Summary
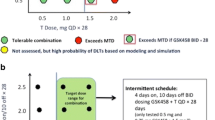
Purpose We previously reported the phase I dose escalation study of buparlisib, a pan-class 1A PI3K inhibitor, combined with platinum/taxane-based chemotherapy in patients with advanced solid tumors. The combination was well tolerated and promising preliminary efficacy was observed in PTEN deficient tumors. This phase I dose expansion study now evaluates buparlisib plus high dose carboplatin and paclitaxel in unselected patients with advanced solid tumors and buparlisib plus standard dose carboplatin and paclitaxel in patients with PTEN deficient tumors (ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT01297452). Methods There were two expansion cohorts: Cohort A received continuous buparlisib (100 mg/daily) orally plus high dose carboplatin AUC 6 and paclitaxel 200 mg/m2; Cohort B treated patients with PTEN deficient tumors only and they received the recommended phase II dose (RP2D) of continuous buparlisib (100 mg/daily) orally plus standard dose carboplatin AUC 5 and paclitaxel 175 mg/m2. Both cohorts received chemotherapy intravenously on day 1 of the 21-day cycle with pegfilgrastim support. Primary endpoint in Cohort A was to evaluate the safety and tolerability of chemotherapy dose intensification with buparlisib and in Cohort B was to describe preliminary efficacy of the combination among patients with tumors harboring a PTEN mutation or homozygous deletion. Results 14 subjects were enrolled, 7 in Cohort A and 7 in Cohort B. Dose reductions were required in 5 (71%) and 3 (43%) patients, in cohort A and B respectively. Grade 3 adverse events in Cohort A included lymphopenia (n = 5 [71%]), hyperglycemia (n = 2, [29%]), diarrhea (n = 2, [29%]) and rash (n = 2, [29%]) and in cohort B included lymphopenia (n = 5 [71%]), hyperglycemia (n = 4 [57%]) and neutropenia (n = 2 [29%]. The mean number of cycles on protocol was 6. The overall objective response rate was 14% (2 /14). No objective responses were observed in the PTEN deficient cohort. Four out of 6 patients with stable disease (SD) had SD or better for ≥6 cycles, 2 of which had PTEN deficient tumors. Conclusion The addition of buparlisib to high dose carboplatin and paclitaxel was not tolerable. The combination did not reveal significant clinical activity amongst a small and heterogenous group of PTEN deficient tumors,
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Engelman JA (2009) Targeting pi3k signalling in cancer: opportunities, challenges, and limitations. Nat Rev Cancer 9(8):550–562
Samuels Y, Wang Z, Bardelli A, Silliman N, Ptak J, Szabo S, Yan H, Gazdar A, Powell SM, Riggins GJ, Willson JKV et al (2004) High frequency of mutations of pik3ca gene in human cancers. Science 304:554
Sansal I, Sellers WR (2004) The biology and clinical relevance of the pten tumor suppressor pathway. J Clin Oncol 22:2954–2963
Vivanco I, Sawyers CL (2002) The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-akt pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2(7):489–501
Dillon LM, Miller TW (2014) Therapeutic targeting of cancers with loss of pten function. Curr Drug Targets 15(1):65–79
Planchon SM, Waite KA, Eng C (2008) The nuclear affairs of pten. J Cell Sci 121(Pt 3):249–253
Yin Y, Shen WH (2008) Pten: a new guardian of the genome. Oncogene 27(41):5443–5453
Song MS, Salmena L, Pandolfi PP (2012) The functions and regulation of the pten tumour suppressor. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13(5):283–296
Goldbrunner M BKM120 Investigator's Brochure, Edition 1, 09-Sep-2008
Maira SM, Pecchi S, Huang A, Burger M, Knapp M, Sterker D, Schnell C, Guthy D, Nagel T, Wiesmann M, Brachmann S et al (2012) Identification and characterization of nvp-bkm120, an orally available pan-class i pi3-kinase inhibitor. Mol Cancer Ther 11(2):317–328
