Summary
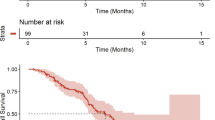
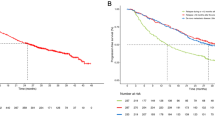
Background MK-5108 is a potent/highly selective Aurora A kinase inhibitor. Methods A randomized Phase I study of MK-5108, administered p.o. BID Q12h on days 1–2 in 14–21 day cycles either alone (MT; Panel1/n = 18; 200 to 1800 mg) or in combination (CT; Panel2/n = 17; 100 to 225 mg) with IV docetaxel 60 mg/m2, determined the maximum tolerated dose (MTD), pharmacokinetics (PK), pharmacodynamics (Panel1, only) and tumor response in patients with advanced solid tumors. This study was terminated early due to toxicities in Panel2 at MK-5108 doses below the anticipated PK exposure target. Results 35 patients enrolled (33 evaluable for tumor response). No dose-limiting toxicities (DLTs) were observed in Panel1; three patients had 3 DLTs in Panel2 (G3 and G4 febrile neutropenia at 200 and 450 mg/day, respectively; G3 infection at 450 mg/day). In Panel1, AUC0-12hr and Cmax increased less than dose proportionally following the first MT dose but increased roughly dose proportionally across 200 to 3600 mg/day after 4th dose. The t1/2 ranged from 6.6 to 13.5 h across both panels. No clear effects on immunohistochemistry markers were observed; however, significant dose-related increases in gene expression were seen pre-/post-treatment. Best responses were 9/17 stable disease (SD) (Panel1) as well as 1/16 PR and 7/16 SD (Panel2) (450 mg/day). Conclusions MK-5108 MT was well tolerated at doses up to 3600 mg/day with plasma levels exceeding the minimum daily exposure target (83 μM*hr). The MTD for MK-5108 + docetaxel (CT) was established at 300 mg/day, below the exposure target. Use of pharmacodynamic gene expression assays to determine target engagement was validated.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marumoto T, Zhang D, Saya H (2005) Aurora-A - a guardian of poles. Nat Rev Cancer 5:42–50
el Rifai W, Powell SM (2002) Molecular and biologic basis of upper gastrointestinal malignancy. Gastric carcinoma. Surg Oncol Clin N Am 11:273–291
Katayama H, Brinkley WR, Sen S (2003) The Aurora kinases: role in cell transformation and tumorigenesis. Cancer Metastasis Rev 22:451–464
Mountzios G, Terpos E, Dimopoulos MA (2008) Aurora kinases as targets for cancer therapy. Cancer Treat Rev 34:175–182
Lee W, Patel JH, Lockhart AC (2009) Novel targets in esophageal and gastric cancer: beyond antiangiogenesis. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 18:1351–1364
Hata T, Furukawa T, Sunamura M, Egawa S, Motoi F, Ohmura N, Marumoto T, Saya H, Horii A (2005) RNA interference targeting aurora kinase a suppresses tumor growth and enhances the taxane chemosensitivity in human pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res 65:2899–2905
Scharer CD, Laycock N, Osunkoya AO, Logani S, McDonald JF, Benigno BB, Moreno CS (2008) Aurora kinase inhibitors synergize with paclitaxel to induce apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells. J Transl Med 6:79
Tanaka E, Hashimoto Y, Ito T, Kondo K, Higashiyama M, Tsunoda S, Ortiz C, Sakai Y, Inazawa J, Shimada Y (2007) The suppression of aurora-A/STK15/BTAK expression enhances chemosensitivity to docetaxel in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 13:1331–1340
Shimomura T, Hasako S, Nakatsuru Y, Mita T, Ichikawa K, Kodera T, Sakai T, Nambu T, Miyamoto M, Takahashi I, Miki S, Kawanishi N, Ohkubo M, Kotani H, Iwasawa Y (2010) MK-5108, a highly selective Aurora-A kinase inhibitor, shows antitumor activity alone and in combination with docetaxel. Mol Cancer Ther 9:157–166
Lyman GH, Kleiner JM (2011) Summary and comparison of myeloid growth factor guidelines in patients receiving cancer chemotherapy. Cancer Treat Res 157:145–165
Goto H, Yasui Y, Nigg EA, Inagaki M (2002) Aurora-B phosphorylates Histone H3 at serine28 with regard to the mitotic chromosome condensation. Genes Cells 7:11–17
Le LT, Vu HL, Nguyen CH, Molla A (2013) Basal aurora kinase B activity is sufficient for histone H3 phosphorylation in prophase. Biol Open 2:379–386
Lin Y, Richards FM, Krippendorff BF, Bramhall JL, Harrington JA, Bapiro TE, Robertson A, Zheleva D, Jodrell DI (2012) Paclitaxel and CYC3, an aurora kinase A inhibitor, synergise in pancreatic cancer cells but not bone marrow precursor cells. Br J Cancer 107:1692–1701
Qi W, Cooke LS, Liu X, Rimsza L, Roe DJ, Manziolli A, Persky DO, Miller TP, Mahadevan D (2011) Aurora inhibitor MLN8237 in combination with docetaxel enhances apoptosis and anti-tumor activity in mantle cell lymphoma. Biochem Pharmacol 81:881–890
Sehdev V, Katsha A, Ecsedy J, Zaika A, Belkhiri A, el Rifai W (2013) The combination of alisertib, an investigational Aurora kinase A inhibitor, and docetaxel promotes cell death and reduces tumor growth in preclinical cell models of upper gastrointestinal adenocarcinomas. Cancer 119:904–914
