.2013.1860
Kim KH, Lim HJ, Kim YJ et al (2014) The oncoprotein, gankyrin, is up-regulated in middle ear cholesteatoma. Acta Otolaryngol 134:238–243. doi:10.3109/00016489
Nanaware PP, Ramteke MP, Somavarapu AK et al (2014) Discovery of multiple interacting partners of gankyrin, a proteasomal chaperone and an oncoprotein--evidence for a common hot spot site at the interface and its functional relevance. Proteins 82:1283–1300. doi:10.1002/prot.24494
Nakamura Y, Nakano K, Umehara T et al (2007) Structure of the oncoprotein gankyrin in complex with S6 ATPase of the 26S proteasome. Structure 15:179–189. doi:10.1016/j.str.2006.11.015
Nakamura Y, Umehara T, Tanaka A et al (2007) Structural basis for the recognition between the regulatory particles Nas6 and Rpt3 of the yeast 26S proteasome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 359:503–509. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.05.138
Dawson S, Higashitsuji H, Wilkinson AJ et al (2006) Gankyrin: a new oncoprotein and regulator of pRb and p53. Trends Cell Biol 16:229–233. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2006.03.001
Mayer RJ, Fujita J (2006) Gankyrin, the 26 S proteasome, the cell cycle and cancer. Biochem Soc Trans 34:746–748. doi:10.1042/BST0340746
Dawson S, Apcher S, Mee M et al (2002) Gankyrin is an ankyrin-repeat oncoprotein that interacts with CDK4 kinase and the S6 ATPase of the 26 S proteasome. J Biol Chem 277:10893–10902. doi:10.1074/jbc.M107313200
Higashitsuji H, Higashitsuji H, Itoh K et al (2005) The oncoprotein gankyrin binds to MDM2/HDM2, enhancing ubiquitylation and degradation of p53. Cancer Cell 8:75–87. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2005.06.006
Lozano G, Zambetti GP (2005) Gankyrin: an intriguing name for a novel regulator of p53 and RB. Cancer Cell 8:3–4. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2005.06.014
Sun W, Ding J, Wu K et al (2011) Gankyrin-mediated dedifferentiation facilitates the tumorigenicity of rat hepatocytes and hepatoma cells. Hepatology 54:1259–1272. doi:10.1002/hep.24530
Luo T, Fu J, Xu A (2015) PSMD10/gankyrin induces autophagy to promote tumor progression through cytoplasmic interaction with ATG7 and nuclear transactivation of ATG7 expression. Autophagy 23:1–17. doi:10.1080/15548627
Yang C, Tan YX, Yang GZ et al (2016) Gankyrin has an antioxidative role through the feedback regulation of Nrf2 in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Exp Med 213:859–875. doi:10.1084/jem.20151208
Iakova P, Timchenko L, Timchenko NA (2011) Intracellular signaling and hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Cancer Biol 21:28–34. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer
Zheng T, Hong X, Wang J et al (2014) Gankyrin promotes tumor growth and metastasis through activation of IL-6/STAT3 signaling in human cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology 59:935–946. doi:10.1002/hep.26705
Dong LW, Yang GZ, Pan YF et al (2011) The oncoprotein p28GANK establishes a positive feedback loop in beta-catenin signaling. Cell Res 21:1248–1261. doi:10.1038/cr.2011.103
Li J, Tian F, Li D et al (2014) MiR-605 represses PSMD10/Gankyrin and inhibits intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cell progression. FEBS Lett 588:3491–3500. doi:10.1016/j.febslet
Liu Y, Xu J, Jiang M et al (2015) Association between functional PSMD10 Rs111638916 variant regulated by MiR-505 and gastric cancer risk in a Chinese population. Cell Physiol Biochem 37:1010–1017. doi:10.1159/000430227
Higashitsuji H, Liu Y, Mayer RJ et al (2005) The oncoprotein gankyrin negatively regulates both p53 and RB by enhancing proteasomal degradation. Cell Cycle 4:1335–1337. doi:10.4161/cc.4.10.2107
Li J, Knobloch TJ, Kresty LA et al (2011) Gankyrin, a biomarker for epithelial carcinogenesis, is overexpressed in human oral cancer. Anticancer Res 31:2683–2692
Jing H, Zhang G, Meng L et al (2014) Gradually elevated expression of Gankyrin during human hepatocarcinogenesis and its clinicopathological significance. Sci Rep 4:5503. doi:10.1038/srep05503
Wang WP, Yan XL, Li WM et al (2015) Clinicopathologic features and prognostic implications of Gankyrin protein expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Pathol Res Pract 211:939–947. doi:10.1016/j.prp.2015.09.010
Liu Y, Zhang J, Qian W et al (2014) Gankyrin is frequently overexpressed in cervical high grade disease and is associated with cervical carcinogenesis and metastasis. PLoS One 9:e95043. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0095043
Umemura A, Itoh Y, Itoh K et al (2008) Association of gankyrin protein expression with early clinical stages and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 5 expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 47:493–502. doi:10.1002/hep.22027