Bendell JC, Rodon J, Burris HA, de Jonge M, Verweij J, Birle D, Demanse D, De Buck SS, Ru QC, Peters M, Goldbrunner M et al (2012) Phase i, dose-escalation study of bkm120, an oral pan-class i pi3k inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol 30(3):282–290
Vansteenkiste JF, Canon JL, De Braud F, Grossi F, De Pas T, Gray JE, Su WC, Felip E, Yoshioka H, Gridelli C, Dy GK et al (2015) Safety and efficacy of buparlisib (bkm120) in patients with pi3k pathway-activated non-small cell lung cancer (nsclc): results from the phase ii basalt-1 study. J Thorac Oncol 10(9):1319–1327
Ando Y, Inada-Inoue M, Mitsuma A, Yoshino T, Ohtsu A, Suenaga N, Sato M, Kakizume T, Robson M, Quadt C, Doi T (2014) Phase i dose-escalation study of buparlisib (bkm120), an oral pan-class i pi3k inhibitor, in japanese patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Sci 105(3):347–353
Saura C, Bendell J, Jerusalem G, Su S, Ru Q, De Buck S, Mills D, Ruquet S, Bosch A, Urruticoechea A, Beck JT et al (2014) Phase ib study of buparlisib plus trastuzumab in patients with her2-positive advanced or metastatic breast cancer that has progressed on trastuzumab-based therapy. Clin Cancer Res 20(7):1935–1945
Mayer IA, Abramson VG, Isakoff SJ, Forero A, Balko JM, Kuba MG, Sanders ME, Yap JT, Van den Abbeele AD, Li Y, Cantley LC et al (2014) Stand up to cancer phase ib study of pan-phosphoinositide-3-kinase inhibitor buparlisib with letrozole in estrogen receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 32(12):1202–1209
Ihle NT, Williams R, Chow S, Chew W, Berggren MI, Paine-Murrieta G, Minion DJ, Halter RJ, Wipf P, Abraham R, Kirkpatrick L et al (2004) Molecular pharmacology and antitumor activity of px-866, a novel inhibitor of phosphoinositide-3-kinase signaling. Mol Cancer Ther 3(7):763–772
Hu L, Hofmann J, Lu Y, Mills GB, Jaffe RB (2002) Inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase increases efficacy of paclitaxel in in vitro and in vivo ovarian cancer models. Cancer Res 62(4):1087–1092
Hyman DM, Snyder AE, Carvajal RD, Gerecitano JF, Voss MH, Ho AL, Konner J, Winkelmann JL, Stasi MA, Monson KR, Iasonos A et al (2015) Parallel phase ib studies of two schedules of buparlisib (bkm120) plus carboplatin and paclitaxel (q21 days or q28 days) for patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 75(4):747–755
Wee S, Wiederschain D, Maira SM, Loo A (2008) Miller C, deBeaumont R, Stegmeier F, Yao YM, Lengauer C: Pten-deficient cancers depend on pik3cb. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(35):13057–13062
Jia S, Liu Z, Zhang S, Liu P, Zhang L, Lee SH, Zhang J, Signoretti S, Loda M, Roberts TM, Zhao JJ (2008) Essential roles of pi(3)k-p110beta in cell growth, metabolism and tumorigenesis. Nature 454(7205):776–779
Bassi C, Ho J, Srikumar T, Dowling RJ, Gorrini C, Miller SJ, Mak TW, Neel BG, Raught B, Stambolic V (2013) Nuclear pten controls DNA repair and sensitivity to genotoxic stress. Science (New York, NY) 341(6144):395–399
Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JB (2001) The phq-9: validity of a brief depression severity measure. J Gen Intern Med 16(9):606–613
Spitzer RL, Kroenke K, Williams JB, Lowe B (2006) A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: the gad-7. Arch Intern Med 166(10):1092–1097
Wagle N, Berger MF, Davis MJ, Blumenstiel B, Defelice M, Pochanard P, Ducar M, Van Hummelen P, Macconaill LE, Hahn WC, Meyerson M et al (2012) High-throughput detection of actionable genomic alterations in clinical tumor samples by targeted, massively parallel sequencing. Cancer Discov 2(1):82–93
Vakiani E, Janakiraman M, Shen R, Sinha R, Zeng Z, Shia J, Cercek A, Kemeny N, D'Angelica M, Viale A, Heguy A et al (2012) Comparative genomic analysis of primary versus metastatic colorectal carcinomas. J Clin Oncol 30(24):2956–2962
Janakiraman M, Vakiani E, Zeng Z, Pratilas CA, Taylor BS, Chitale D, Halilovic E, Wilson M, Huberman K, Ricarte Filho JC, Persaud Y et al (2010) Genomic and biological characterization of exon 4 kras mutations in human cancer. Cancer Res 70(14):5901–5911
