Summary
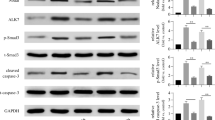
We have previously shown that the insulinotropic imidazoline compound RX871024 induces death of insulinoma MIN6 cells, an effect involving stimulation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and caspase 3. It has also been reported that AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activates JNK and induces β-cell death. Here we show that RX871024, but not another insulinotropic imidazoline compound (BL11282), suppressed AMPK activity in MIN6 cells. The inhibitory effect of RX871024 on AMPK was supported by the observation that the imidazoline induced lipid droplet formation in the cytoplasm of MIN6 cells. This reflects stimulation of anabolic pathways and inhibition of catabolic pathways in the cell that happen under conditions when AMPK is inhibited. Activation of AMPK by 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide riboside (AICAR) elevated basal and cytokine-induced death in primary β-cells and in insulinoma MIN6 cells. RX871024 aggravated AICAR-induced insulinoma MIN6 cell death regardless of the presence of pro-inflammatory cytokines. The specific cytotoxic effect of imidazoline compound RX871024 on insulinoma cell death but not primary β-cell death is independent of its action on AMPK and may suggest the possibility of using this type of compound in the treatment of insulinomas.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mandrup-Poulsen T (2003) Beta cell death and protection. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1005:32–42
Donath MY, Ehses JA, Maedler K, Schumann DM, Ellingsgaard H, Eppler E, Reinecke M (2005) Mechanisms of β-cell death in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 54(Suppl 2):S108–S113
Ekeblad S (2010) Islet cell tumours. Adv Exp Med Biol 654:771–789
Xu J, Han J, Long YS, Epstein PN, Liu YQ (2008) The role of pyruvate carboxylase in insulin secretion and proliferation in rat pancreatic beta cells. Diabetologia 51(11):2022–2030
Hardie DG (2007) AMP-activated protein kinase as a drug target. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 47:185–210
Fu A, Eberhard CE, Screaton RA (2013) Role of AMPK in pancreatic beta cell function. Mol Cell Endocrinol 366(2):127–134
Kefas BA, Cai Y, Ling Z, Heimberg H, Hue L, Pipeleers D, Van de Casteele M (2003) AMP-activated protein kinase can induce apoptosis of insulin-producing MIN6 cells through stimulation of c-Jun-N-terminal kinase. J Mol Endocrinol 30(2):151–161
Giri S, Nath N, Smith B, Viollet B, Singh AK, Singh I (2004) 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-beta-4-ribofuranoside inhibits proinflammatory response in glial cells: a possible role of AMP-activated protein kinase. J Neurosci 24(2):479–487
Di Marco S, Mazroui R, Dallaire P, Chittur S, Tenenbaum SA, Radzioch D, Marette A, Gallouzi IE (2005) NF-kappa B-mediated MyoD decay during muscle wasting requires nitric oxide synthase mRNA stabilization, HuR protein, and nitric oxide release. Mol Cell Biol 25(15):6533–6545
Zaitsev SV, Efanov AM, Efanova IB, Larsson O, Ostenson CG, Gold G, Berggren PO, Efendic S (1996) Imidazoline compounds stimulate insulin release by inhibition of K(ATP) channels and interaction with the exocytotic machinery. Diabetes 45(11):1610–1618
Efanov AM, Zaitsev SV, Mest HJ, Raap A, Appelskog IB, Larsson O, Berggren PO, Efendic S (2001) The novel imidazoline compound BL11282 potentiates glucose-induced insulin secretion in pancreatic beta-cells in the absence of modulation of K(ATP) channel activity. Diabetes 50(4):797–802
Efendic S, Efanov AM, Berggren PO, Zaitsev SV (2002) Two generations of insulinotropic imidazoline compounds. Diabetes 51(Suppl 3):S448–S454
Jagerbrink T, Lexander H, Palmberg C, Shafqat J, Sharoyko V, Berggren PO, Efendic S, Zaitsev S, Jornvall H (2007) Differential protein expression in pancreatic islets after treatment with an imidazoline compound. Cell Mol Life Sci 64(10):1310–1316
Zaitseva II, Storling J, Mandrup-Poulsen T, Berggren PO, Zaitsev SV (2008) The imidazoline RX871024 induces death of proliferating insulin-secreting cells by activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase. Cell Mol Life Sci 65(7–8):1248–1255
Zaitsev SV, Appelskog IB, Kapelioukh IL, Yang SN, Kohler M, Efendic S, Berggren PO (2001) Imidazoline compounds protect against interleukin 1beta-induced beta-cell apoptosis. Diabetes 50(Suppl 1):S70–S76
Zaitseva II, Sharoyko V, Storling J, Efendic S, Guerin C, Mandrup-Poulsen T, Nicotera P, Berggren PO, Zaitsev SV (2006) RX871024 reduces NO production but does not protect against pancreatic beta-cell death induced by proinflammatory cytokines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 347(4):1121–1128
Schneider MB, Matsuzaki H, Haorah J, Ulrich A, Standop J, Ding XZ, Adrian TE, Pour PM (2001) Prevention of pancreatic cancer induction in hamsters by metformin. Gastroenterology 120(5):1263–1270
Evans JM, Donnelly LA, Emslie-Smith AM, Alessi DR, Morris AD (2005) Metformin and reduced risk of cancer in diabetic patients. BMJ 330(7503):1304–1305