Qiu W, Wu J, Walsh EM et al (2008) Retinoblastoma protein modulates gankyrin-MDM2 in regulation of p53 stability and chemosensitivity in cancer cells. Oncogene 27:4034–4043. doi:10.1038/onc.2008.43
Fu J, Chen Y, Cao J et al (2011) p28GANK overexpression accelerates hepatocellular carcinoma invasiveness and metastasis via phosphoinositol 3-kinase/AKT/hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha pathways. Hepatology 53:181–192. doi:10.1002/hep.24015
Ferraiuolo M, Di Agostino S, Blandino G et al (2016) Oncogenic intra-p53 family member interactions in human cancers. Front Oncol 6:77. doi:10.3389/fonc.2016.00077
Chuang LS, Ito K, Ito Y (2013) RUNX family: regulation and diversification of roles through interacting proteins. Int J Cancer 132:1260–1271. doi:10.1002/ijc.27964
He W, Wang X, Chen L et al (2012) A crosstalk imbalance between p27(Kip1) and its interacting molecules enhances breast carcinogenesis. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 27:399–402. doi:10.1089/cbr.2010.0802
Krzywda S, Brzozowski AM, Higashitsuji H et al (2004) The crystal structure of gankyrin, an oncoprotein found in complexes with cyclin-dependent kinase 4, a 19 S proteasomal ATPase regulator, and the tumor suppressors Rb and p53. J Biol Chem 279:1541–1545. doi:10.1074/jbc.M310265200
Chapman AM, Rogers BE, McNaughton BR (2014) Characterization of the binding interaction between the oncoprotein gankyrin and a grafted S6 ATPase. Biochemistry 53:6857–6859. doi:10.1021/bi5012354
Gasparini C, Celeghini C, Monasta L et al (2014) NF-kappaB pathways in hematological malignancies. Cell Mol Life Sci 71:2083–2102. doi:10.1007/s00018-013-1545-4
Lu X, Yarbrough WG (2015) Negative regulation of RelA phosphorylation: emerging players and their roles in cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 26:7–13. doi:10.1016/j.cytogfr.2014.09.003
Jakkampudi A, Jangala R, Reddy BR et al (2016) NF-kappaB in acute pancreatitis: mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Pancreatology 16:477–488. doi:10.1016/j.pan.2016.05.001
Chen Y, Li HH, Fu J et al (2007) Oncoprotein p28 GANK binds to RelA and retains NF-kappaB in the cytoplasm through nuclear export. Cell Res 17:1020–1029. doi:10.1038/cr.2007.99
Higashitsuji H, Higashitsuji H, Liu Y et al (2007) The oncoprotein gankyrin interacts with RelA and suppresses NF-kappaB activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 363:879–884. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.09.072
Yamagata K (2014) Roles of HNF1alpha and HNF4alpha in pancreatic beta-cells: lessons from a monogenic form of diabetes (MODY). Vitam Horm 95:407–423. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-800174-5.00016-8
Walesky C, Apte U (2015) Role of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha (HNF4alpha) in cell proliferation and cancer. Gene Expr 16:101–108. doi:10.3727/105221615X14181438356292
Watson AS, Mortensen M, Simon AK (2011) Autophagy in the pathogenesis of myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia. Cell Cycle 10:1719–1725. doi:10.4161/cc.10.11.15673
Cui J, Gong Z, Shen HM (2013) The role of autophagy in liver cancer: molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. Biochim Biophys Acta 1836:15–26. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2013.02.003
Subramani S, Malhotra V (2013) Non-autophagic roles of autophagy-related proteins. EMBO Rep 14:143–151. doi:10.1038/embor.2012.220
Kim J, Keum YS (2016) NRF2, a key regulator of antioxidants with two faces towards cancer. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2016:2746457. doi:10.1155/2016/2746457
Lu MC, Ji JA, Jiang ZY et al (2016) The Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway as a potential preventive and therapeutic target: an update. Med Res Rev 36:924–963. doi:10.1002/med.21396
Menegon S, Columbano A, Giordano S (2016) The dual roles of NRF2 in cancer. Trends Mol Med 22:578–593. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2016.05.002
Wang X, Jiang B, Zhang Y (2016) Gankyrin regulates cell signaling network. Tumour Biol 37:5675–5682. doi:10.1007/s13277-016-4854-z
Pei T, Li Y, Wang J et al (2015) YAP is a critical oncogene in human cholangiocarcinoma. Oncotarget 6:17206–17220. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.4043
Zhao X, Fu J, Xu A et al (2015) Gankyrin drives malignant transformation of chronic liver damage-mediated fibrosis via the Rac1/JNK pathway. Cell Death Dis 6:e1751. doi:10.1038/cddis.2015.120