Engels FK, Verweij J (2005) Docetaxel administration schedule: from fever to tears? A review of randomised studies. Eur J Cancer 41:1117–1126
Harvey V, Mouridsen H, Semiglazov V, Jakobsen E, Voznyi E, Robinson BA, Groult V, Murawsky M, Cold S (2006) Phase III trial comparing three doses of docetaxel for second-line treatment of advanced breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 24:4963–4970
Dees EC, Cohen RB, von Mehren M, Stinchcombe TE, Liu H, Venkatakrishnan K, Manfredi M, Fingert H, Burris HA III, Infante JR (2012) Phase I study of aurora A kinase inhibitor MLN8237 in advanced solid tumors: safety, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and bioavailability of two oral formulations. Clin Cancer Res 18:4775–4784
Cervantes A, Elez E, Roda D, Ecsedy J, Macarulla T, Venkatakrishnan K, Rosello S, Andreu J, Jung J, Sanchis-Garcia JM, Piera A, Blasco I, Manos L, Perez-Fidalgo JA, Fingert H, Baselga J, Tabernero J (2012) Phase I pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic study of MLN8237, an investigational, oral, selective aurora a kinase inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res 18:4764–4774
Diamond JR, Bastos BR, Hansen RJ, Gustafson DL, Eckhardt SG, Kwak EL, Pandya SS, Fletcher GC, Pitts TM, Kulikowski GN, Morrow M, Arnott J, Bray MR, Sidor C, Messersmith W, Shapiro GI (2011) Phase I safety, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic study of ENMD-2076, a novel angiogenic and Aurora kinase inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res 17:849–860
Carpinelli P, Moll J (2008) Aurora kinase inhibitors: identification and preclinical validation of their biomarkers. Expert Opin Ther Targets 12:69–80
Sardon T, Cottin T, Xu J, Giannis A, Vernos I (2009) Development and biological evaluation of a novel aurora A kinase inhibitor. Chembiochem 10:464–478
Pflug A, de Oliveira TM, Bossemeyer D, Engh RA (2011) Mutants of protein kinase A that mimic the ATP-binding site of Aurora kinase. Biochem J 440:85–93
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, NJ, USA. The authors wish to thank Dr. Amy O. Johnson-Levonas (Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, NJ, USA) for her assistance with writing and editing this paper. In addition, the authors thank Kristen Lewis (Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, NJ, USA) for her assistance with preparing this manuscript for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical standards
The research complies with the current laws of the United States.
Funding
Funding for this study was provided by Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, NJ, USA.
Disclosures
JL, DH, DM are current or former employees of Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, NJ, USA and may hold stock/stock options in the company. CP was an employee of Merck & Co., Inc. at the time of the study and held stock in the company; she is currently an employee of Amgen and holds stock in the company. SSK has received funding for this study from Merck & Co., Inc. AW-G has received advisory board payments from Merrimack and Pfizer and study funding from Takeda. MA, SEM, PML, MNS, ACL and LT have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author contributions
All authors are responsible for the work described in this manuscript. All authors were involved in at least one of the following: [conception, design, acquisition, analysis, statistical analysis, interpretation of data] and [drafting the manuscript and/or revising it for important intellectual content]. All authors provided final approval of the version to be published.
Funding statement
This study was funded by Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, New Jersey, USA.
Additional information
The results described in this paper were previously published in abstract form at the 2010 American Society for the College of Oncology meeting (A phase I study of MK-5108, an oral aurora A kinase inhibitor, in both monotherapy and in combination with docetaxel in patients with advanced solid tumors, Minton SE et al. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:e13026).
clinicaltrials.gov: NCT00543387
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amin, M., Minton, S.E., LoRusso, P.M. et al. A phase I study of MK-5108, an oral aurora a kinase inhibitor, administered both as monotherapy and in combination with docetaxel, in patients with advanced or refractory solid tumors. Invest New Drugs 34, 84–95 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-015-0306-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-015-0306-7