Sharoyko VV, Zaitseva II, Varsanyi M, Portwood N, Leibiger B, Leibiger I, Berggren PO, Edendic S, Zaitsev SV (2005) Monomeric G-protein, Rhes, is not an imidazoline-regulated protein in pancreatic beta-cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 338(3):1455–1459
Lernmark A (1974) The preparation of, and studies on, free cell suspensions from mouse pancreatic islets. Diabetologia 10(5):431–438
Luo Z, Zang M, Guo W (2010) AMPK as a metabolic tumor suppressor: control of metabolism and cell growth. Future Oncol 6(3):457–470
Greenspan P, Mayer EP, Fowler SD (1985) Nile red: a selective fluorescent stain for intracellular lipid droplets. J Cell Biol 100(3):965–973
Kefas BA, Heimberg H, Vaulont S, Meisse D, Hue L, Pipeleers D, Van de Casteele M (2003) AICA-riboside induces apoptosis of pancreatic beta cells through stimulation of AMP-activated protein kinase. Diabetologia 46(2):250–254
Kohler M, Zaitsev SV, Zaitseva II, Leibiger B, Leibiger IB, Turunen M, Kapelioukh IL, Bakkman L, Appelskog IB, de Monvel JB, Imreh G, Berggren PO (2003) On-line monitoring of apoptosis in insulin-secreting cells. Diabetes 52(12):2943–2950
Lee JP, Chen W, Wu HT, Lin KC, Cheng JT (2011) Metformin can activate imidazoline I-2 receptors to lower plasma glucose in type 1-like diabetic rats. Horm Metab Res 43(1):26–30
Lui TN, Tsao CW, Huang SY, Chang CH, Cheng JT (2010) Activation of imidazoline I2B receptors is linked with AMP kinase pathway to increase glucose uptake in cultured C2C12 cells. Neurosci Lett 474(3):144–147
McDonald GR, Olivieri A, Ramsay RR, Holt A (2010) On the formation and nature of the imidazoline I2 binding site on human monoamine oxidase-B. Pharmacol Res 62(6):475–488
Choi SL, Kim SJ, Lee KT, Kim J, Mu J, Birnbaum MJ, Soo Kim S, Ha J (2001) The regulation of AMP-activated protein kinase by H(2)O(2). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 287(1):92–97
Ryu GR, Lee MK, Lee E, Ko SH, Ahn YB, Kim JW, Yoon KH, Song KH (2009) Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase mediates acute and severe hypoxic injury to pancreatic beta cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 386(2):356–362
Bour S, Iglesias-Osma MC, Marti L, Duro P, Garcia-Barrado MJ, Pastor MF, Prevot D, Visentin V, Valet P, Moratinos J, Carpene C (2006) The imidazoline I2-site ligands BU 224 and 2-BFI inhibit MAO-A and MAO-B activities, hydrogen peroxide production, and lipolysis in rodent and human adipocytes. Eur J Pharmacol 552(1–3):20–30
Efanova IB, Zaitsev SV, Brown G, Berggren PO, Efendic S (1998) RX871024 induces Ca2+ mobilization from thapsigargin-sensitive stores in mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Diabetes 47(2):211–218
Efanova IB, Zaitsev SV, Efanov AM, Ostenson C, Raap A, Mest H, Berggren P, Efendi (1998) Effects of imidazoline derivative RX871024 on insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin secretion from isolated perfused rat pancreas. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 252(1):162–165
Leclerc I, Sun G, Morris C, Fernandez-Millan E, Nyirenda M, Rutter GA (2011) AMP-activated protein kinase regulates glucagon secretion from mouse pancreatic alpha cells. Diabetologia 54(1):125–134
Richards SK, Parton LE, Leclerc I, Rutter GA, Smith RM (2005) Over-expression of AMP-activated protein kinase impairs pancreatic β-cell function in vivo. J Endocrinol 187(2):225–235
Kiely A, McClenaghan NH, Flatt PR, Newsholme P (2007) Pro-inflammatory cytokines increase glucose, alanine and triacylglycerol utilization but inhibit insulin secretion in a clonal pancreatic beta-cell line. J Endocrinol 195(1):113–123
Gong J, Robbins LA, Lugea A, Waldron RT, Jeon CY, Pandol SJ (2014) Diabetes, pancreatic cancer, and metformin therapy. Front Physiol 5:426
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grant N5-2001-34 from the Juvenile Diabetes Foundation International, the Swedish Foundation for Strategic Research, the European Foundation for the Study of Diabetes, the Swedish Research Council, the Swedish Diabetes Association, the Novo Nordisk Foundation, The Family Erling-Persson Foundation, the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation, Torsten and Ragnar Söderberg Foundation, Berth von Kantzow’s Foundation, the Stichting af Jochnick Foundation, the Strategic Research Program in Diabetes at Karolinska Institutet, Skandia Insurance Company, Ltd., Karolinska Institutet, and Novo Nordisk A/S.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical approval
All experiments involving animals were approved by the Animal Experiment Ethics Committee at Karolinska Institutet.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zaitseva, I.I., Zaitsev, S.V. & Berggren, PO. The imidazoline compound RX871024 promotes insulinoma cell death independent of AMP-activated protein kinase inhibition. Invest New Drugs 34, 522–529 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-016-0362-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-016-0362-7