Chen J, Bai M, Ning C et al (2016) Gankyrin facilitates follicle-stimulating hormone-driven ovarian cancer cell proliferation through the PI3K/AKT/HIF-1alpha/cyclin D1 pathway. Oncogene 35:2506–2517. doi:10.1038/onc.2015.316
Qin X, Wang X, Liu F et al (2016) Gankyrin activates mTORC1 signaling by accelerating TSC2 degradation in colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett 376:83–94. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2016.03.013
Sun S, Irvine KD (2016) Cellular organization and cytoskeletal regulation of the Hippo signaling network. Trends Cell Biol 26:694–704. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2016.05.003
Kang W, Cheng AS, Yu J et al (2016) Emerging role of Hippo pathway in gastric and other gastrointestinal cancers. World J Gastroenterol 22:1279–1288. doi:10.3748/wjg.v22.i3.1279
Xiao Y, Leach J, Wang J et al (2016) Hippo/yap signaling in cardiac development and regeneration. Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med 18:38. doi:10.1007/s11936-016-0461-y
Yarza R, Vela S, Solas M et al (2015) C-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling as a therapeutic target for Alzheimer's disease. Front Pharmacol 6:321. doi:10.3389/fphar.2015.00321
Yan D, An G, Kuo MT (2016) C-Jun N-terminal kinase signalling pathway in response to cisplatin. J Cell Mol Med 20:2013–2019. doi:10.1111/jcmm.12908
Yang SX, Polley E, Lipkowitz S (2016) New insights on PI3K/AKT pathway alterations and clinical outcomes in breast cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 45:87–96. doi:10.1016/j.ctrv.2016.03.004
Robbins HL, Hague A (2015) The PI3K/Akt pathway in tumors of endocrine tissues. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 6:188. doi:10.3389/fendo.2015.00188
Singh SS, Yap WN, Arfuso F et al (2015) Targeting the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in gastric carcinoma: a reality for personalized medicine? World J Gastroenterol 21:12261–12273. doi:10.3748/wjg.v21.i43.12261
Zhang J, Yang Y, Zhang Z et al (2013) Gankyrin plays an essential role in estrogen-driven and GPR30-mediated endometrial carcinoma cell proliferation via the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Cancer Lett 339:279–287. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2012.10.037
Ren W, Yin J, Duan J et al (2016) mTORC1 signaling and IL-17 expression: defining pathways and possible therapeutic targets. Eur J Immunol 46:291–299. doi:10.1002/eji.201545886
Wang X, Chu Y, Wang W et al (2016) mTORC signaling in hematopoiesis. Int J Hematol 103:510–518. doi:10.1007/s12185-016-1944-z
Armijo ME, Campos T, Fuentes-Villalobos F et al (2016) Rheb signaling and tumorigenesis: mTORC1 and new horizons. Int J Cancer 138:1815–1823. doi:10.1002/ijc.29707
Song S, Ajani JA (2013) The role of microRNAs in cancers of the upper gastrointestinal tract. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 10:109–118. doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2012.210
Nugent M (2015) microRNA and bone cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol 889:201–230. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-23730-5_11
Rachagani S, Macha MA, Heimann N et al (2015) Clinical implications of miRNAs in the pathogenesis, diagnosis and therapy of pancreatic cancer. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 81:16–33. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2014.10.020
Her GM, Hsu CC, Hong JR et al (2011) Overexpression of gankyrin induces liver steatosis in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Biochim Biophys Acta 1811:536–548. doi:10.1016/j.bbalip.2011.06.011
Misiewicz-Krzeminska I, Sarasquete ME, Quwaider D et al (2013) Restoration of microRNA-214 expression reduces growth of myeloma cells through positive regulation of P53 and inhibition of DNA replication. Haematologica 98:640–648. doi:10.3324/haematol.2012.070011
Thakur PK, Hassan I (2011) Discovering a potent small molecule inhibitor for gankyrin using de novo drug design approach. Int J Comput Biol Drug Des 4:373–386. doi:10.1504/IJCBDD.2011.044404
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors confirm that they have no conflict of interest with the content of this article.
Funding
This work is supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (1708085QH215) and the Foundation of Anhui Medical University (2015xkj034) to Li Cheng.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain studies with human participants or animals.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Cheng, L. Gankyrin as a potential therapeutic target for cancer. Invest New Drugs 35, 655–661 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-017-0474-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-017-0474-8