Reidy DL, Vakiani E, Fakih MG, Saif MW, Hecht JR, Goodman-Davis N, Hollywood E, Shia J, Schwartz J, Chandrawansa K, Dontabhaktuni A et al (2010) Randomized, phase ii study of the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor inhibitor imc-a12, with or without cetuximab, in patients with cetuximab- or panitumumab-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 28(27):4240–4246
Sakr RA, Barbashina V, Morrogh M, Chandarlapaty S, Andrade VP, Arroyo CD, Olvera N, King TA (2010) Protocol for pten expression by immunohistochemistry in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded human breast carcinoma. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 18(4):371–374
Wong KM, Capasso A, Eckhardt SG (2016) The changing landscape of phase i trials in oncology. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 13(2):106–117
Ivy SP, Siu LL, Garrett-Mayer E, Rubinstein L (2010) Approaches to phase 1 clinical trial design focused on safety, efficiency, and selected patient populations: a report from the clinical trial design task force of the national cancer institute investigational drug steering committee. Clin Cancer Res 16(6):1726–1736
Nagata Y, Lan KH, Zhou X, Tan M, Esteva FJ, Sahin AA, Klos KS, Li P, Monia BP, Nguyen NT, Hortobagyi GN et al (2004) Pten activation contributes to tumor inhibition by trastuzumab, and loss of pten predicts trastuzumab resistance in patients. Cancer Cell 6(2):117–127
Berns K, Horlings HM, Hennessy BT, Madiredjo M, Hijmans EM, Beelen K, Linn SC, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Stemke-Hale K, Hauptmann M, Beijersbergen RL et al (2007) A functional genetic approach identifies the pi3k pathway as a major determinant of trastuzumab resistance in breast cancer. Cancer Cell 12(4):395–402
Saal LH, Johansson P, Holm K, Gruvberger-Saal SK, She QB, Maurer M, Koujak S, Ferrando AA, Malmstrom P, Memeo L, Isola J et al (2007) Poor prognosis in carcinoma is associated with a gene expression signature of aberrant pten tumor suppressor pathway activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(18):7564–7569
Stemke-Hale K, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Lluch A, Neve RM, Kuo WL, Davies M, Carey M, Hu Z, Guan Y, Sahin A, Symmans WF et al (2008) An integrative genomic and proteomic analysis of pik3ca, pten, and akt mutations in breast cancer. Cancer Res 68(15):6084–6091
Razis E, Bobos M, Kotoula V, Eleftheraki AG, Kalofonos HP, Pavlakis K, Papakostas P, Aravantinos G, Rigakos G, Efstratiou I, Petraki K et al (2011) Evaluation of the association of pik3ca mutations and pten loss with efficacy of trastuzumab therapy in metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 128(2):447–456
Esteva FJ, Guo H, Zhang S, Santa-Maria C, Stone S, Lanchbury JS, Sahin AA, Hortobagyi GN, Yu D (2010) Pten, pik3ca, p-akt, and p-p70s6k status: association with trastuzumab response and survival in patients with her2-positive metastatic breast cancer. Am J Pathol 177(4):1647–1656
Dave B, Migliaccio I, Gutierrez MC, Wu MF, Chamness GC, Wong H, Narasanna A, Chakrabarty A, Hilsenbeck SG, Huang J, Rimawi M et al (2011) Loss of phosphatase and tensin homolog or phosphoinositol-3 kinase activation and response to trastuzumab or lapatinib in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-overexpressing locally advanced breast cancers. J Clin Oncol 29(2):166–173
Morrow PK, Wulf GM, Ensor J, Booser DJ, Moore JA, Flores PR, Xiong Y, Zhang S, Krop IE, Winer EP, Kindelberger DW et al (2011) Phase i/ii study of trastuzumab in combination with everolimus (rad001) in patients with her2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer who progressed on trastuzumab-based therapy. J Clin Oncol 29(23):3126–3132
Shen Y, Yang J, Xu Z, Gu DY, Chen JF (2012) Phosphatase and tensin homolog expression related to cetuximab effects in colorectal cancer patients: a meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol 18(21):2712–2718
Loupakis F, Pollina L, Stasi I, Ruzzo A, Scartozzi M, Santini D, Masi G, Graziano F, Cremolini C, Rulli E, Canestrari E et al (2009) Pten expression and kras mutations on primary tumors and metastases in the prediction of benefit from cetuximab plus irinotecan for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 27(16):2622–2629
Edgar KA, Wallin JJ, Berry M, Lee LB, Prior WW, Sampath D, Friedman LS, Belvin M (2010) Isoform-specific phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitors exert distinct effects in solid tumors. Cancer Res 70(3):1164–1172
Ni J, Liu Q, Xie S, Carlson C, Von T, Vogel K, Riddle S, Benes C, Eck M, Roberts T, Gray N et al (2012) Functional characterization of an isoform-selective inhibitor of pi3k-p110beta as a potential anticancer agent. Cancer Discov 2(5):425–433
Chen H, Mei L, Zhou L, Shen X, Guo C, Zheng Y, Zhu H, Zhu Y, Huang L (2011) Pten restoration and pik3cb knockdown synergistically suppress glioblastoma growth in vitro and in xenografts. J Neuro-Oncol 104(1):155–167
Loibl S, de la Pena L, Nekljudova V, Zardavas D, Michiels S, Denkert C, Rezai M, Bermejo B, Lee S-C, Turri S, Urban P, Kümmel S, Lux M, Piccart M, von Minckwitz G, Baselga J, Loi S (2015) Phase II, randomized, parallel-cohort study of neoadjuvant buparlisib (BKM120) in combination with trastuzumab and paclitaxel in women with HER2-positive, PIK3CA mutant and PIK3CA wild-type primary breast cancer – NeoPHOEBE. In: Proceedings of the Thirty-Eighth Annual CTRC-AACR San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium: 2015 Dec 8-12; San Antonio, TX. Philadelphia
Alex A, Adjei, JB, Leighl NB, Felip Enriqueta, Cortinovis DL, Alt J, Schaefer ES, Thomas M, Chouaid C, Morabito A, Castro De J, Grossi F, Paz-Ares L, Pas De TM, Maier J, Chakravartty A, Chol M, Aimone P, Planchard D (2016) Safety and efficacy of buparlisib (bkm120) and chemotherapy in advanced, squamous non-small cell lung cancer (sqnsclc): Results from the phase ib/ii basalt-2 and basalt-3 studies ASCO 2016 Annual meeting
Denis, S SJF, Mesia R, Remenar E, Li S-H, Karpenko A, Dechaphunkul A, Keilholz U, Kiss LA, Lin JC, Nagarkar RV, Tamas L, Kim S-B, Erfán J, Turri S, Dey D, Chakravartty A, Aimone P, Massacesi C, Licitra LF (2016) Beril-1: A phase ii, placebo-controlled study of buparlisib (bkm120) plus paclitaxel in patients withplatinum-pretreated recurrent/metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (hnscc). ASCO 2016 Annual meeting
Acknowledgements
This study received funding from Novartis Pharmaceuticals. Saiprasad Boddu, of Sai Life Sciences, performed the pharmacokinetic analyses. The authors of this study are supported by the Core Grant (P30 CA008748) at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center from the National Institutes of Health, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
M.F., K.J., A.H., M.L, and M.V. have served on advisory boards and/or consulted for Novartis.
LMS: Advisory- Genentech, Research - AstraZeneca.
KJ: Consulting/Advisory - Novartis.
DH: Consulting - Chugai, CytomX, Atara, Research/Grants-AstraZeneca, PUMA, LOXO.
AH: Advisory/ Speaker- Novartis.
MV: Consulting- Novartis, Exelixis, Pfizer, Alexion, Research- BMS, Genentech.
No potential conflict of interest was disclosed by the other authors.
Funding
Funding was received from Novartis Pharmaceuticals. Saiprasad Boddu, of Sai Life Sciences, performed the pharmacokinetic analyses.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Table 1
(DOCX 17 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smyth, L.M., Monson, K.R., Jhaveri, K. et al. A phase 1b dose expansion study of the pan-class I PI3K inhibitor buparlisib (BKM120) plus carboplatin and paclitaxel in PTEN deficient tumors and with dose intensified carboplatin and paclitaxel. Invest New Drugs 35, 742–750 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-017-0445-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-017-0445-0